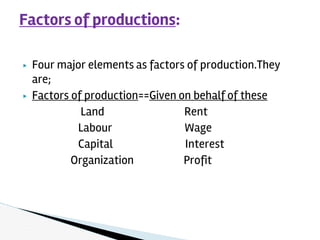
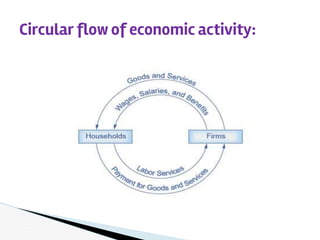
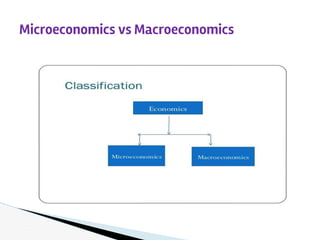
This document introduces some key concepts in economics. It defines economics as dealing with limited resources to meet unlimited wants. The four major factors of production are land, labor, capital, and organization. Two basic problems in economics are scarcity, due to limited resources, and choice, which requires selecting some goods to produce from many options. Three interrelated economic problems are determining what to produce, how to produce, and for whom to produce. Microeconomics examines topics like demand and supply at the individual level, while macroeconomics looks at aggregate concepts like GDP and unemployment at the national level. Opportunity cost refers to the next best alternative given up when making a choice. The production possibilities curve models the tradeoffs between two goods based on














![Production Possibility Curve(PPC) [Continued from previous]:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontoeconomics-180110165127/85/Introduction-to-economics-ppsx-18-320.jpg)
![If technology improves,PPC will be
shifted upwards.Shifted PPC shows
the components which increases
PPC.Concavity of PPC shows
increasing Opportunity cost.
Production Possibility Curve(PPC) [Continued from previous]:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontoeconomics-180110165127/85/Introduction-to-economics-ppsx-19-320.jpg)