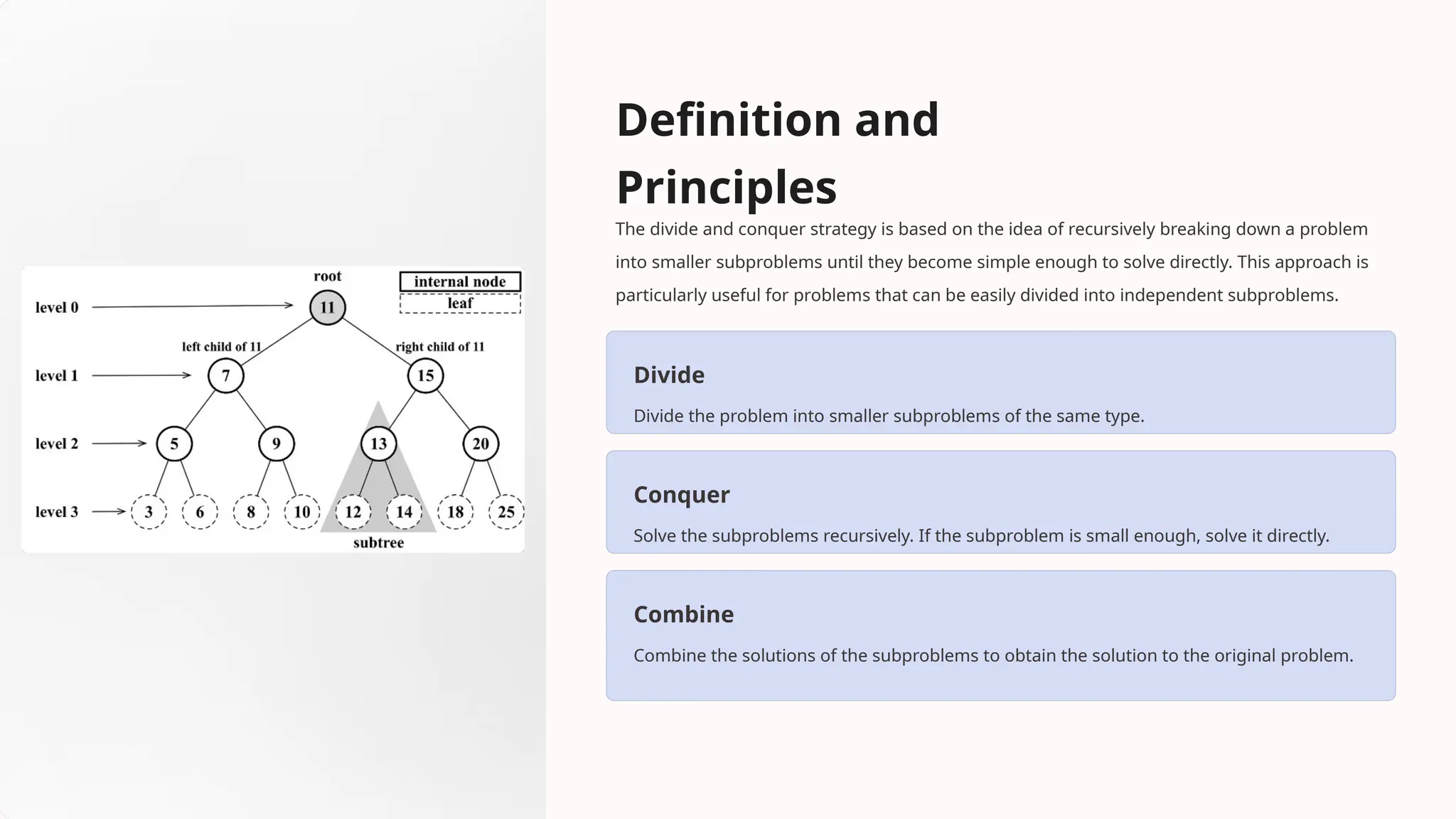
Divide and conquer is a problem-solving strategy that involves breaking complex problems into smaller, manageable subproblems. It offers benefits such as efficiency, parallelism, and simplicity, but also has drawbacks like overhead and high memory usage. This technique is widely used in various applications, including sorting algorithms like merge sort and quick sort, as well as searching algorithms like binary search.