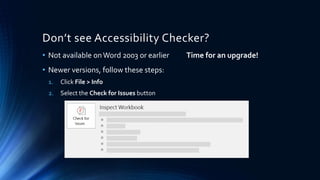
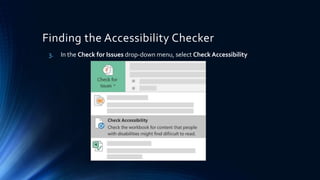
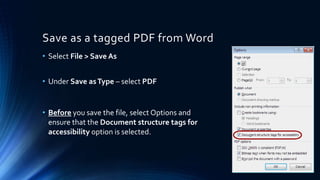
The document provides an introduction to digital accessibility, highlighting its importance and legal requirements. It emphasizes that accessibility is a shared responsibility among all involved in creating digital content and outlines tools for making documents accessible, particularly in Word and PDF formats. Key features of accessible documents include proper structure, alternative text for images, and adequate color contrast.