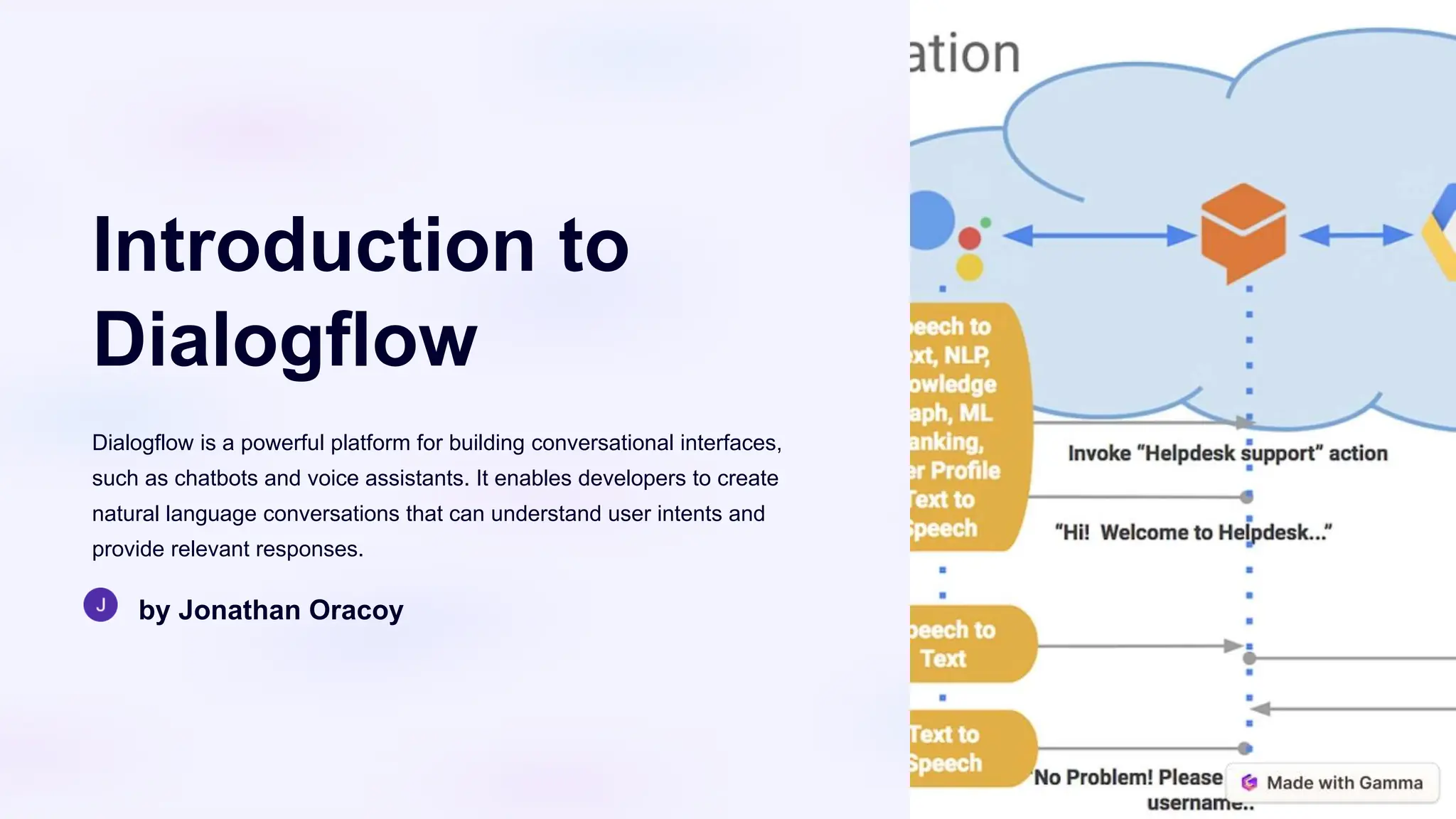
This document provides an overview and introduction to Dialogflow, including its core components like intents, entities, and contexts that enable building conversational agents. It describes how to set up a Dialogflow project, create intents and entities to handle user requests, use contexts to maintain conversation state, integrate with external services via webhooks, test and deploy agents, and best practices for monitoring and improving conversational experiences.