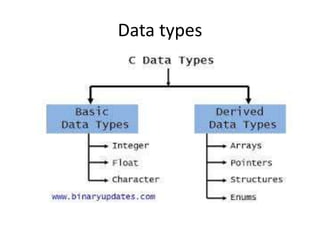
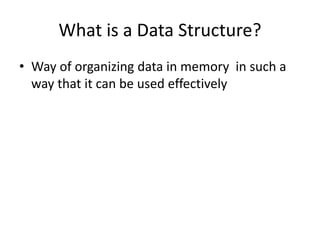
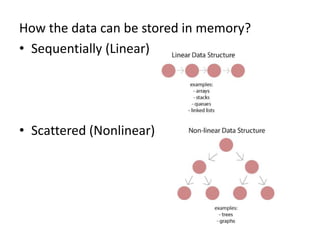
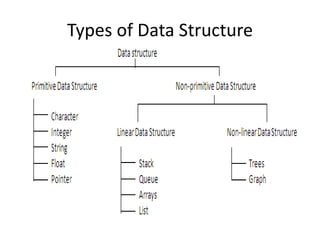
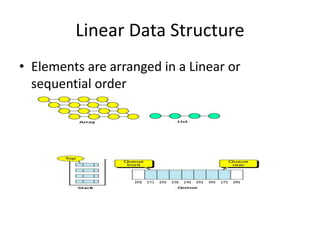
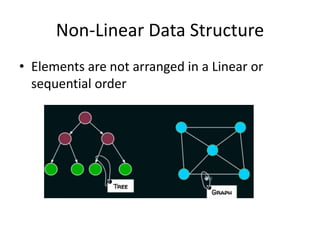
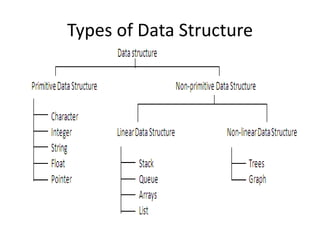
This document introduces data structures by first defining data and variables. It explains that data structures organize data in memory so it can be used effectively. Different types of data structures exist, including linear structures that arrange elements sequentially and non-linear structures that do not use a sequential order. Common data structure types are also abstract data types that define operations on values without specifying the implementation.