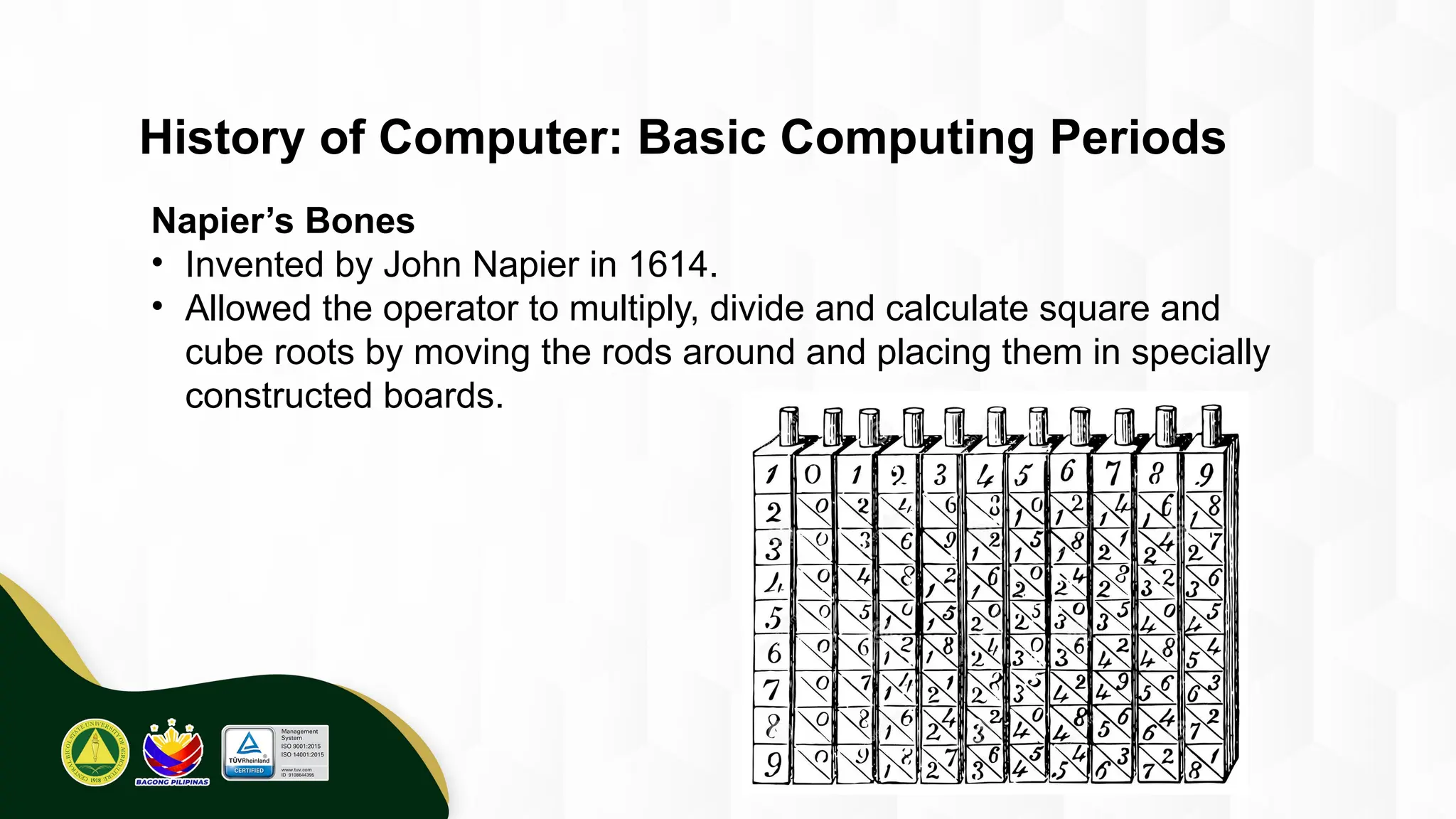
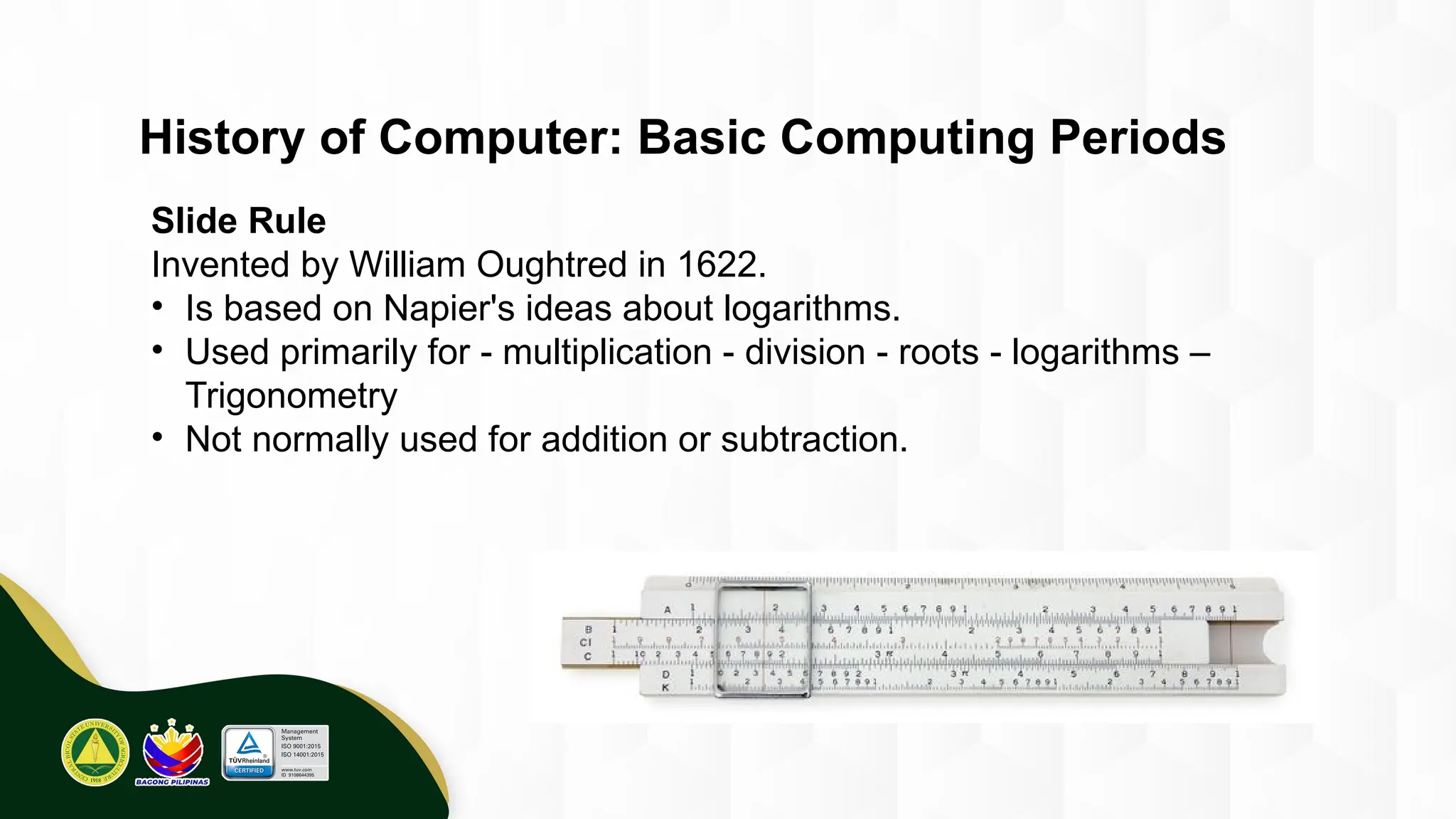
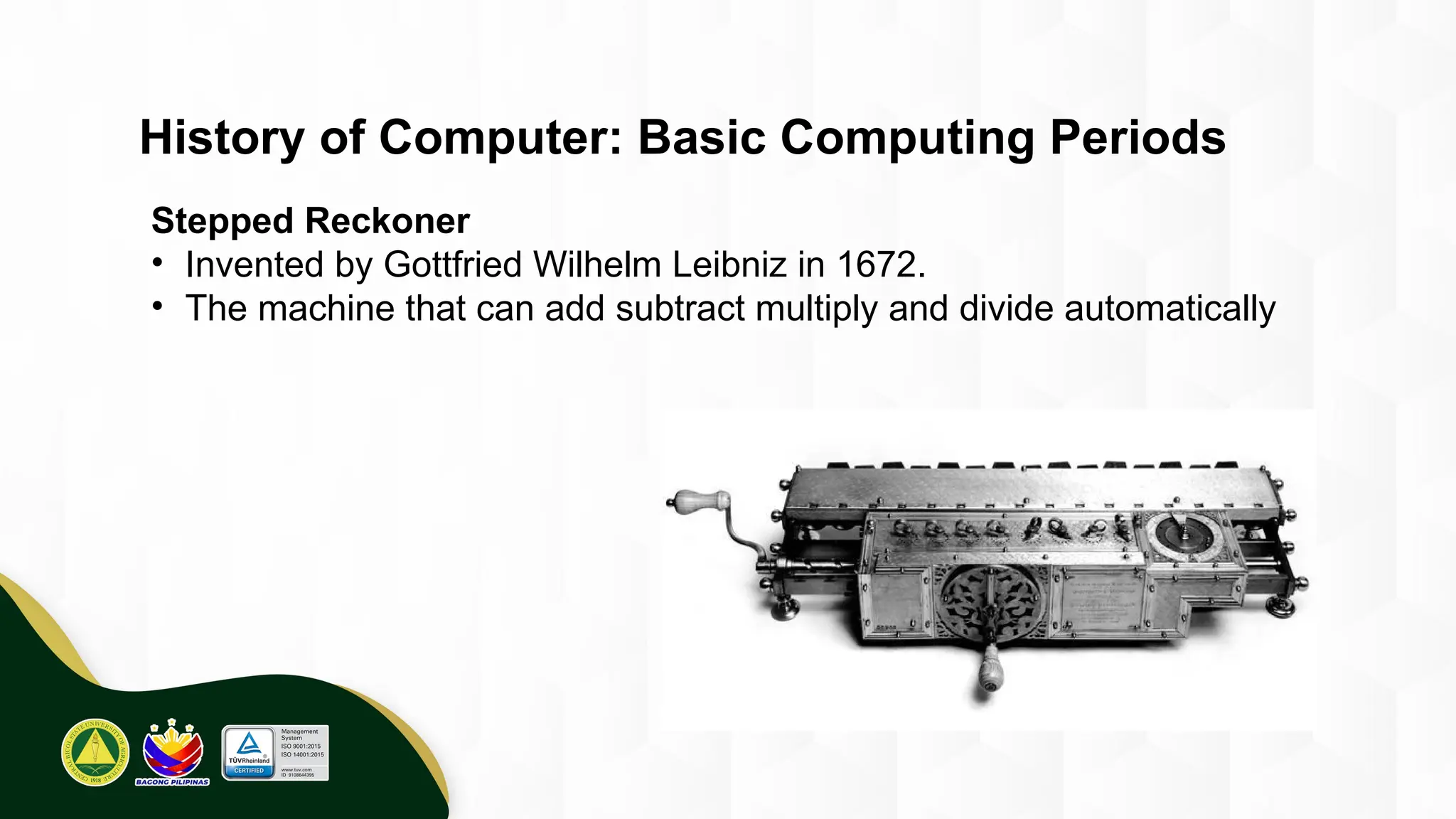
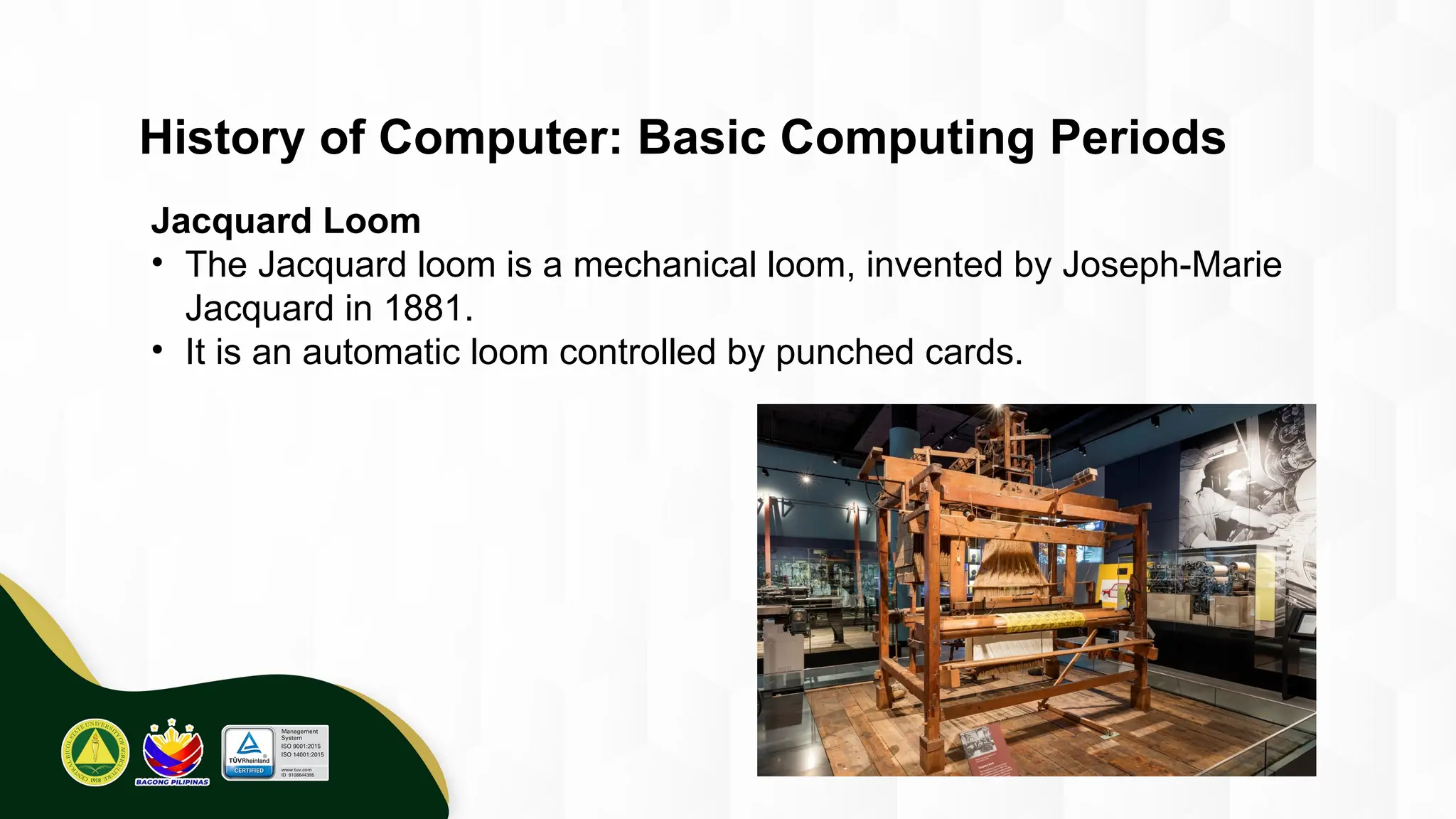
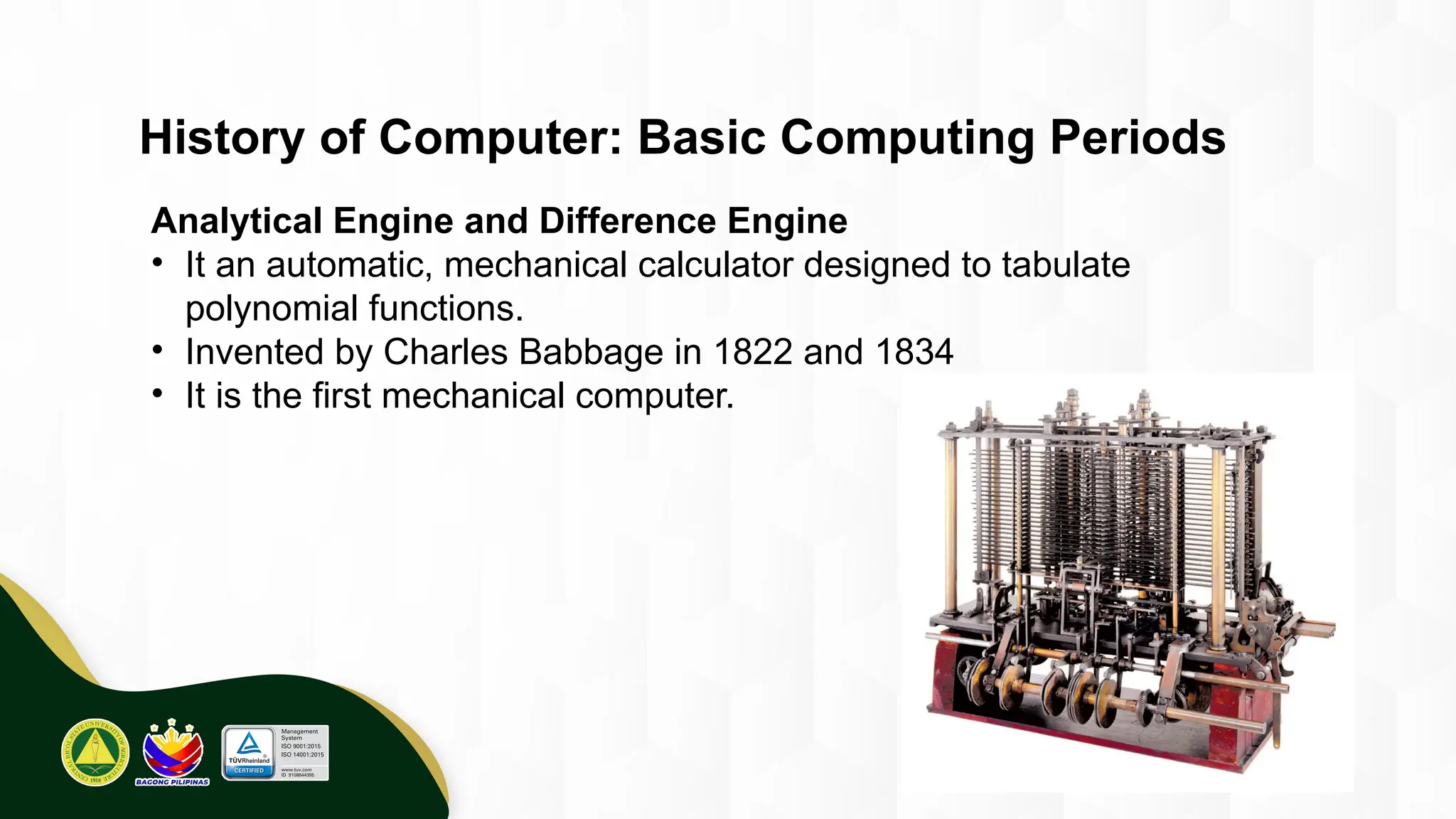
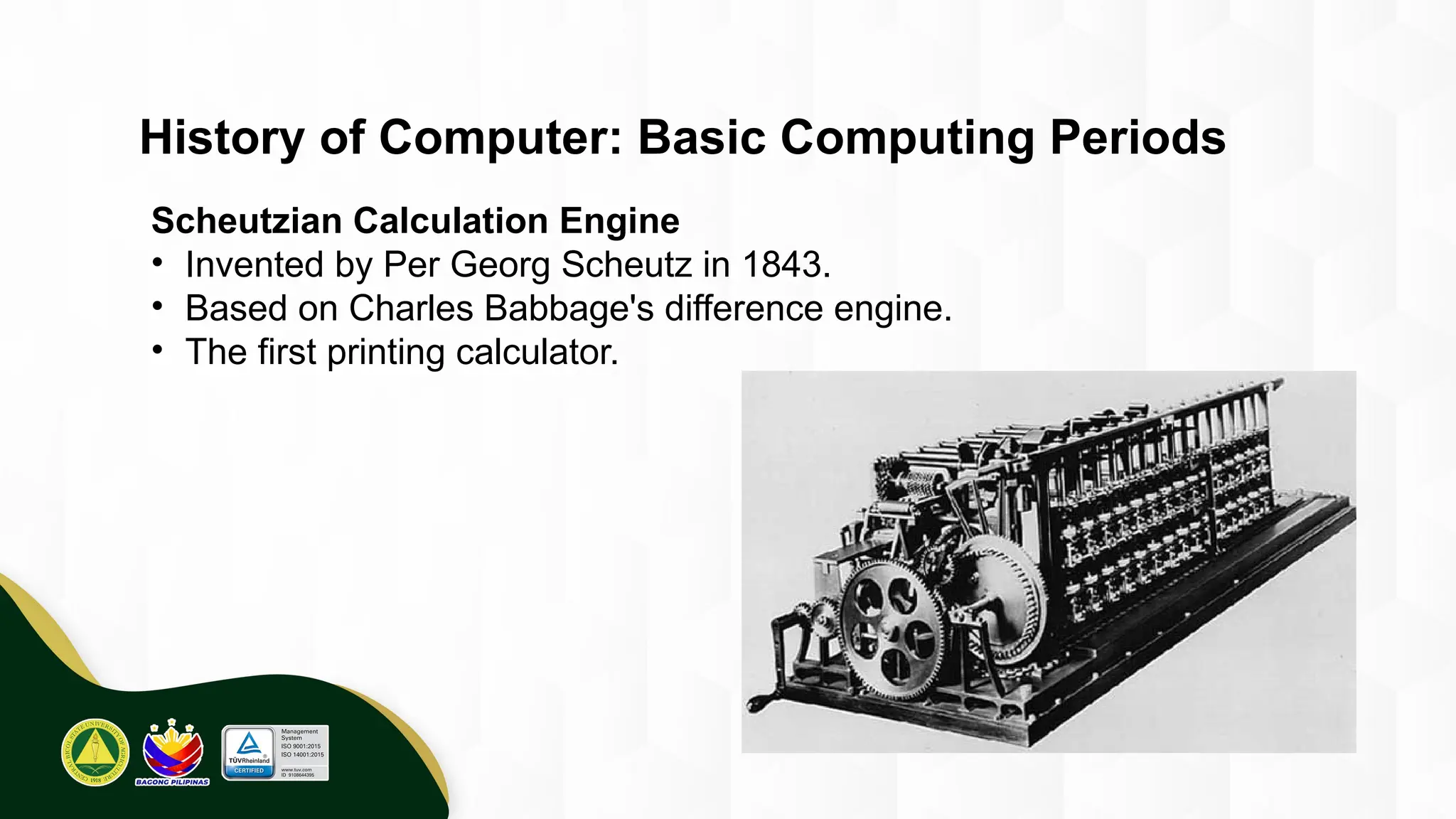
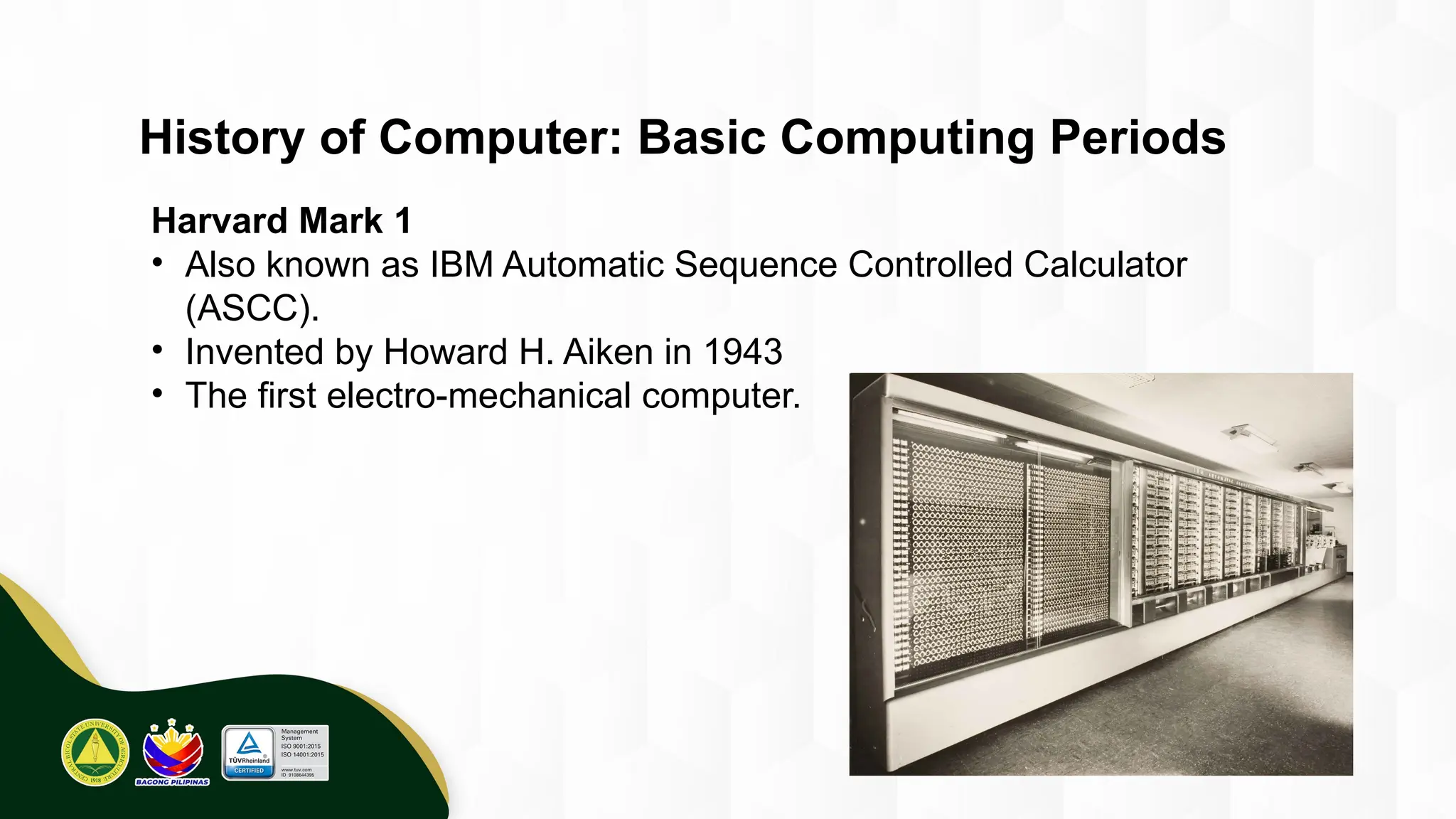
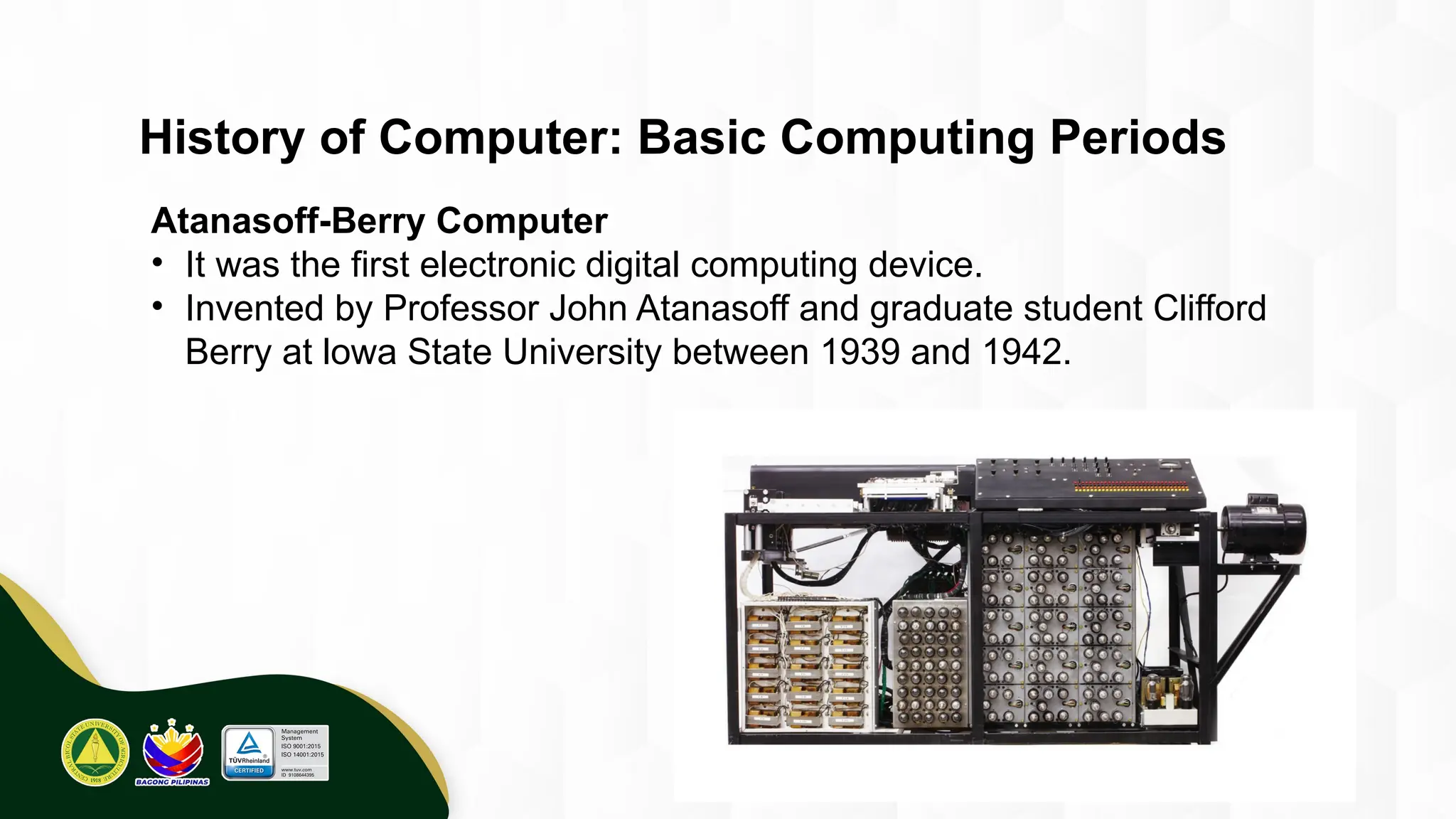
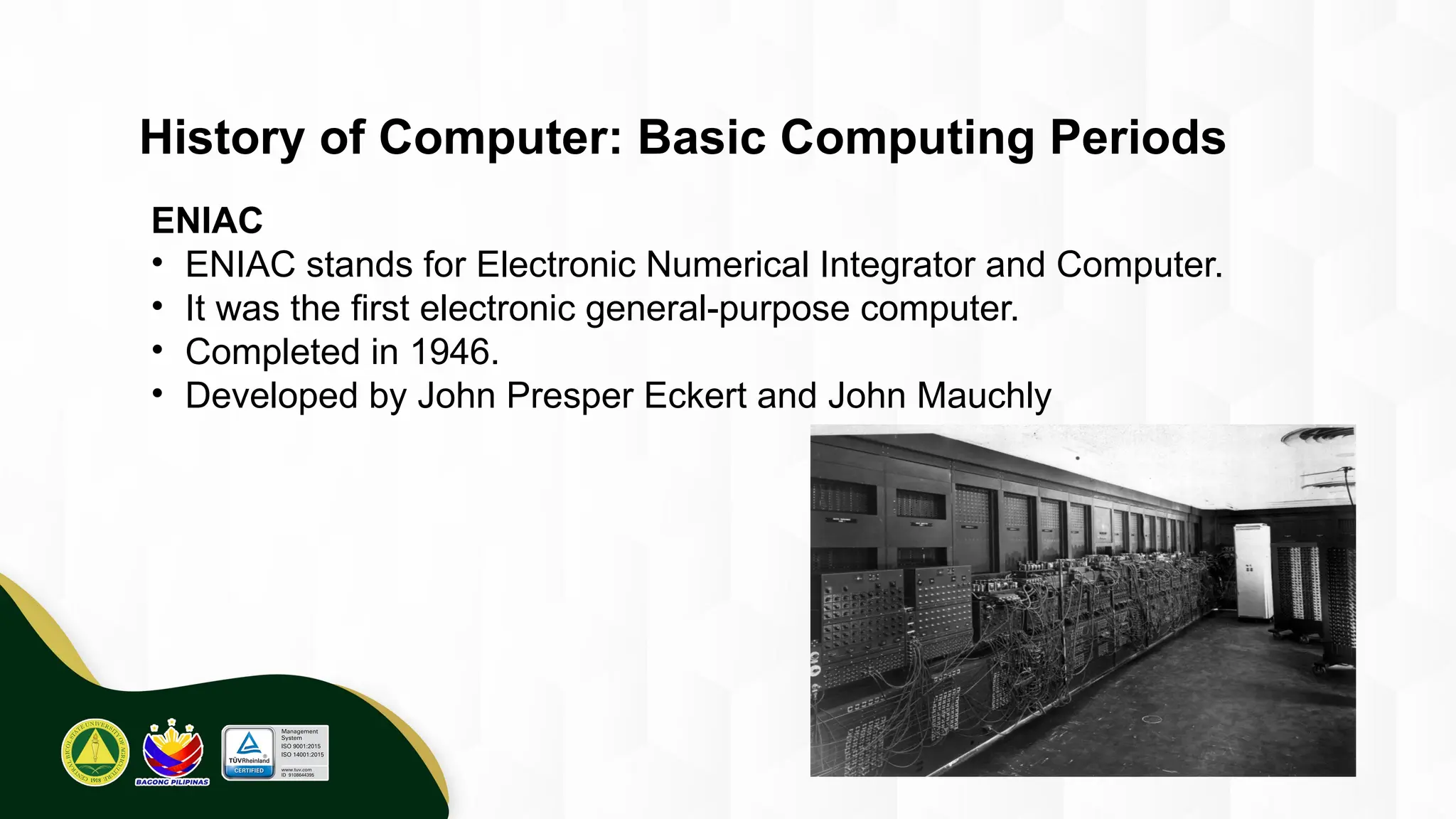
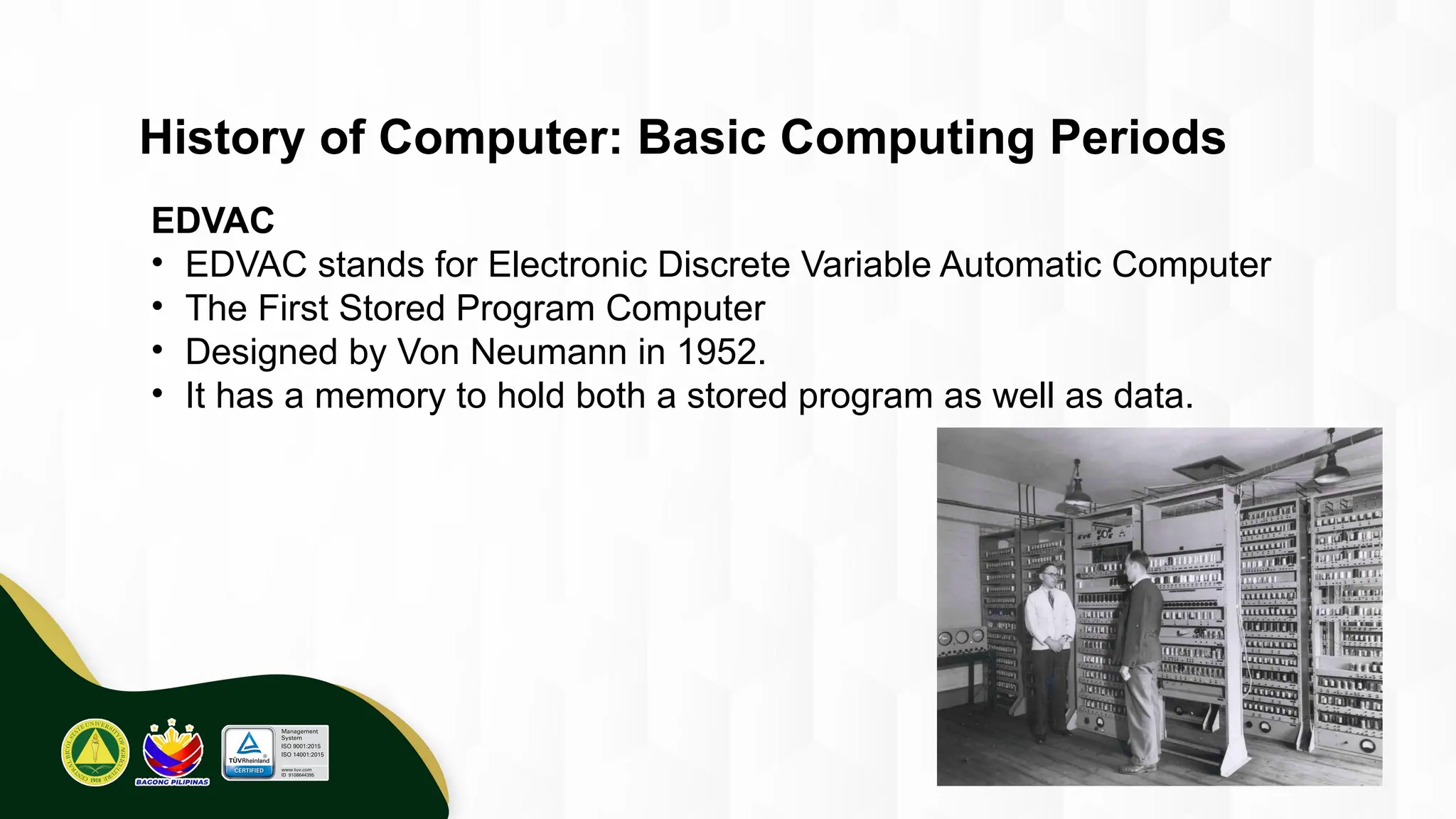
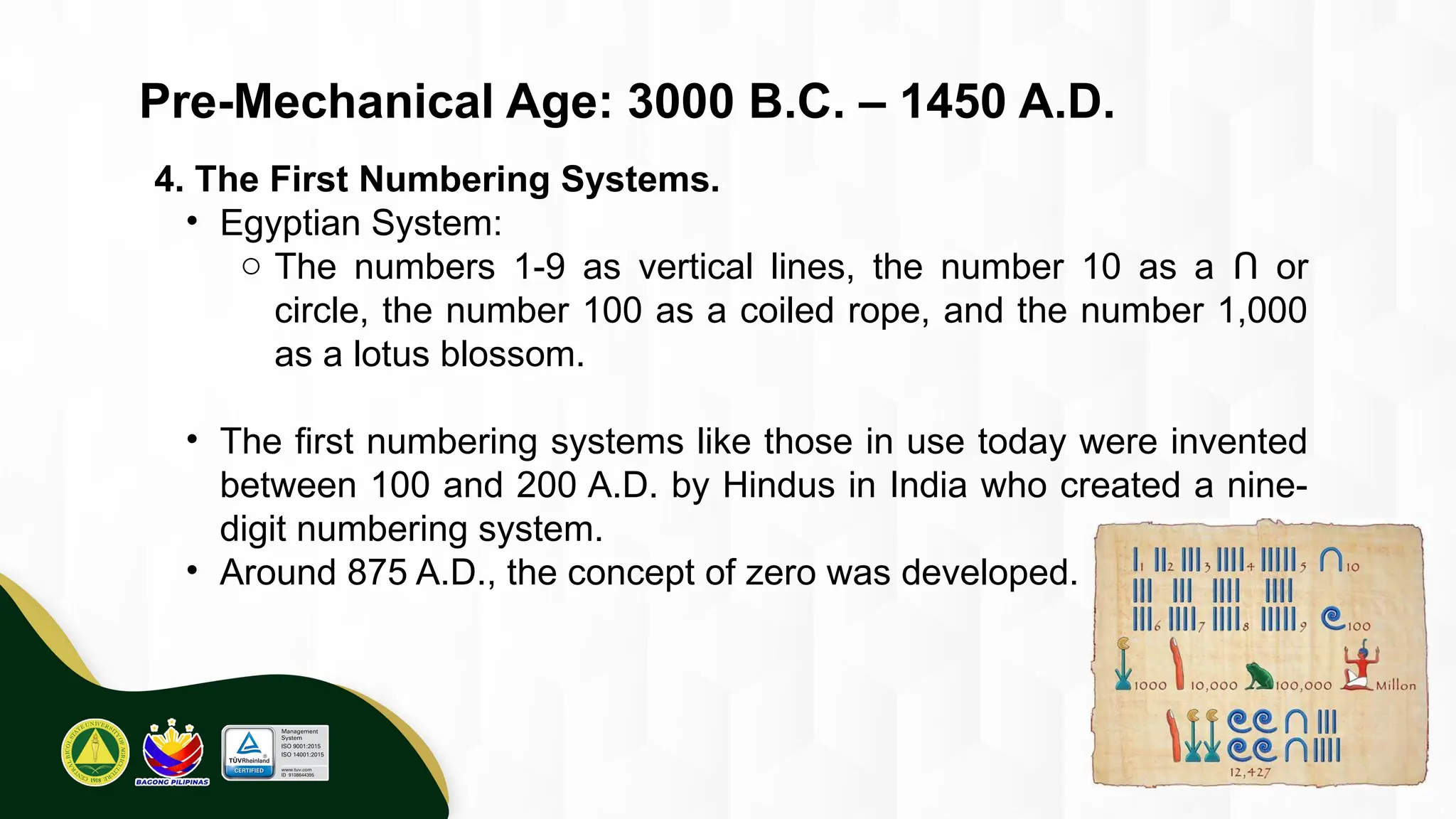
The introduction to computing describes a computer as a programmable, electronic device that accepts data, processes it according to instructions, and produces information by storing and retrieving data. Basic computing periods are often divided into four main ages: Pre-Mechanical (early calculation aids), Mechanical (early mechanical calculators), Electromechanical (telegraphs, early electronic relays), and Electronic (modern digital computers). The modern era also includes the concept of computer Generations, categorized by the core electronic components used, such as vacuum tubes, transistors, integrated circuits, and microprocessors.