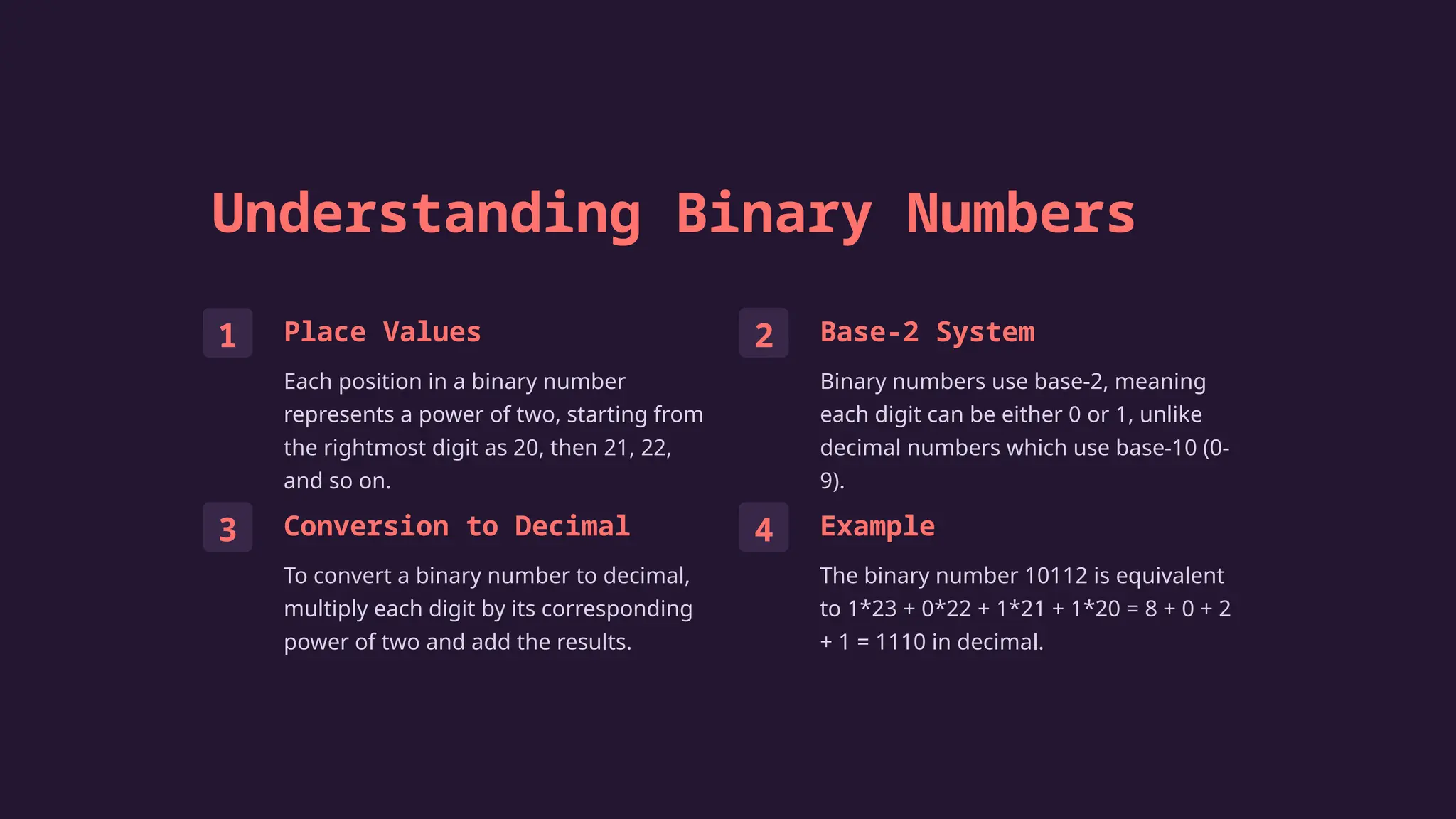
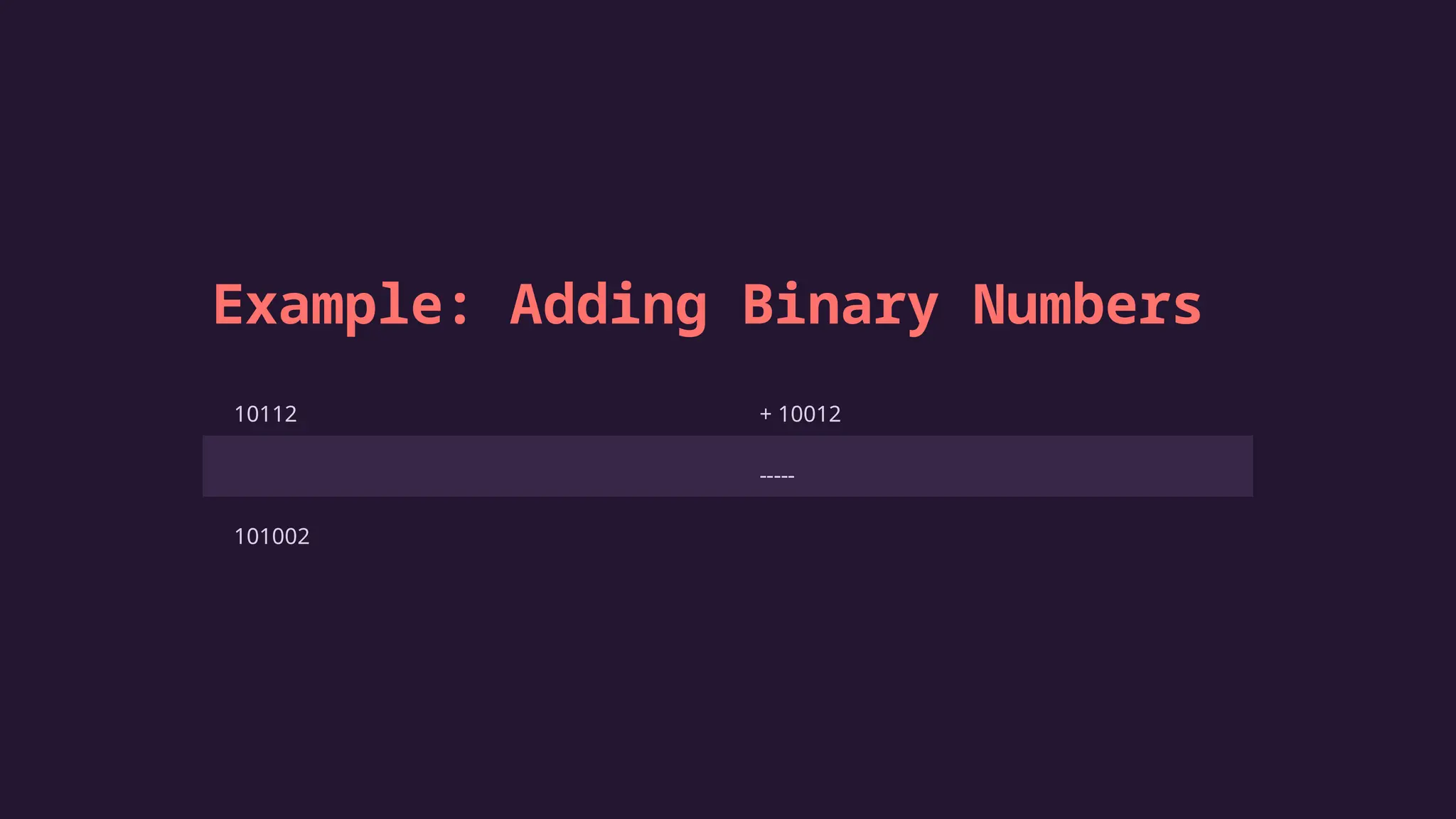
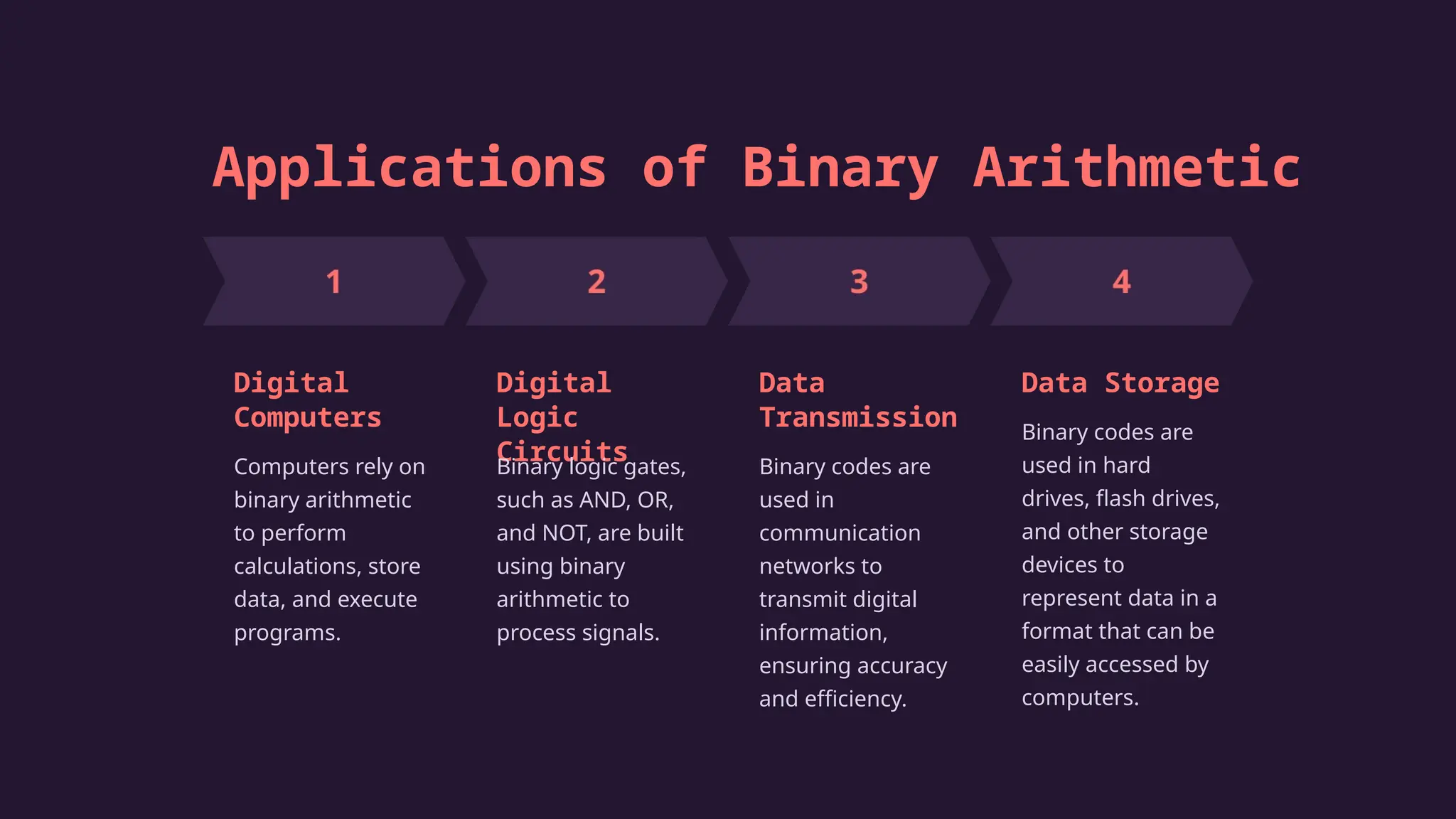
The document explains binary arithmetic, a mathematical system using only 0 and 1, which is essential for modern computing. It covers fundamental concepts including place values, binary operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division), and practical applications such as digital computers and data storage. Understanding binary arithmetic is crucial for anyone interested in computing technology.