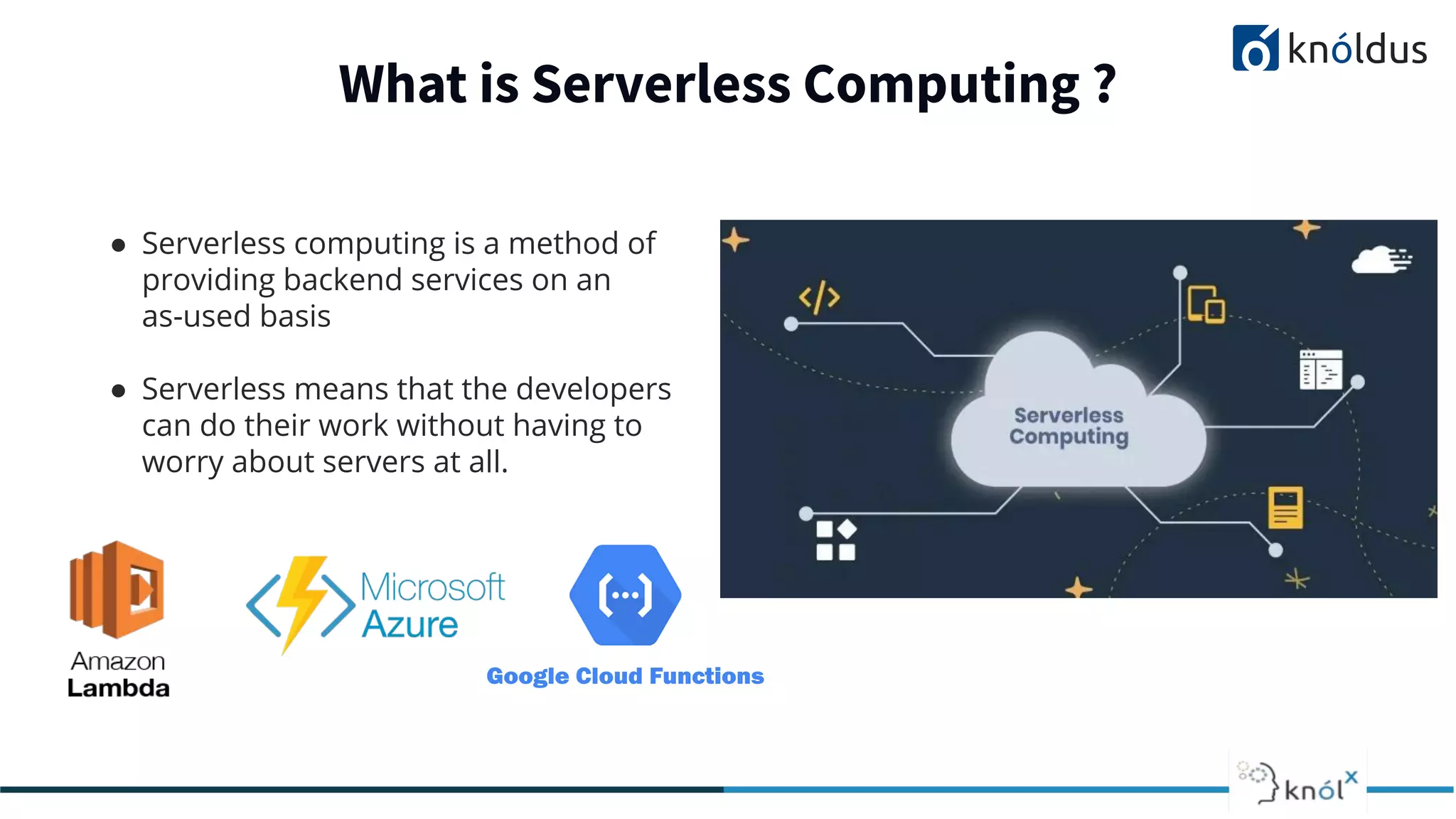
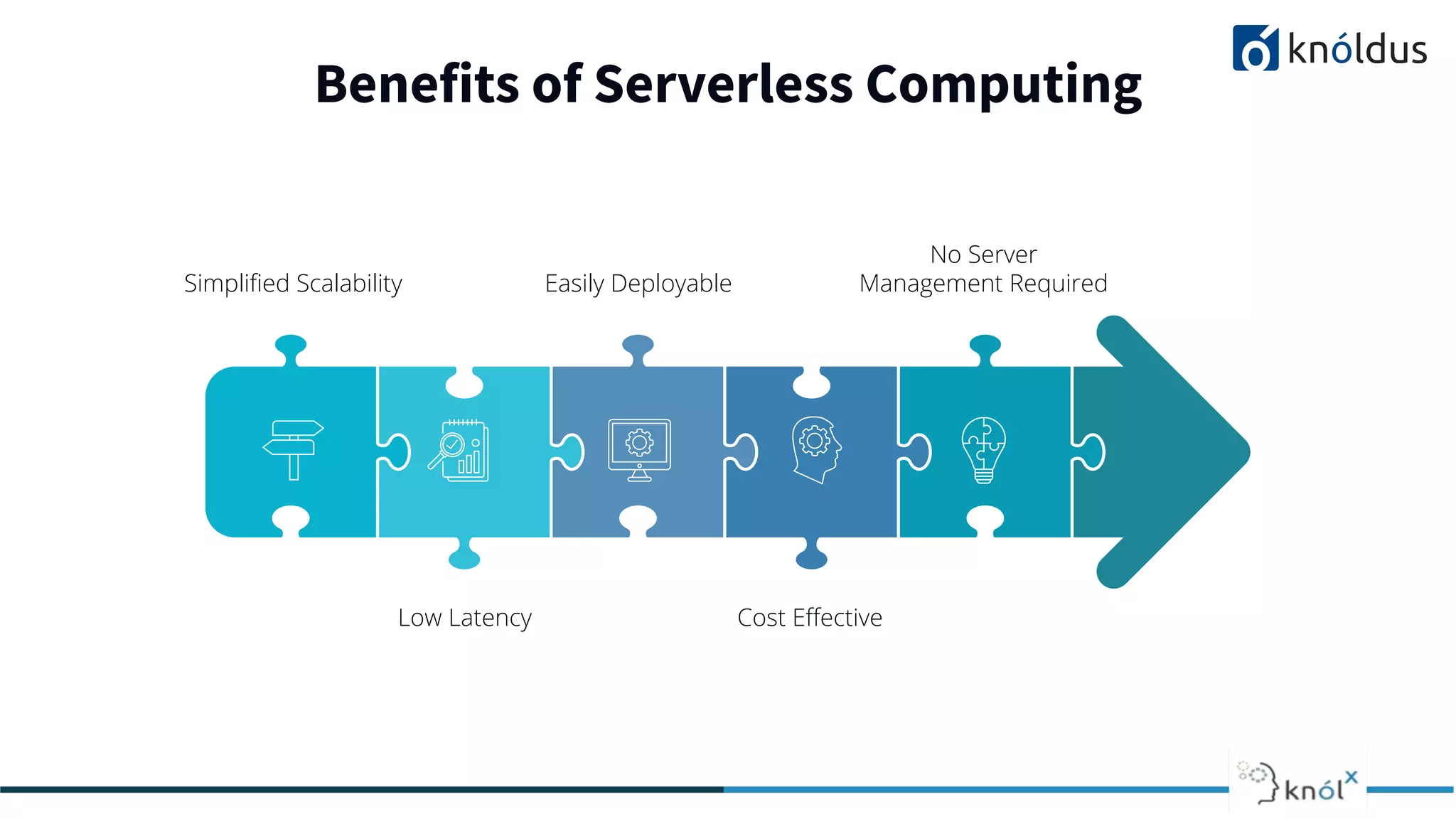
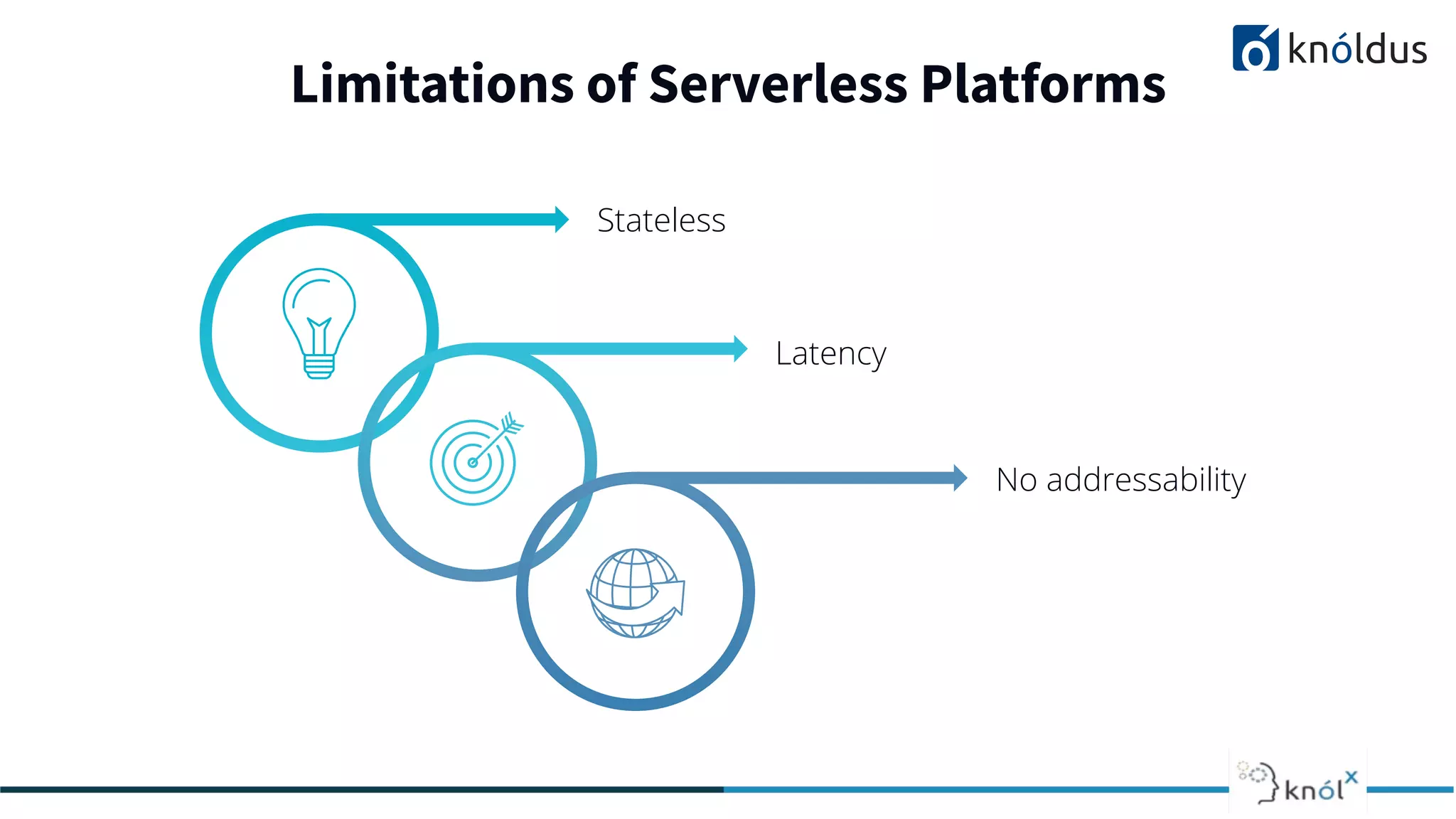
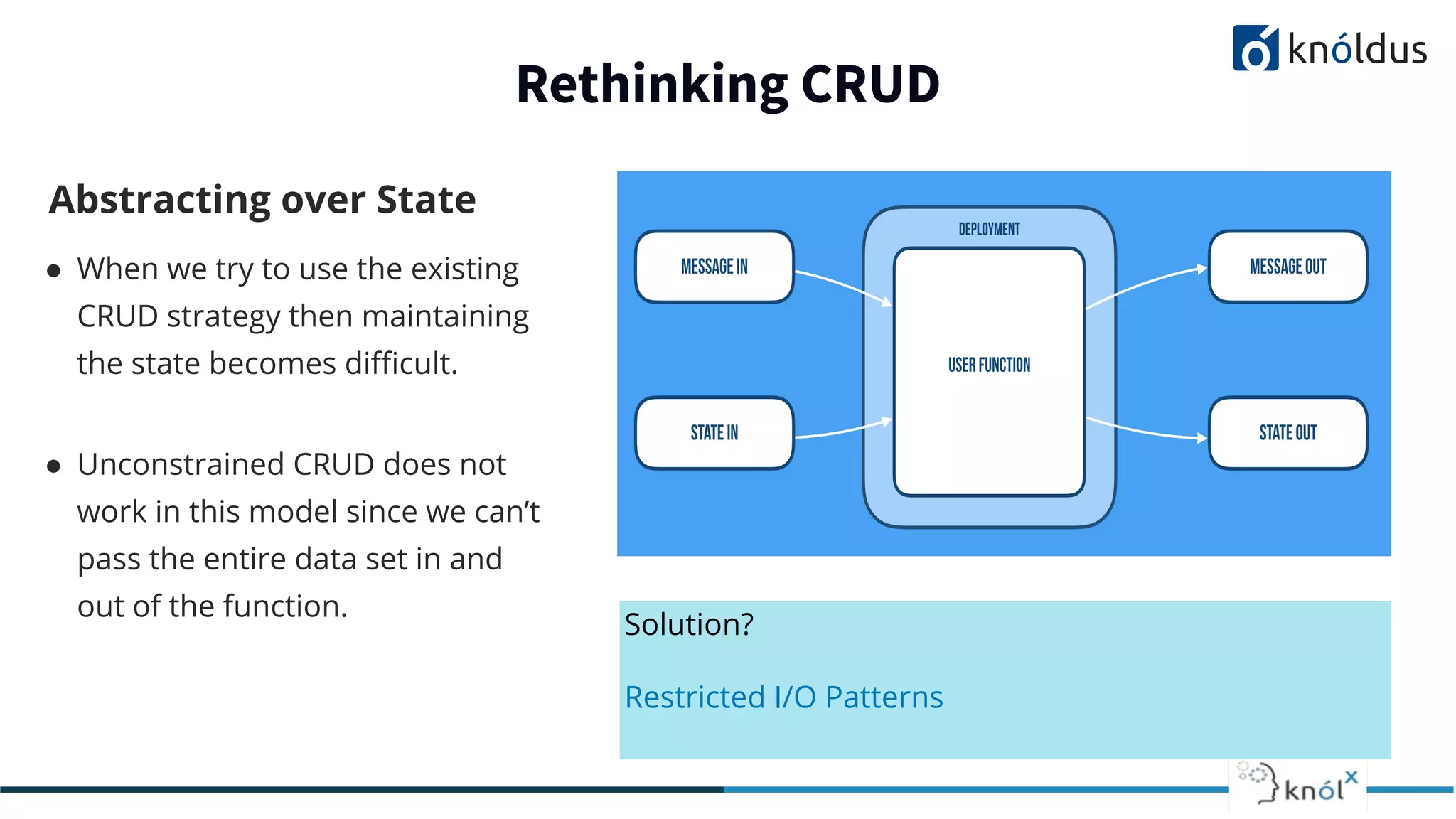
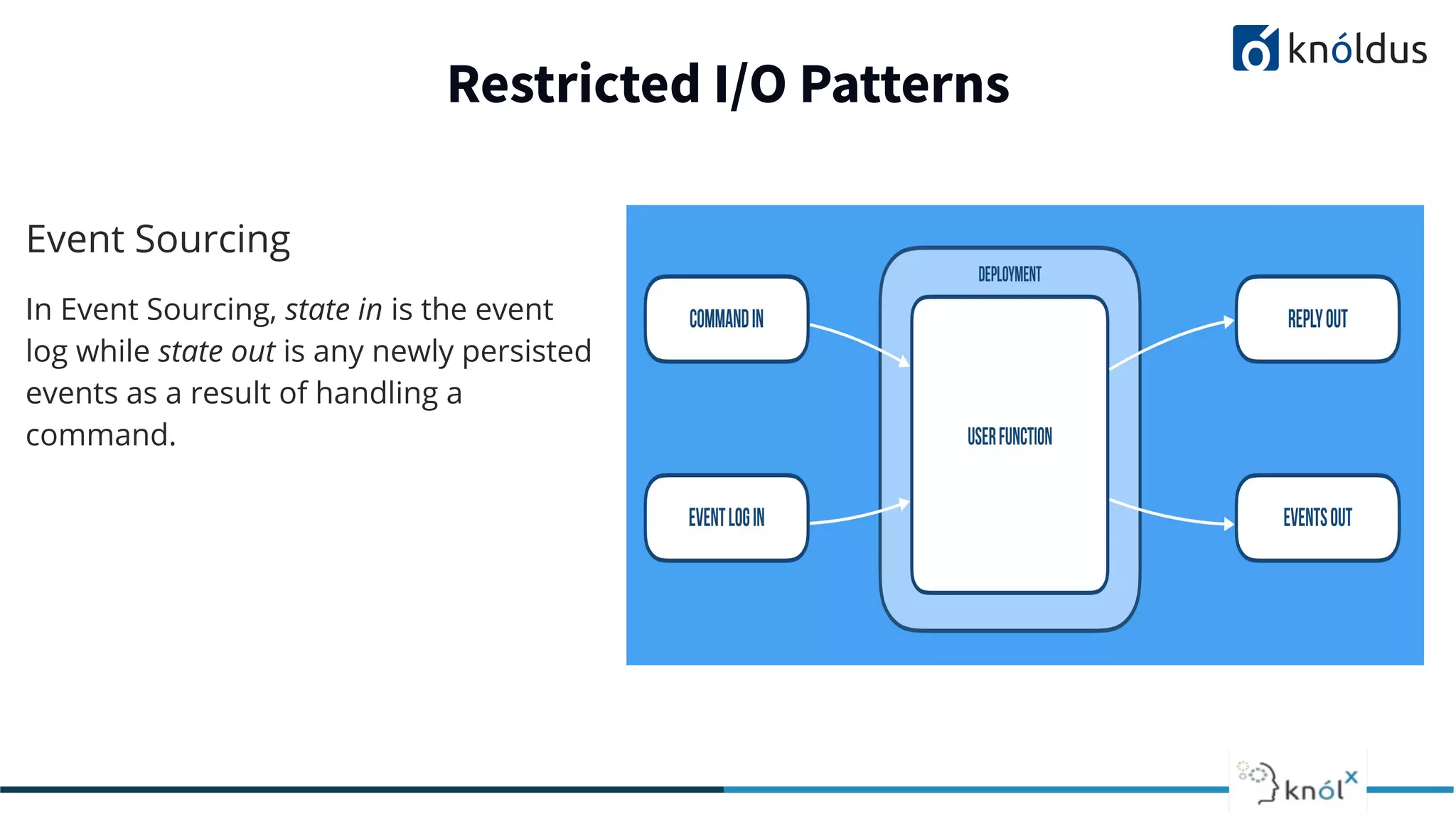
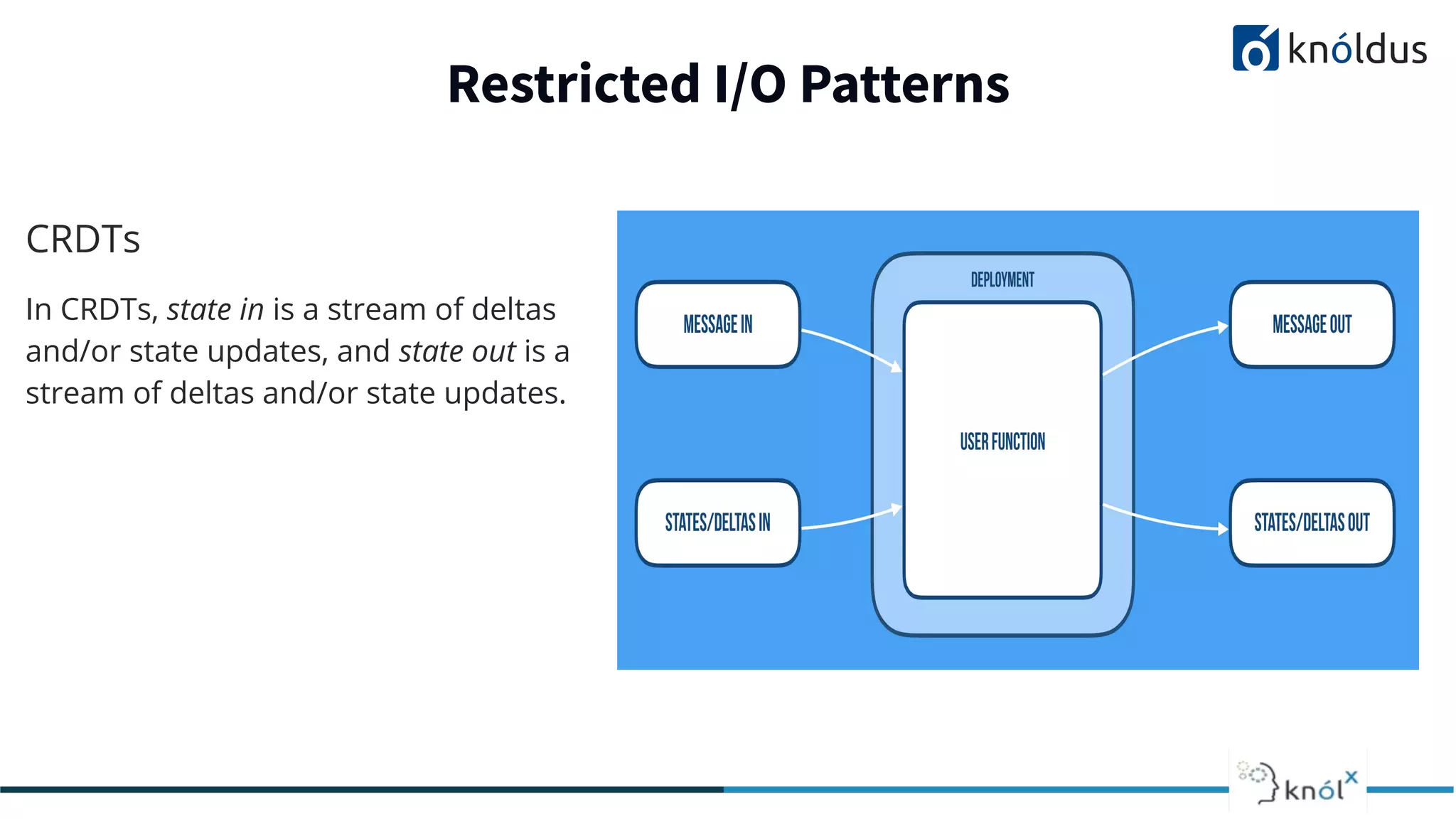
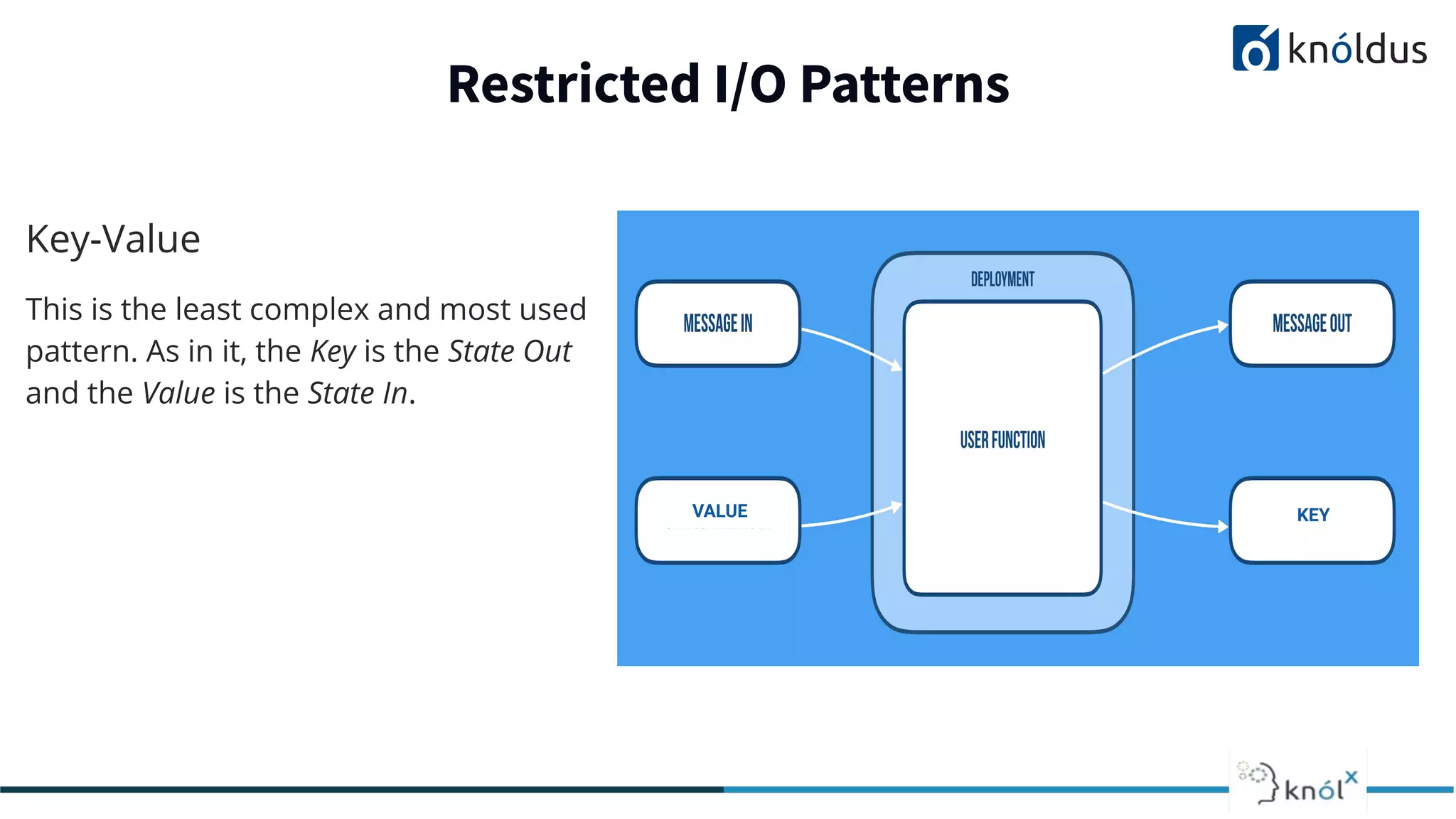
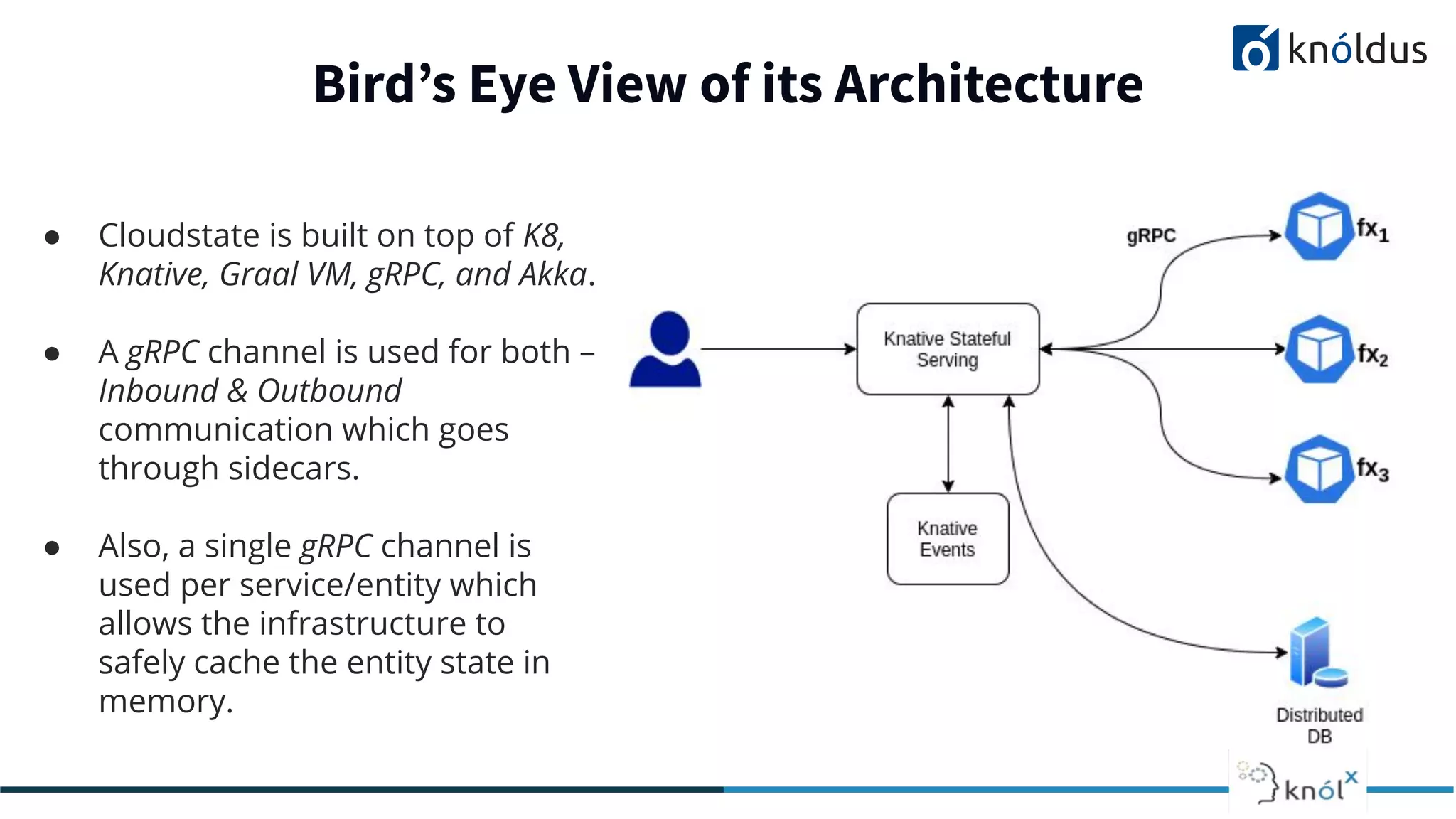
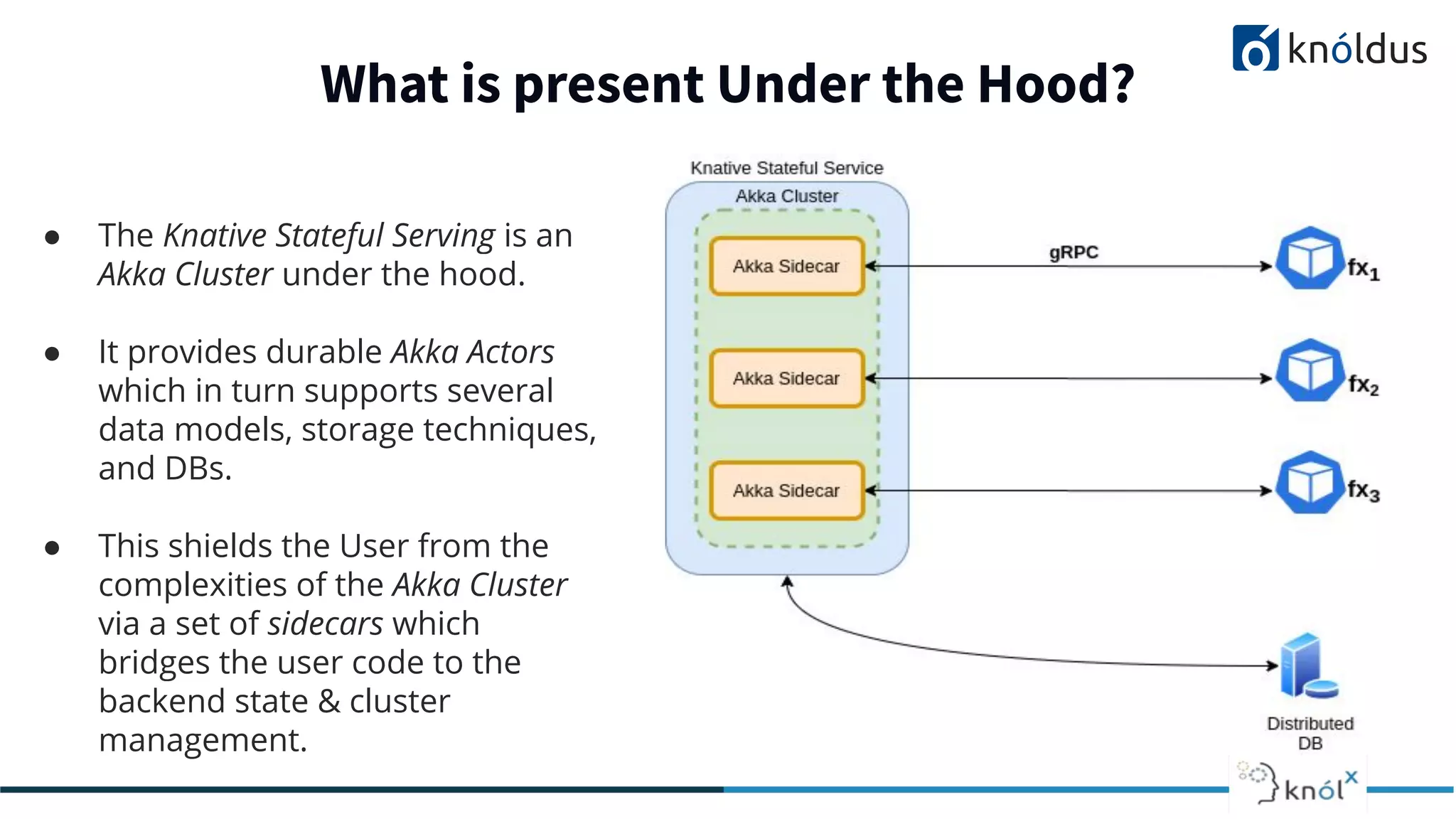
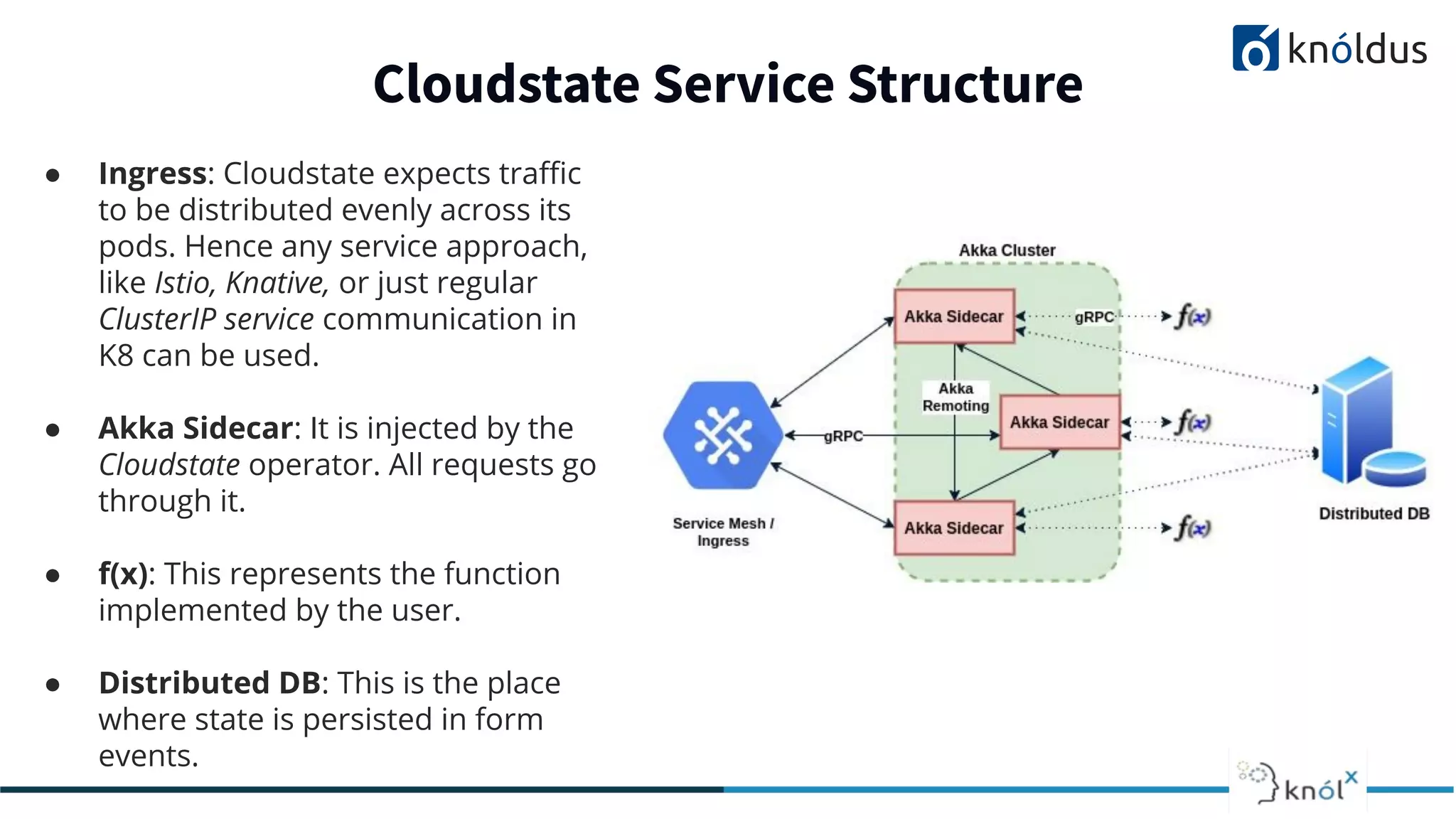
The document discusses serverless computing, outlining its benefits and limitations, such as statelessness, latency issues, and addressability challenges. It introduces Cloudstate, a framework designed for managing distributed state in serverless applications, supporting various patterns like event sourcing and CRDTs. The document emphasizes the importance of focusing on business logic while utilizing Cloudstate in a Kubernetes environment.