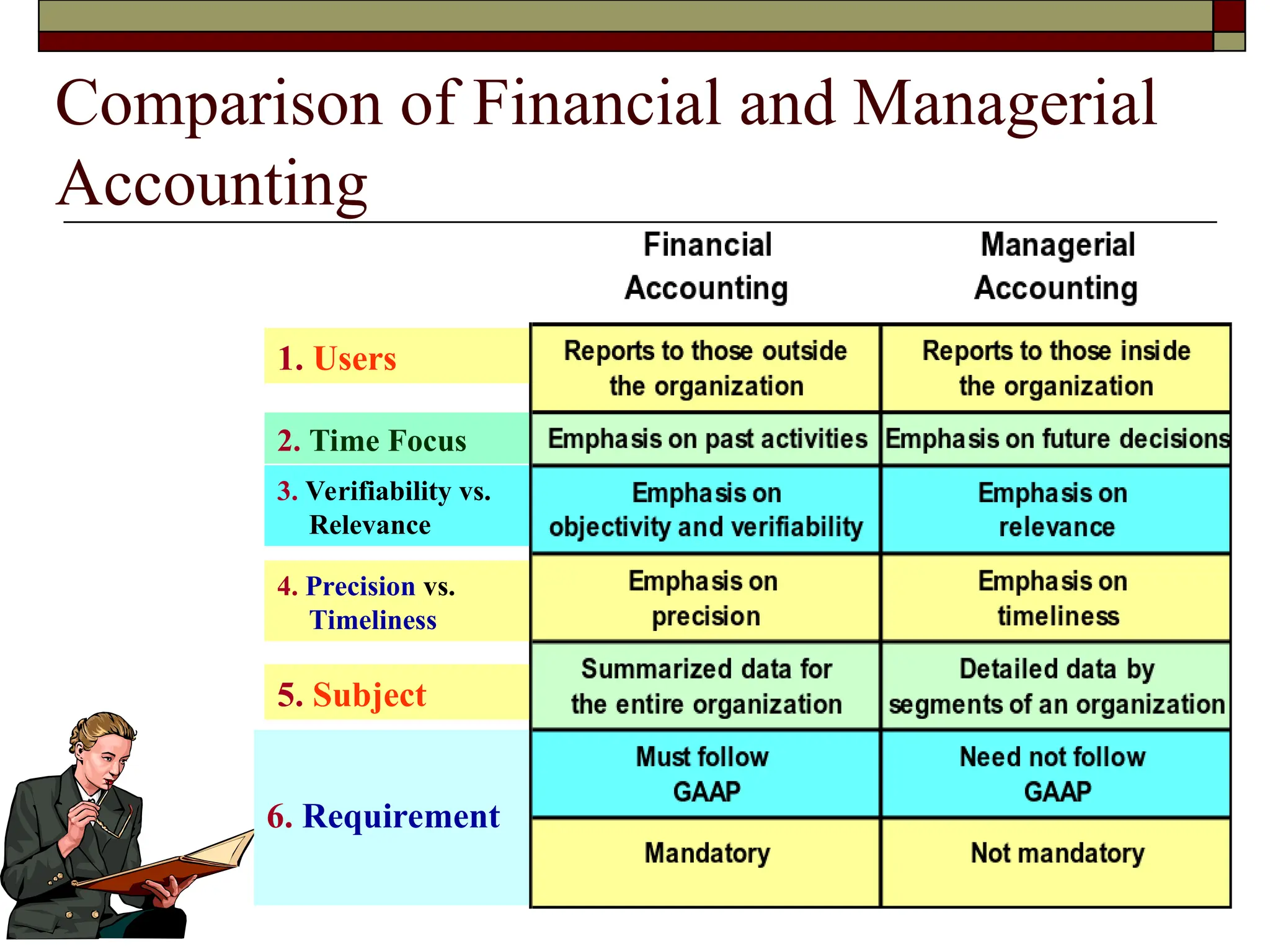
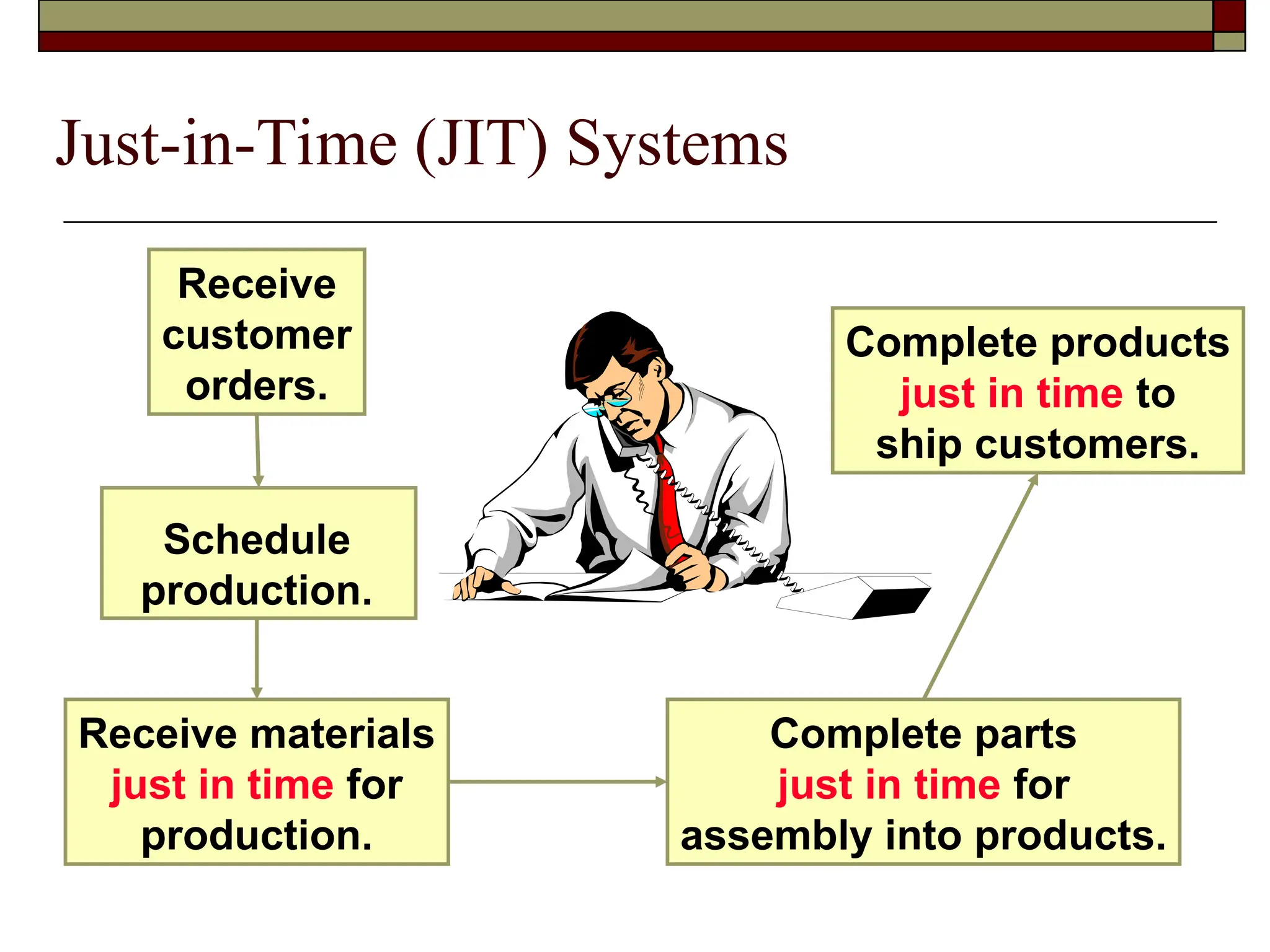
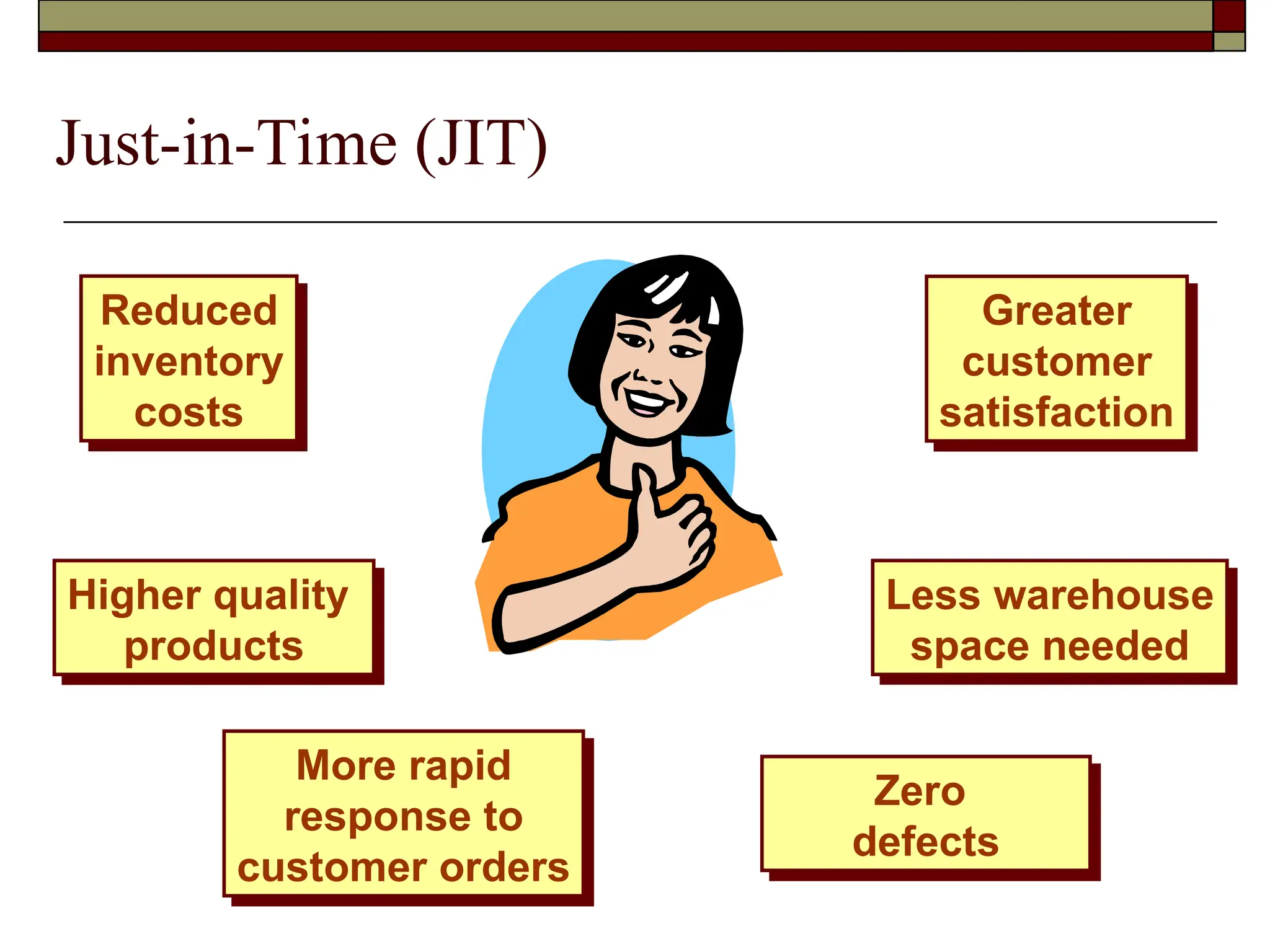
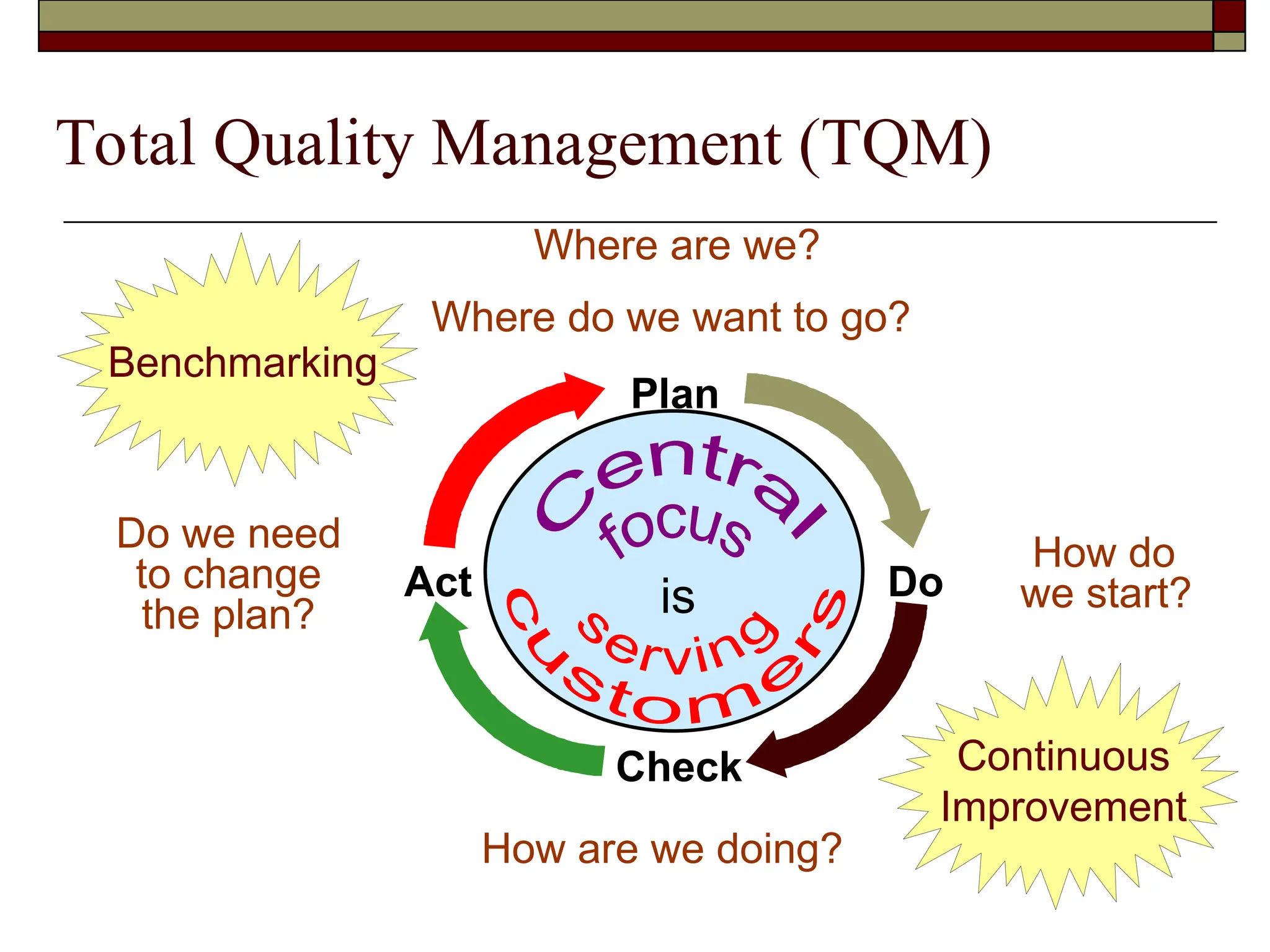
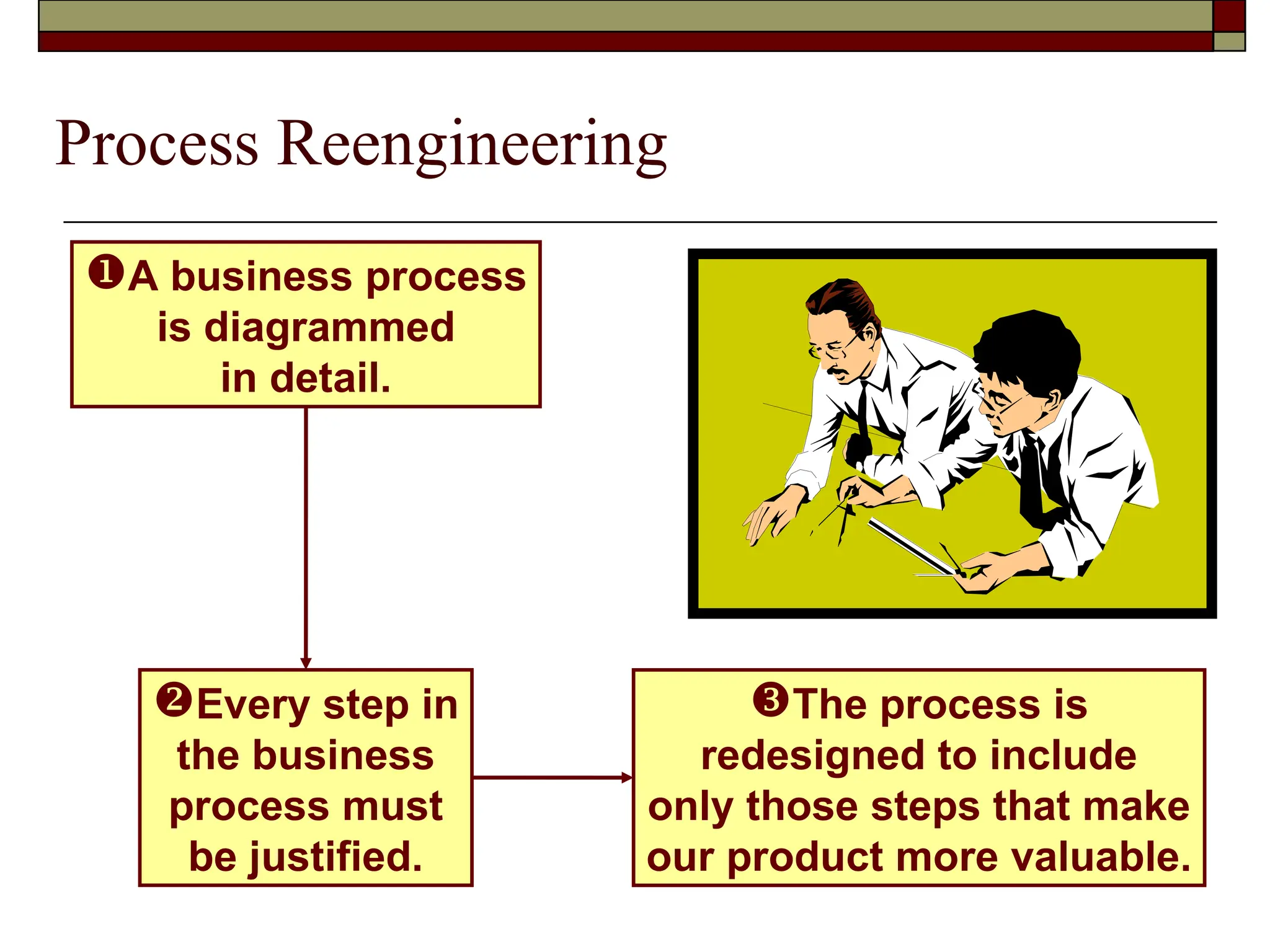
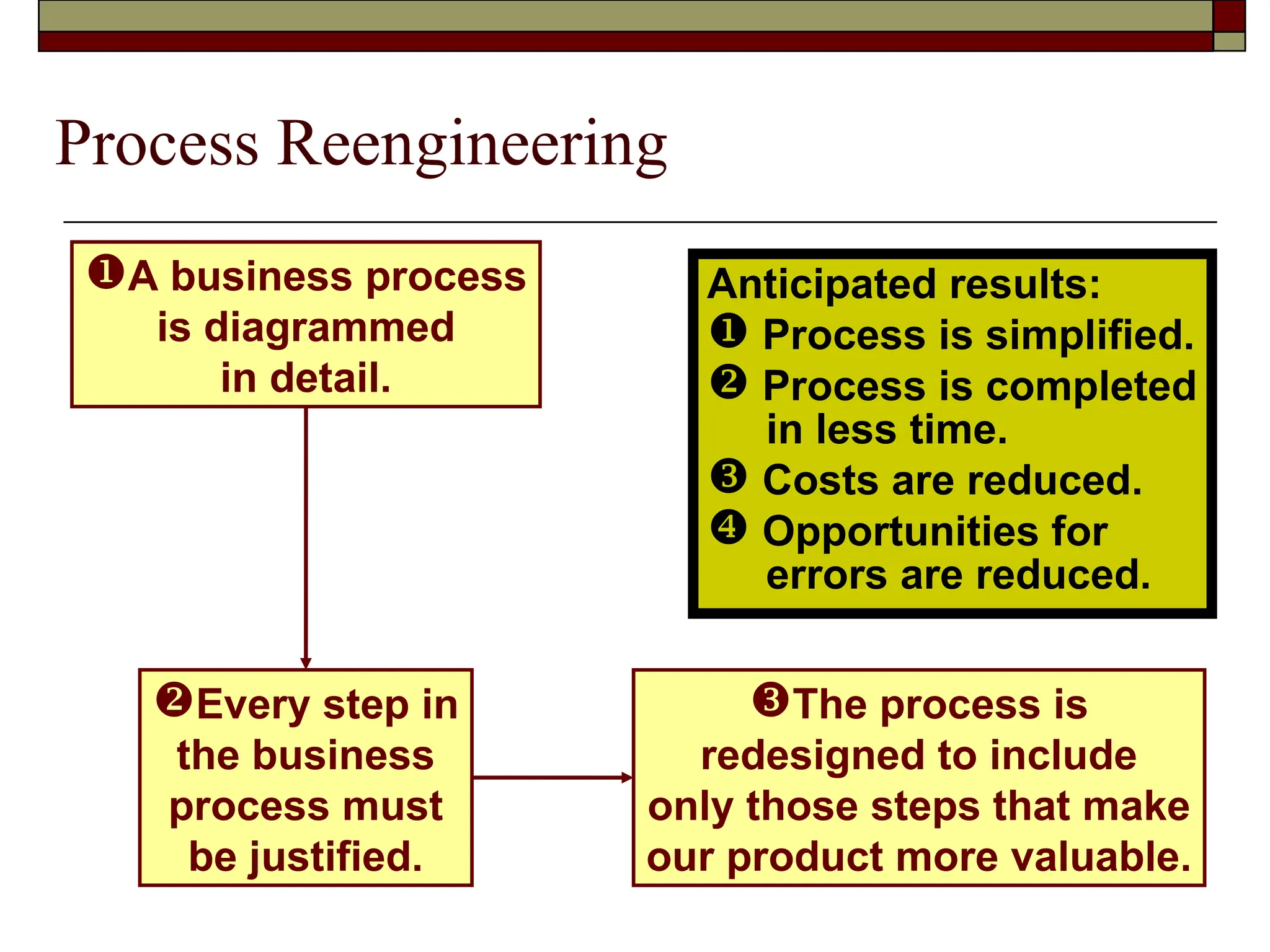
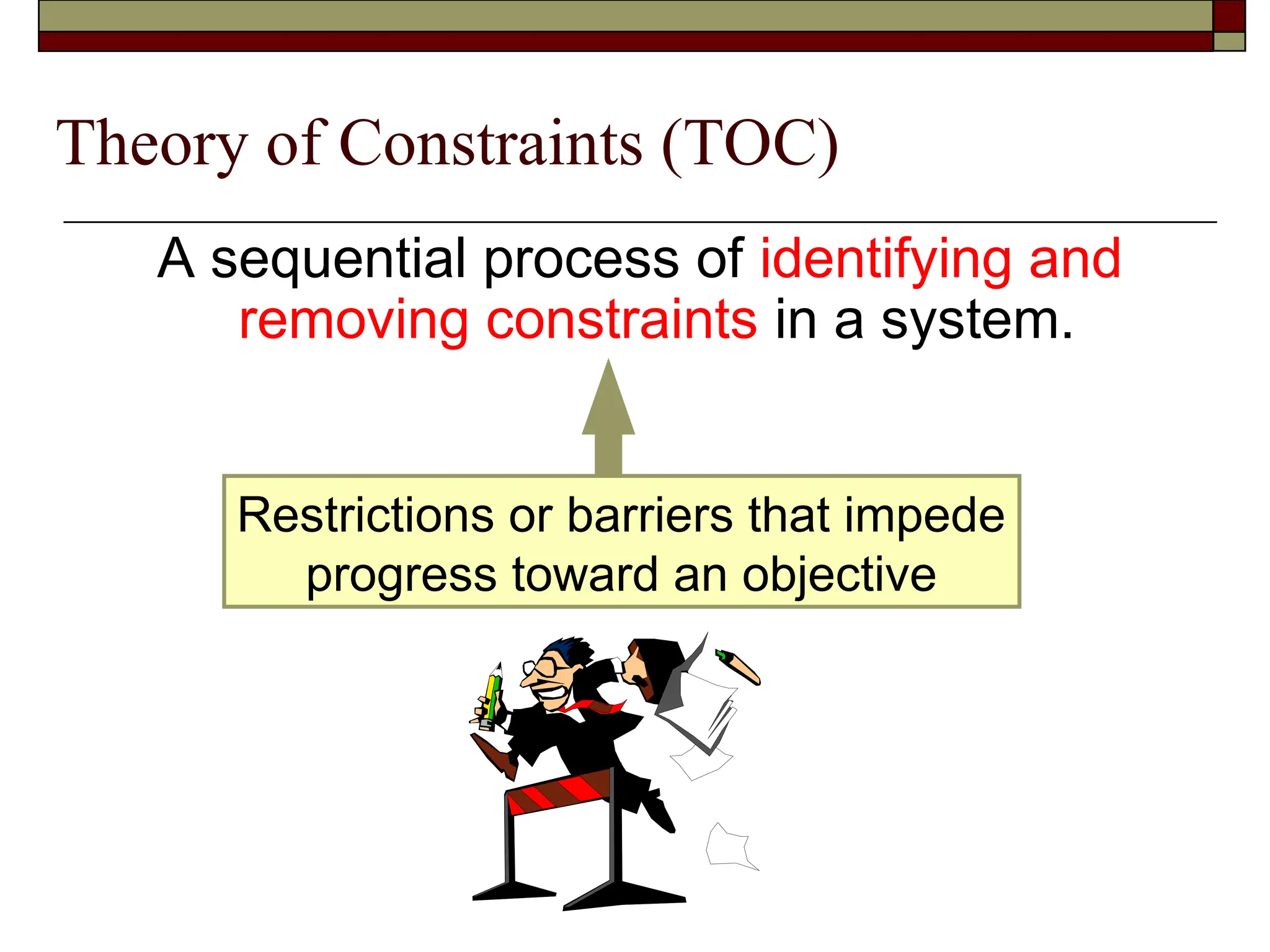
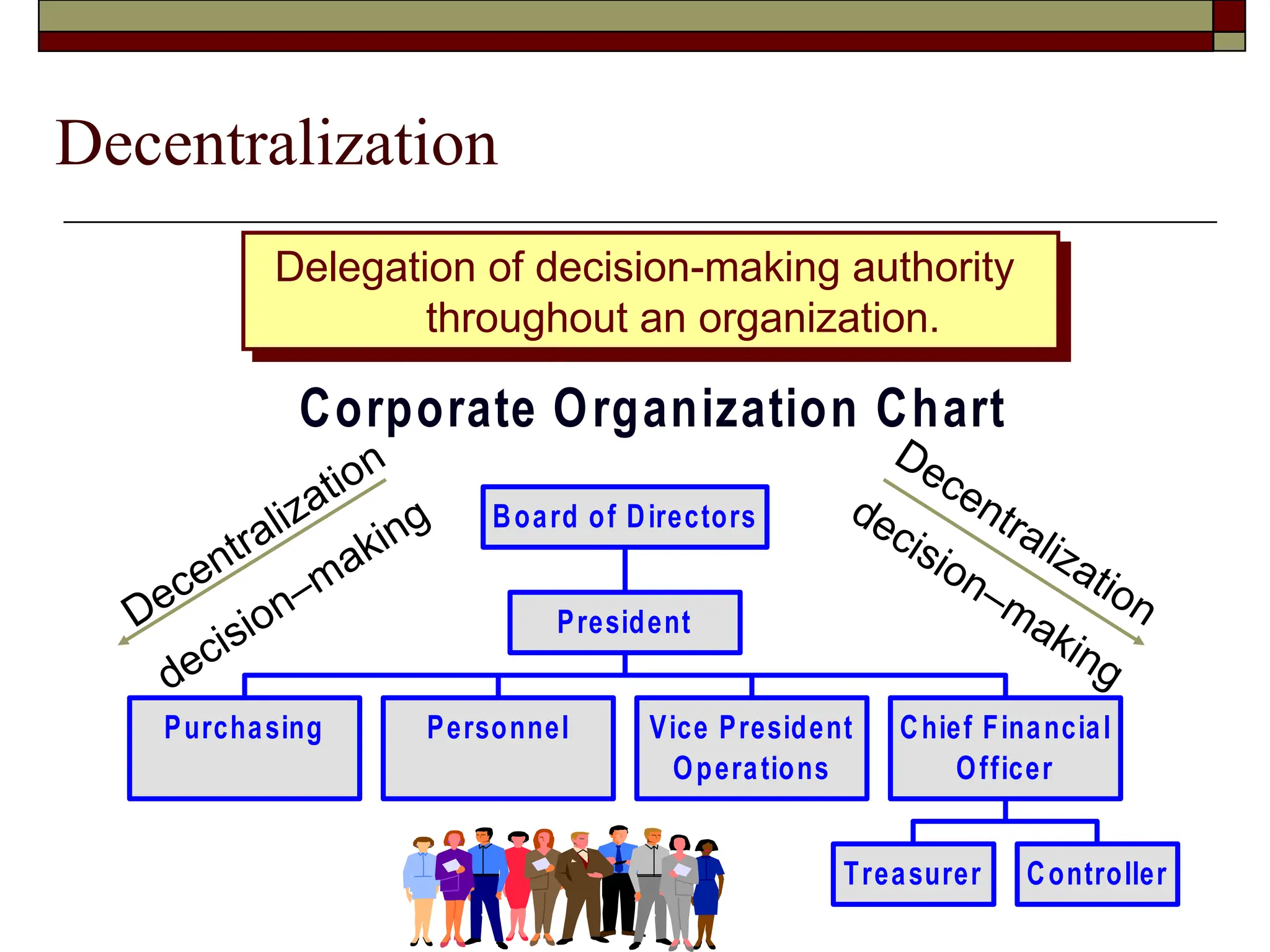
The document covers managerial accounting, highlighting its role in providing financial and nonfinancial information to assist managers in decision-making and performance evaluation within organizations. It distinguishes between financial accounting, which serves external reporting needs, management accounting for internal decision-making, and cost accounting that informs both. Additionally, it addresses the changing business environment and the necessity for new managerial tools like just-in-time systems and total quality management.