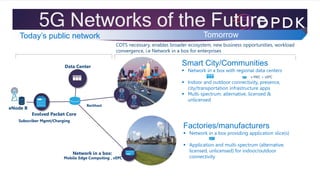
5G and IoT will require network transformation to support 50 billion connected devices by 2020 generating 2 zettabytes of annual global data traffic. 5G will deliver 50x peak data rates, 10x latency reduction and 1000x capacity compared to 4G. It will transform lives through ultra-reliability and low latency enabling applications like autonomous driving, smart cities, drones and virtual/augmented reality. Intel technology can deliver the diverse processing requirements through 5G network slicing to match cloud services to bandwidth, latency and energy needs. 5G networks of the future will utilize network functions virtualization, mobile edge computing and spectrum including millimeter waves, small cells, massive MIMO and beam forming to support the growth of Io