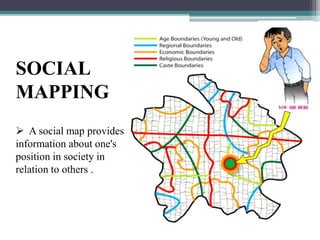
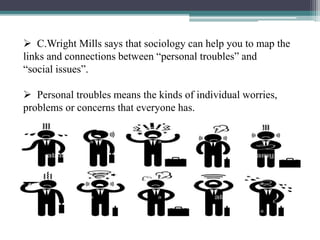
Sociology is defined as the scientific study of human social behavior and society. It is made up of two root words - "socio" meaning society and "logos" meaning study. Prior knowledge about society is often incomplete or biased and needs to be "unlearned" to properly learn sociology. C.W. Wright Mills introduced the concept of "self-reflexivity" where sociology allows one to view themselves from the outside. It also helps map the connections between personal issues and larger social issues. Colonialism in India created new social classes and communities while also giving rise to Indian nationalism and consciousness during the colonial period.