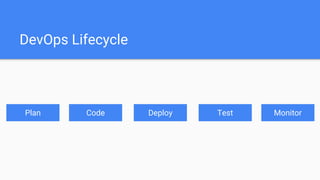
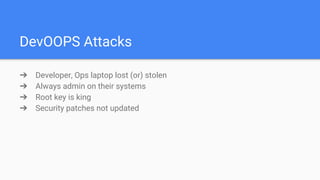
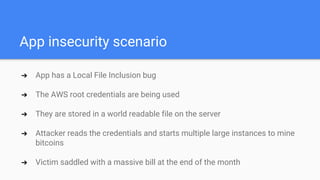
The document introduces DevSecOps, emphasizing the shared responsibility for security within the DevOps lifecycle. It outlines various security risks and scenarios, including attacks resulting from misconfigurations and exposed credentials, and provides solutions like secure authentication, logging, and proper infrastructure management. A DevSecOps playbook checklist is suggested to integrate security throughout the project lifecycle, foster collaboration, and promote a culture of security awareness and continuous improvement.