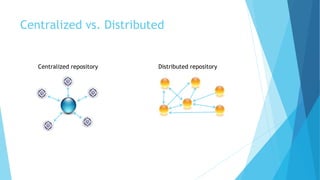
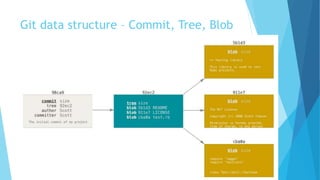
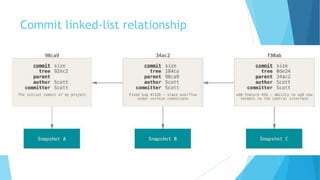
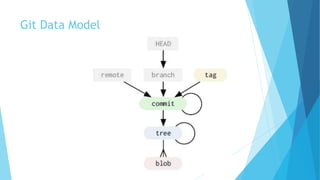
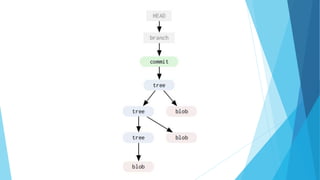
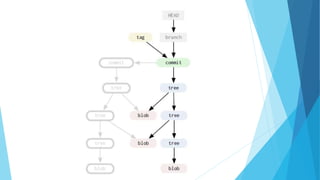
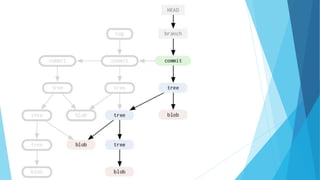
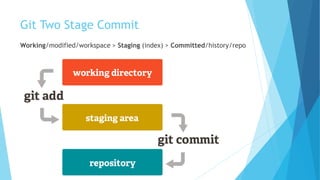
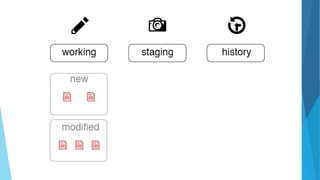
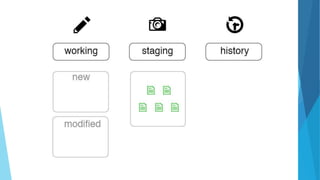
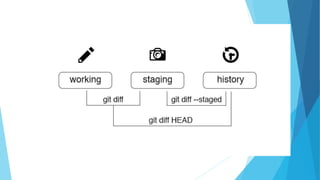
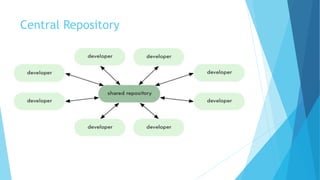
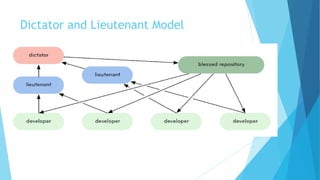
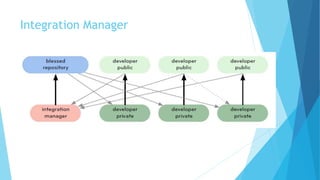
This document provides an introduction to Git and GitHub. It discusses what Git is, including that it is a distributed version control system that tracks changes to source code. It covers key Git concepts like repositories, commits, branches, remotes, and the two stage commit process. It also introduces GitHub and how it builds on Git by providing additional collaboration features like forking repositories, pull requests, and code review.