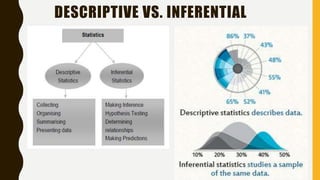
This document provides an introduction to statistics. It defines statistics as a tool for creating new understanding from a set of numbers. It discusses different types of research such as experimental and non-experimental research. It also discusses descriptive versus inferential statistics and how inferences about populations can be made by selecting a representative sample. Finally, it defines what a variable is, including different types of variables like independent, dependent, moderating, and extraneous variables. It provides examples of how variables are used in statistical research.