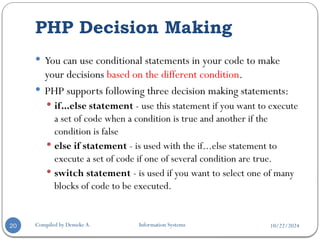
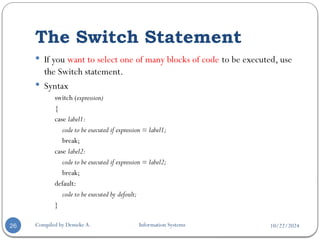
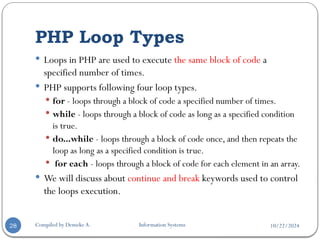
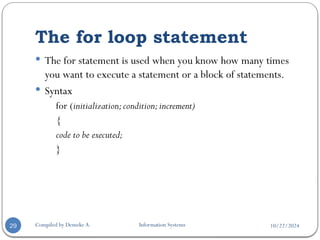
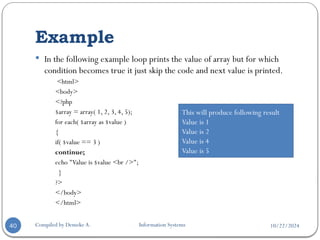
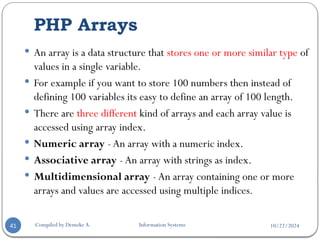
The document provides an overview of PHP, a server-side scripting language used for web development, covering its definition, basic syntax, variables, comments, operators, condition statements, and looping constructs. It explains PHP's compatibility with various databases and servers, highlights the different types of operators, decision-making statements, and loops, alongside examples and syntax. The document also elaborates on PHP's variable and constant usage, the formats for writing comments, and the structure of conditional statements like if-else and switch.



















![10/22/2024
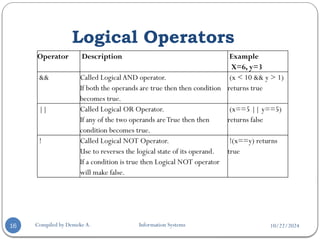
Numeric Array…
Compiled by Demeke A. Information Systems
43
Second method to create array.
<html>
<body>
<?php
$numbers[0] = "one";
$numbers[1] = "two";
$numbers[2] = "three";
$numbers[3] = "four";
$numbers[4] = "five";
foreach( $numbers as $value )
{
echo "Value is $value <br />";
}
?>
</body>
</html>
This will produce following result:
Value is one
Value is two
Value is three
Value is four
Value is five](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter5php-241022121707-ed9be94b/85/Chapter-5Internet-Programming-one-PHP-pptx-43-320.jpg)

![10/22/2024
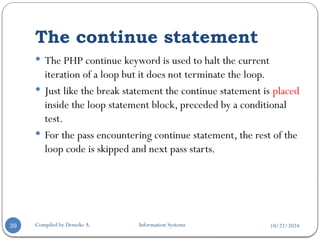
Example
Compiled by Demeke A. Information Systems
45
<html>
<body>
<?php
/* First method to create associate array. */
$salaries = array(
"mohammad" => 2000,
“kadir" => 1000,
"zara" => 500
);
echo "Salary of mohammad is ". $salaries['mohammad'] . "<br />";
echo "Salary of kadir is ". $salaries[‘kadir']. "<br />";
echo "Salary of zara is ". $salaries['zara']. "<br />";
?>
</body>
</html>
Output
Salary of mohammad is 2000
Salary of kadir is 1000
Salary of zara is 500](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter5php-241022121707-ed9be94b/85/Chapter-5Internet-Programming-one-PHP-pptx-45-320.jpg)
![10/22/2024
Second method to create an associative array
Compiled by Demeke A. Information Systems
46
<html>
<body>
<?php
$salaries['mohammad'] = "high";
$salaries['qadir'] = "medium";
$salaries['zara'] = "low";
echo "Salary of mohammad is ". $salaries['mohammad'] . "<br />";
echo "Salary of qadir is ". $salaries['qadir']. "<br />";
echo "Salary of zara is ". $salaries['zara']. "<br />";
?>
</body>
</html>
Output
Salary of mohammad is high
Salary of qadir is medium
Salary of zara is low](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter5php-241022121707-ed9be94b/85/Chapter-5Internet-Programming-one-PHP-pptx-46-320.jpg)

![10/22/2024
Example
Compiled by Demeke A. Information Systems
48
<html>
<body>
<?php
$marks = array(
“Ali" => array
(
"physics" => 35,
"maths" => 30,
"chemistry" => 39
),
“kadir" => array
(
"physics" => 30,
"maths" => 32,
"chemistry" => 29
),
"zara" => array
(
"physics" => 31,
"maths" => 22,
"chemistry" => 39
)
);
/*Accessing multi-dimensional array values */
echo "Marks forAli in physics : " ;
echo $marks[‘Ali']['physics'] . "<br />";
echo "Marks for qadir in maths : ";
echo $marks[‘kadir']['maths'] . "<br />";
echo "Marks for zara in chemistry : " ;
echo $marks['zara']['chemistry'] . "<br />";
?>
</body>
</html>
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter5php-241022121707-ed9be94b/85/Chapter-5Internet-Programming-one-PHP-pptx-48-320.jpg)








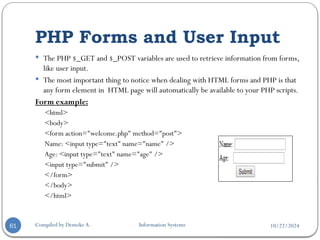
![10/22/2024
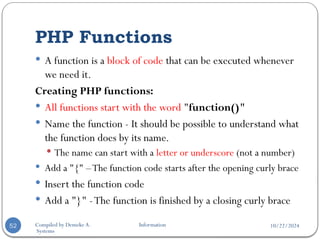
PHP Forms and User Input…
Compiled by Demeke A. Information Systems
62
The example HTML page above contains two input fields and a
submit button.
When the user fills in this form and click on the submit button,
the form data is sent to the "welcome.php" file.
The "welcome.php" file looks like this:
<html>
<body>
Welcome <?php echo $_POST["name"]; ?>.<br />
You are <?php echo $_POST["age"]; ?> years old.
</body>
</html>
Welcome John.
You are 28 years old.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter5php-241022121707-ed9be94b/85/Chapter-5Internet-Programming-one-PHP-pptx-62-320.jpg)

![10/22/2024
PHP $_GET…
Compiled by Demeke A. Information Systems
64
When the user clicks the "Submit" button, the URL sent
could look something like this:
localhost/welcome.php?name=Ax&age=50
The "welcome.php" file can now use the $_GET variable to
catch the form data
Note that the names of the form fields will automatically be
the ID keys in the $_GET array:
Welcome <?php echo $_GET["name"]; ?>.<br />
You are <?php echo $_GET["age"]; ?> years old!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter5php-241022121707-ed9be94b/85/Chapter-5Internet-Programming-one-PHP-pptx-64-320.jpg)



![10/22/2024
The $_REQUEST Variable
Compiled by Demeke A. Information Systems
68
The PHP $_REQUEST variable contains the contents of both
$_GET and $_POST variables.
The PHP $_REQUEST variable can be used to get the result
from form data sent with both the GET and POST methods.
Example
Welcome <?php echo $_REQUEST["name"]; ?>.<br />
You are <?php echo $_REQUEST["age"]; ?> years old!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter5php-241022121707-ed9be94b/85/Chapter-5Internet-Programming-one-PHP-pptx-68-320.jpg)