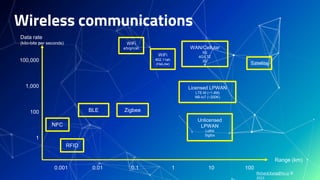
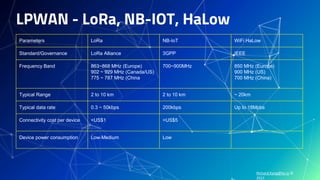
The document provides an overview of edge computing case studies presented by Richard Kang. It discusses Richard's professional experience and the architecture of IoT applications. It then examines the role of edge computing and several edge computing case studies in industries like automobiles, agriculture, manufacturing, smart homes and smart cities. It also compares different wireless communication technologies and low-power wide area network standards. In the end, it provides Richard's contact details and links to additional resources.