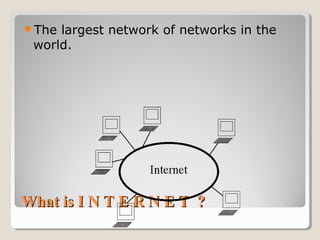
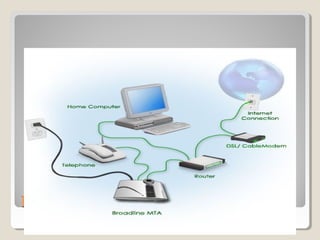
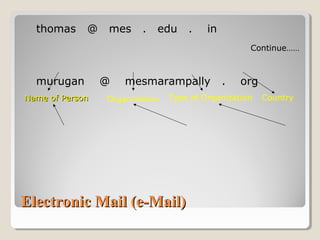
The document discusses the Internet, providing definitions and a brief history. It defines the Internet as a network of networks that connects government, university, and private computers globally. The history notes that ARPA developed the first experimental computer network in 1969, which was later renamed the Internet and adopted TCP/IP. The document then outlines some key Internet services like email, the World Wide Web, search engines, and Wikipedia.