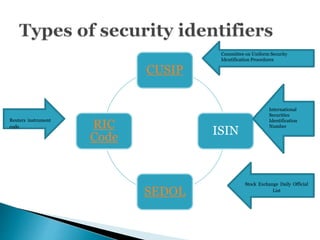
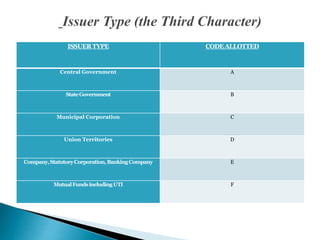
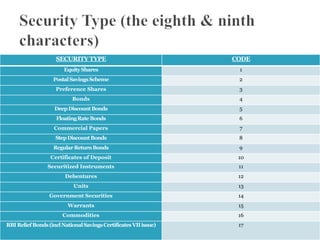
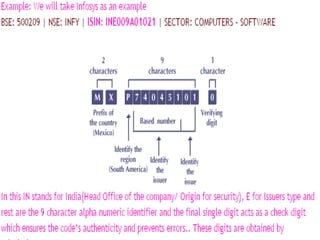
An International Securities Identification Number (ISIN) is a 12-character alphanumeric code that uniquely identifies securities, including stocks, bonds, commercial paper, and warrants traded on a public exchange. ISINs are composed of a two-letter country code, nine-character national number, and check digit. They facilitate unambiguous clearing and settlement of securities globally. The organization that allocates ISINs in each country is that country's National Numbering Agency, such as SEBI in India.