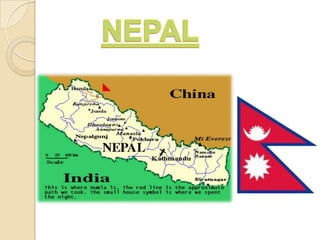
The document discusses the importance of relocation training for international managers moving to Nepal. It provides context on Nepali culture, communication norms, and the business impact of international relocation. Effective relocation training programs should prepare managers and their spouses for cultural adjustment, reduce stress, and ensure spouse satisfaction. Such training is critical to supporting international assignees and avoiding relocation failures. The training should cover topics like cross-cultural skills, language, and helping families integrate into the local community.