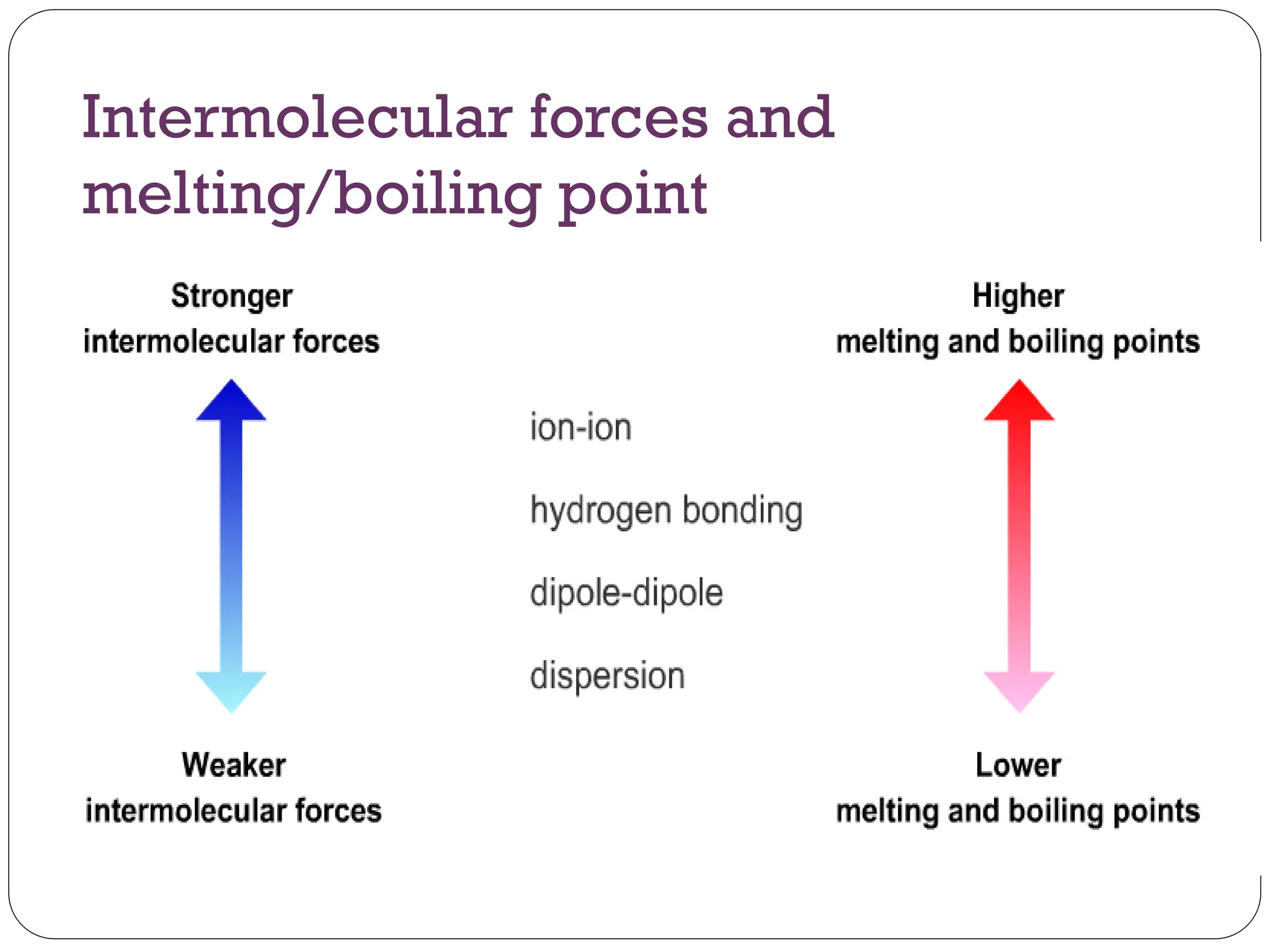
Intermolecular forces are interactions that hold molecules together, influencing whether substances exist as solids, liquids, or gases at room temperature. The three main types of intermolecular forces are hydrogen bonding, dipole-dipole interactions, and dispersion forces, with hydrogen bonding being the strongest. These forces determine the melting and boiling points of substances.