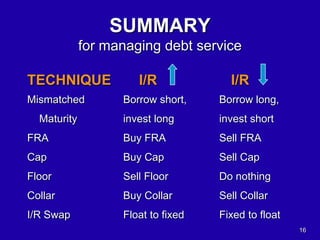
The document discusses interest rate risk management techniques used by companies. It describes two main types of interest rate risk: mismatching of interest rate bases for assets and liabilities, and mismatching in the timing of repricing interest rate sensitive assets and liabilities. To manage these risks, the document outlines various outright and option based instruments that companies can use, including interest rate swaps, forwards, caps, floors, and collars. The goal is for companies to forecast interest rates and select the appropriate tools to match their assets and liabilities.








![9
FORWARD RATE AGREEMENT
Illustration :
USA Co. borrow USD 2,000,000 and buy 90 against 181
days FRA for a notional principal of USD 2,000,000
Agreed rate = 7.5 % Actual rate = 9.0 %
Interest rate payment
USD 2,000,000 x 0.09 x 91/360 = USD 45,500
Seller of FRA will pay
USD 2,000,000 x [(0.09 - 0.075) x 91/360] = USD 7,583.33
CF of USA Co. at end of loan :
Interest rate payment = USD 45,500.00
Cash Inflow from FRA = USD 7,583.33
Net Payment = USD 37,916.67](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interestrateriskmanagement-230925024252-20a0ff38/85/Interest-Rate-Risk-Management-pdf-9-320.jpg)