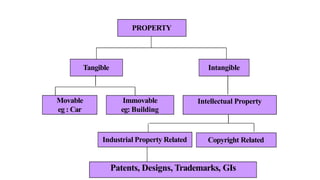
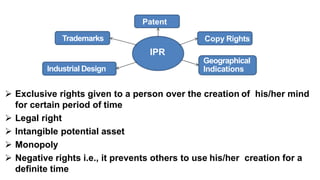
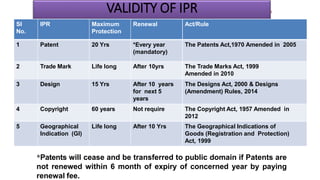
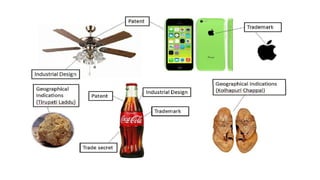
Intellectual property rights (IPRs) provide exclusive rights over creations and inventions for a certain period of time. The main types of IPRs are patents, copyrights, trademarks, industrial designs, and geographical indications. IPRs incentivize individuals to create new works and inventions by according legal protection and monetary rewards. They ensure authentic and original goods are available in the market. The validity period and renewal process varies for each type of IPR, ranging from 15 years for designs to life-long protection for trademarks, with the goal of promoting continued innovation.