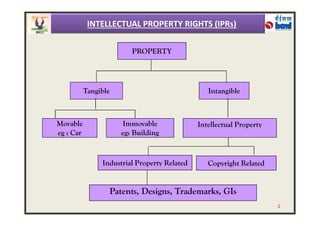
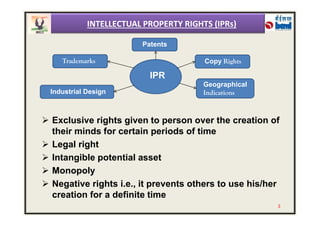
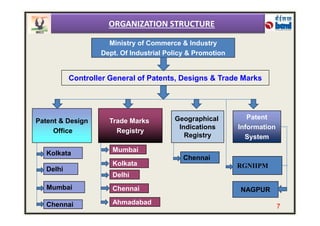
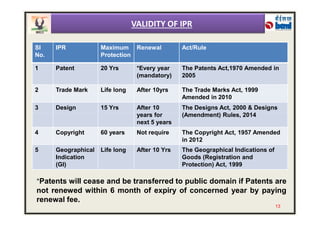
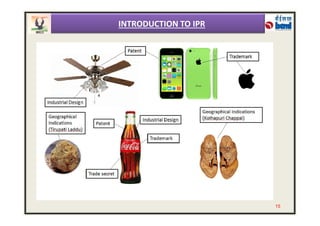
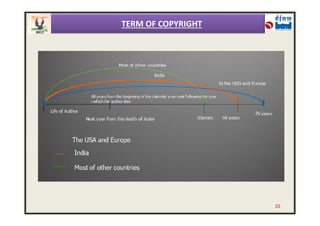
The document provides an overview of intellectual property rights (IPRs) in India. It discusses the various types of IPRs including patents, copyrights, trademarks, industrial designs, and geographical indications. For each type of IPR, it describes what qualifies for protection, how long protection lasts, and some key examples. It also outlines the organizations responsible for IPRs in India and summarizes the criteria for patentability according to the country's Patent Act and Rules.