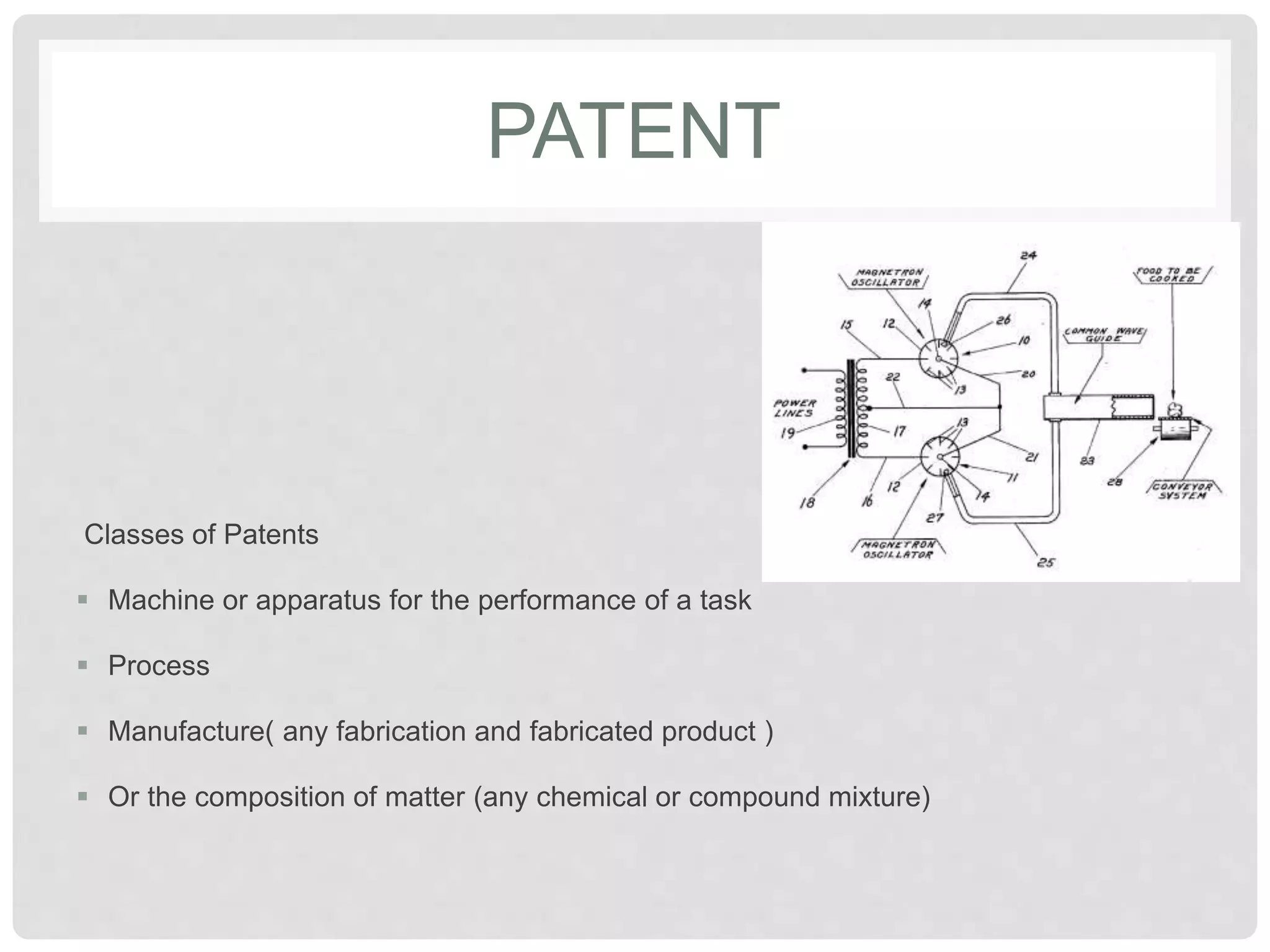
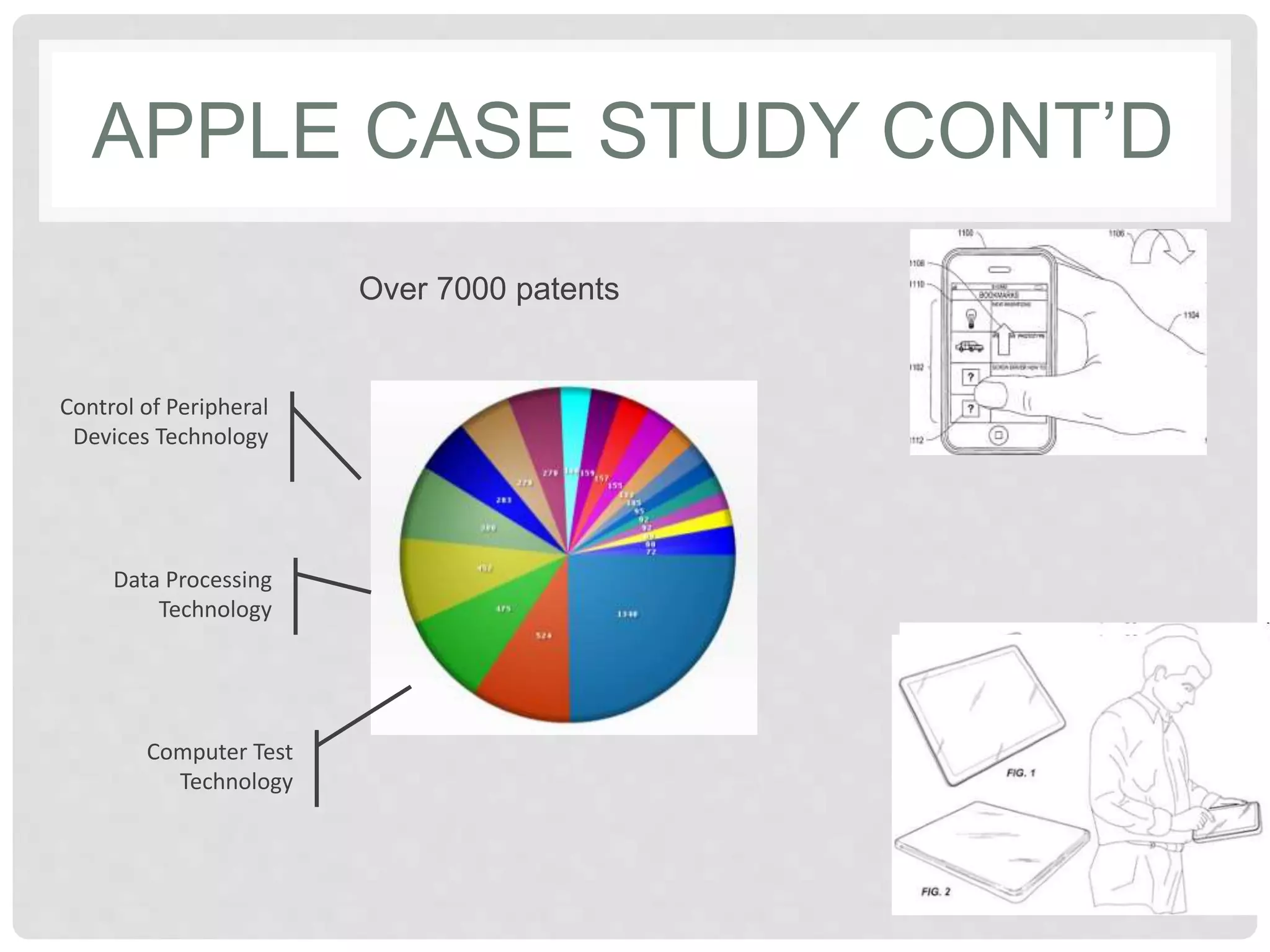
The document discusses various ways to protect intellectual property. It describes intellectual property as legal rights over things people create or invent. The main types of intellectual property protection discussed are trademarks, patents, copyright, and trade secrets. Trade secrets protect confidential information like formulas as long as secrecy is maintained. The document also provides a case study of the intellectual property considerations for Apple's launch of the iPad, including its large patent portfolio and use of trade secrets, copyrights, and contracts to protect technologies.