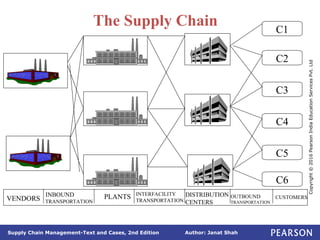
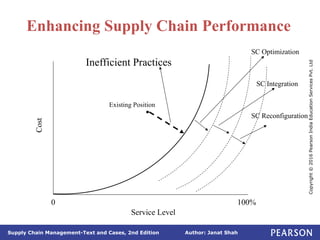
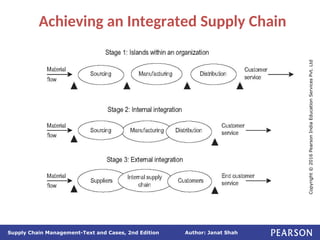
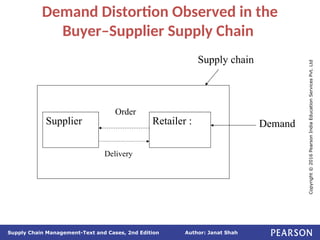
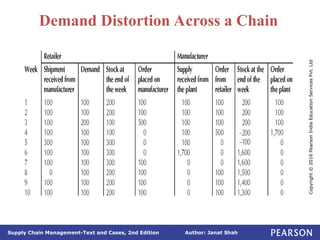
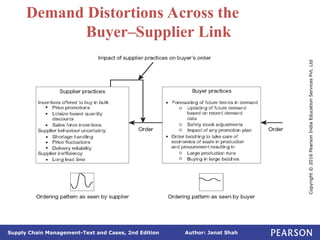
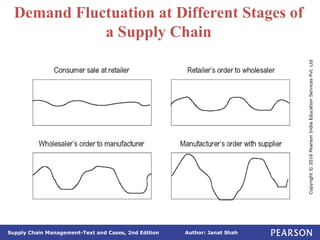
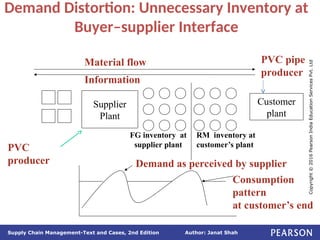
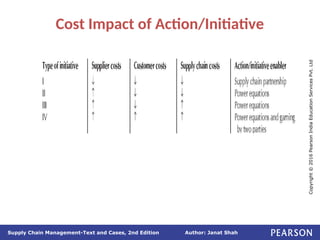
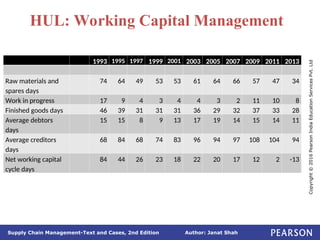
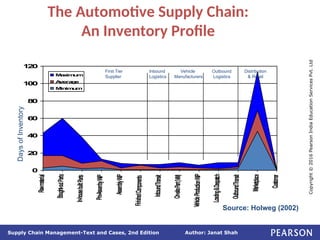
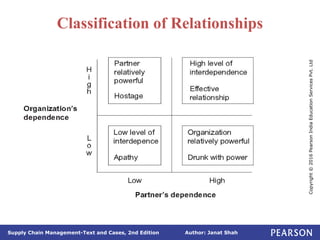
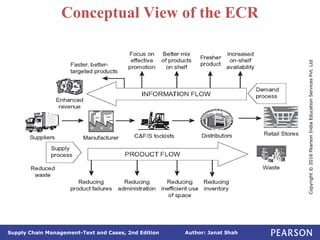
The document discusses supply chain integration, emphasizing the stages involved, causes of the bullwhip effect, and barriers to successful collaboration among firms. It outlines strategies for improving integration and mitigating demand distortions, such as sharing information and aligning incentives. Successful relationships in supply chains are highlighted as essential for achieving operational efficiencies and overcoming external coordination challenges.