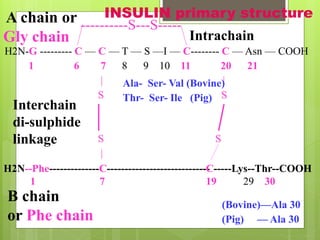
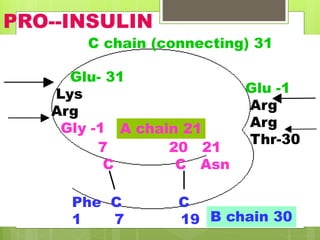
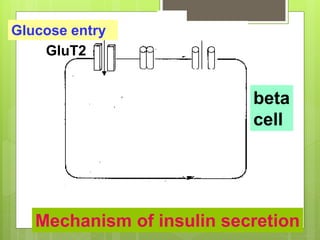
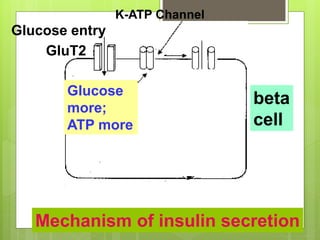
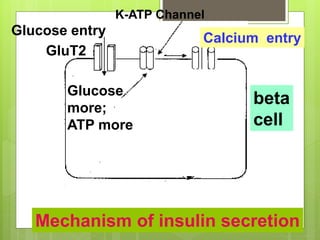
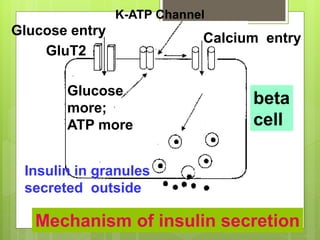
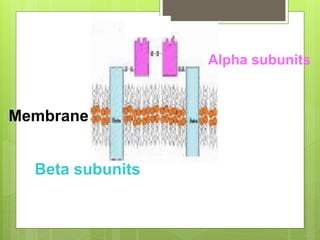
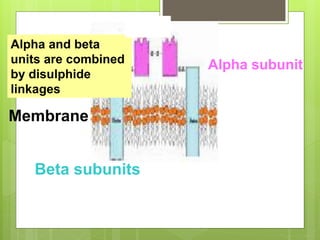
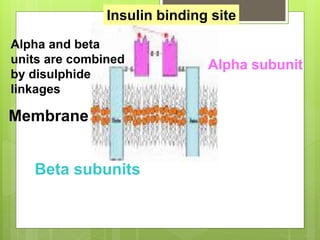
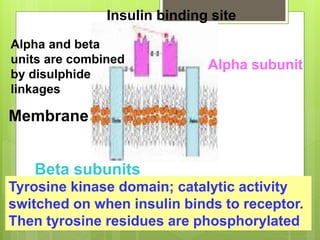
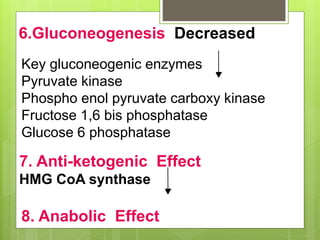
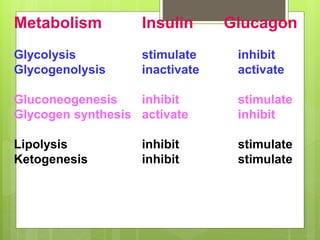
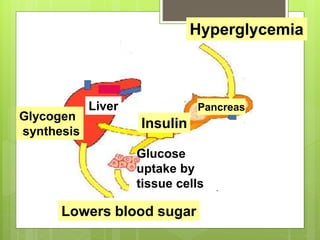
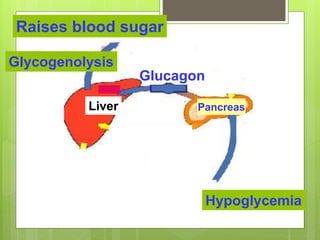
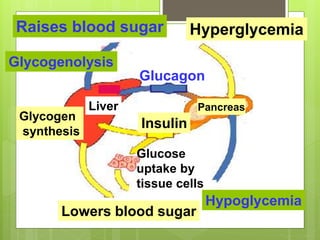
Insulin is a protein hormone composed of two polypeptide chains, the A and B chains, which are linked by disulfide bonds. It is synthesized in the beta cells of the pancreas as pre-proinsulin and then cleaved to form the active hormone. Insulin regulates carbohydrate and fat metabolism by stimulating glucose uptake in muscle and fat cells, glycogen synthesis in the liver, and inhibiting lipolysis and gluconeogenesis. This helps to lower blood glucose levels.