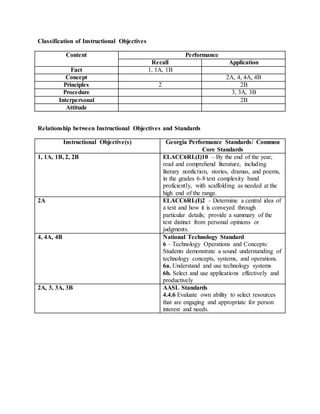
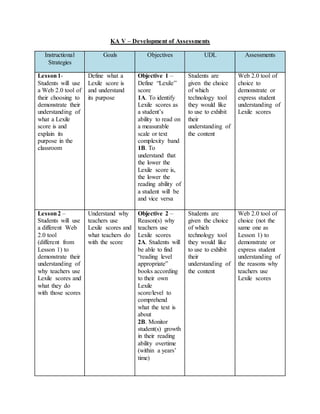
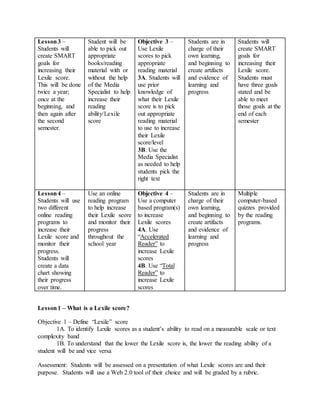
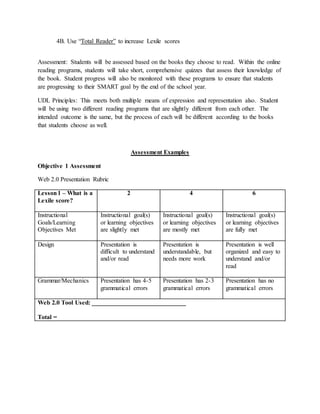
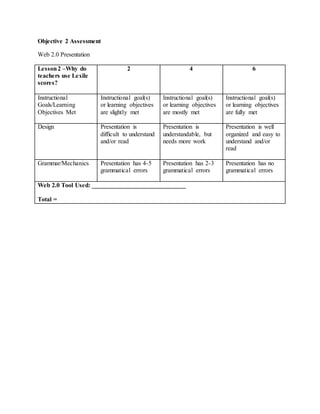
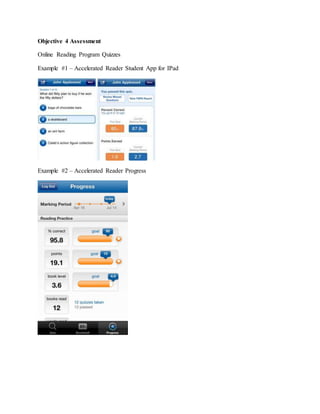
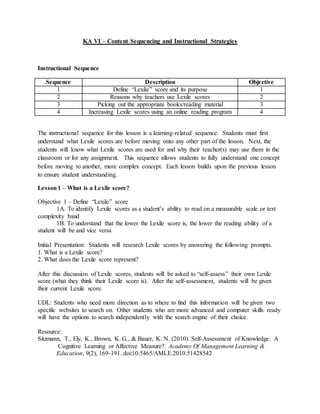
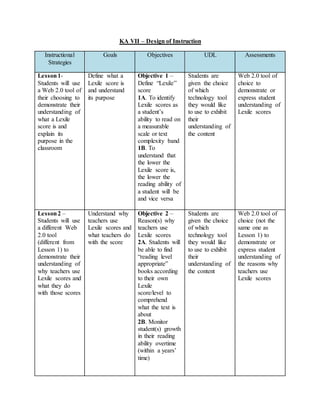
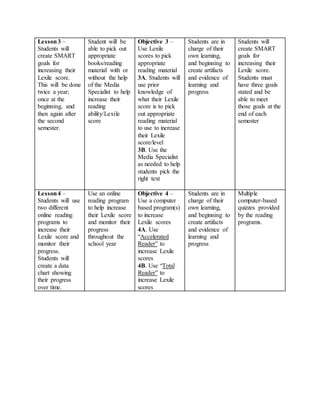
The document provides information on identifying a learning problem and target audience for an instructional plan. It discusses a problem identified by teachers at Harlem Middle School, where many 6th-8th grade students are reading below grade level. Two online reading programs will be used to help students increase their Lexile scores, which measure reading ability, and improve their reading comprehension. The instructional goals are to provide opportunities for students to increase their Lexile scores, learn reading strategies, and boost comprehension in all subjects.