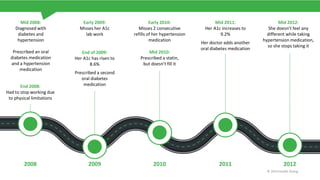
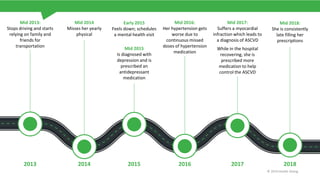
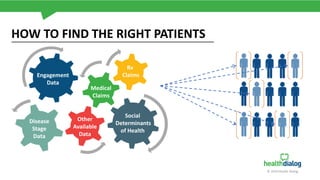
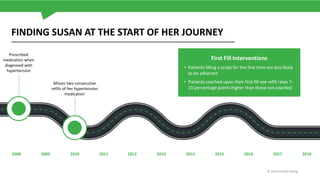
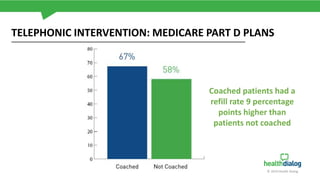
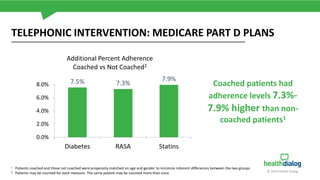
The document discusses the critical issue of medication adherence, highlighting that 50% of patients with chronic conditions do not take their medications as prescribed, leading to significant health risks and costs. It uses the case of a patient named Susan to illustrate predictive models and early interventions to improve adherence, particularly through telephonic coaching and tailored support. The analysis suggests that engaging patients early and addressing barriers can substantially enhance medication adherence rates.