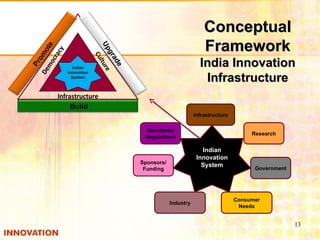
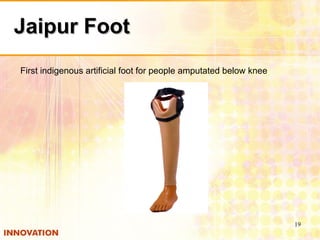
The document discusses the Indian innovation system, highlighting its infrastructure, capabilities, challenges, and opportunities for improvement. It provides examples of successful innovations, such as the Tata Nano, and emphasizes the need for collaboration between academia and industry to enhance technology commercialization and address market demands. Recommendations are made for creating a supportive environment for innovation by increasing partnerships, enhancing awareness, and ensuring that incubators respond to market needs.