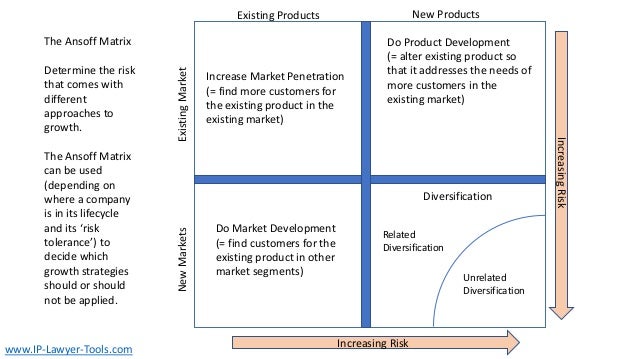
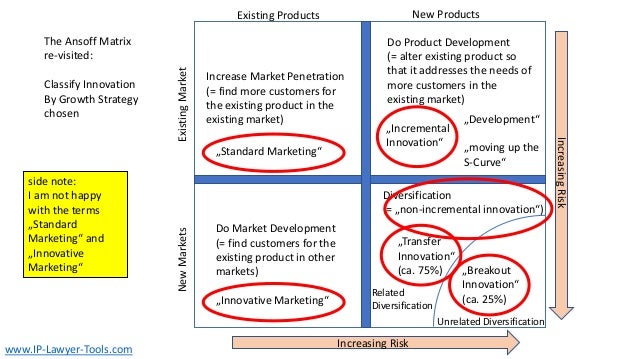
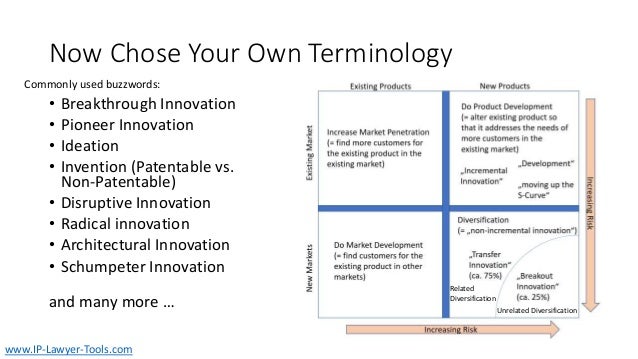
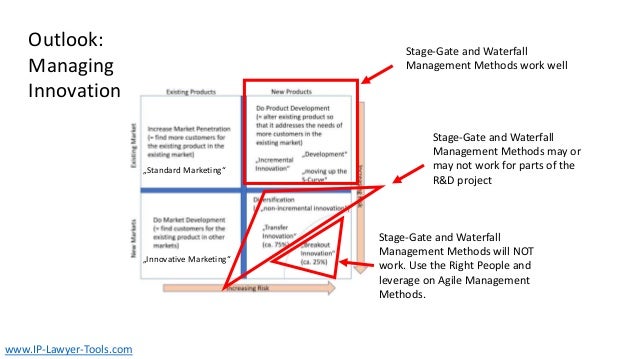
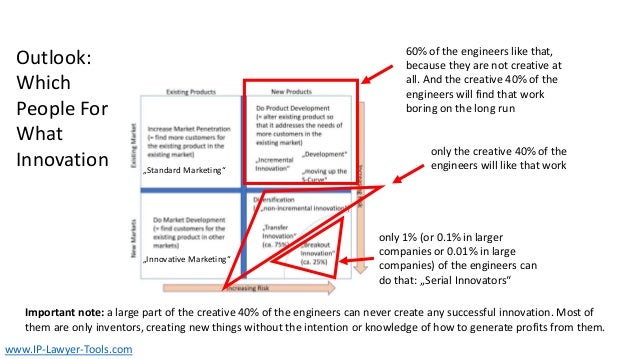
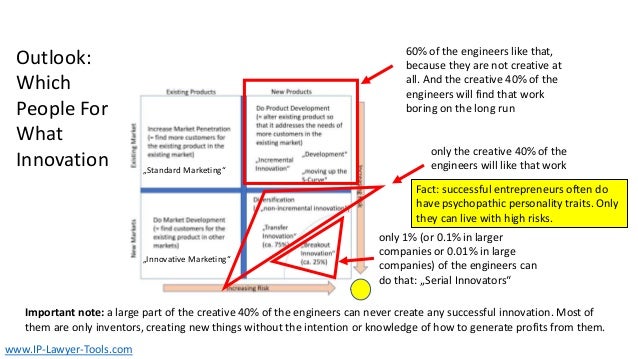
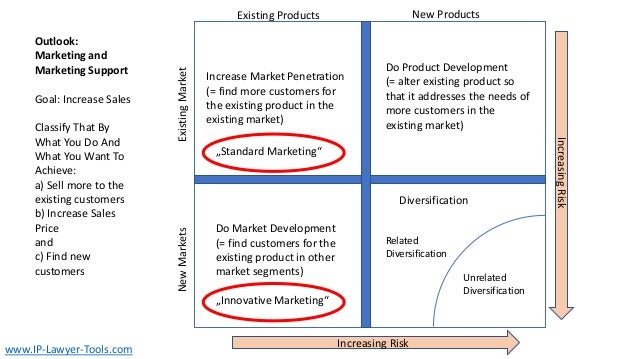
The document discusses innovation, defining it as the creation of something new that generates profit within a constrained timeframe. It introduces the Ansoff matrix for classifying growth strategies, including market penetration, product development, market development, and diversification, while emphasizing the associated risks. Furthermore, it explores various innovation terminologies and highlights the importance of matching growth strategies with appropriate marketing approaches to enhance sales and success in a competitive environment.