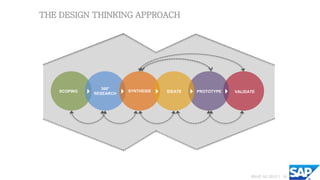
The document provides an overview of design thinking and the design thinking process. It discusses scoping, 360 degree research including field research, synthesis to gain insights and create personas/points of view, ideation to generate ideas, and validation by getting feedback from end users. The design thinking approach aims to combine the right people, needed space, and supporting process to create innovation by meeting user needs.

































![SYNTHESIS
Coming up with a POV Point of View
POV = User + Need + Insight Template:
[Attributed user] needs (to) [Position]
The Point of View is one sentence that
because [Insight]
creates an image in your mind. Based on
Example:
an understanding of a user group and an The Department Supervisor needs time with
insight into a specific need, it narrows the customers, since knowing who they are
focus and makes the problem specific. enables her to optimize her ordering plan.
©SAP AG 2012 | 35](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/innojamdeckit3604sap-121217160234-phpapp02/85/Inno-jam-deck_it3604sap-35-320.jpg)










