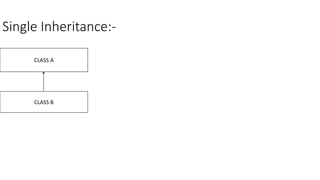
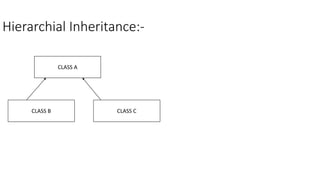
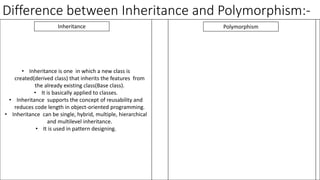
Inheritance allows new classes to inherit properties and behaviors from parent classes. This allows code reuse and extension of existing classes. There are different types of inheritance like single, multilevel, and hierarchical. Polymorphism allows performing the same action in different forms through method overloading and overriding. The key difference is that inheritance is applied to classes for code reuse while polymorphism uses polymorphic methods to perform the same action in different forms.