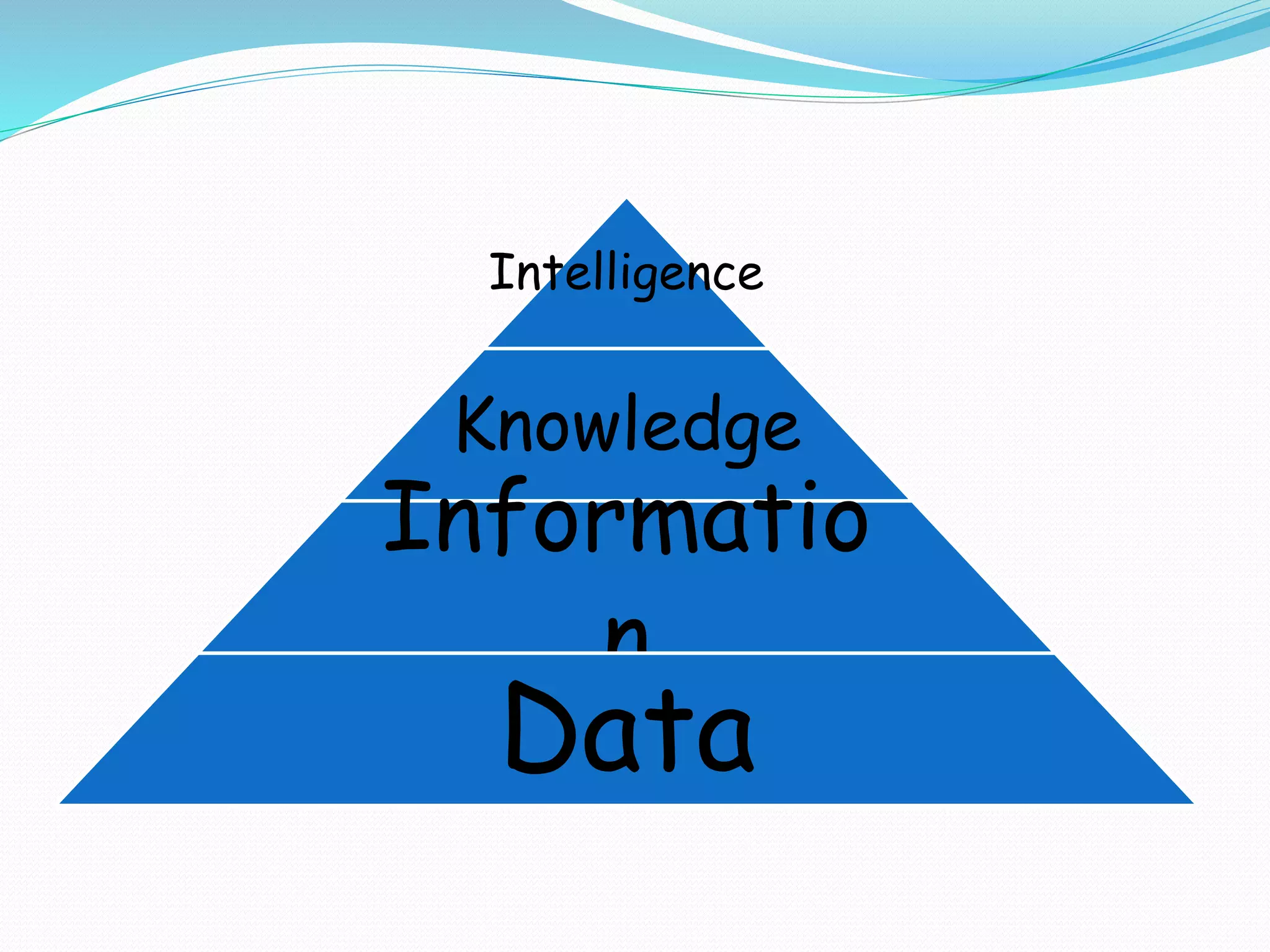
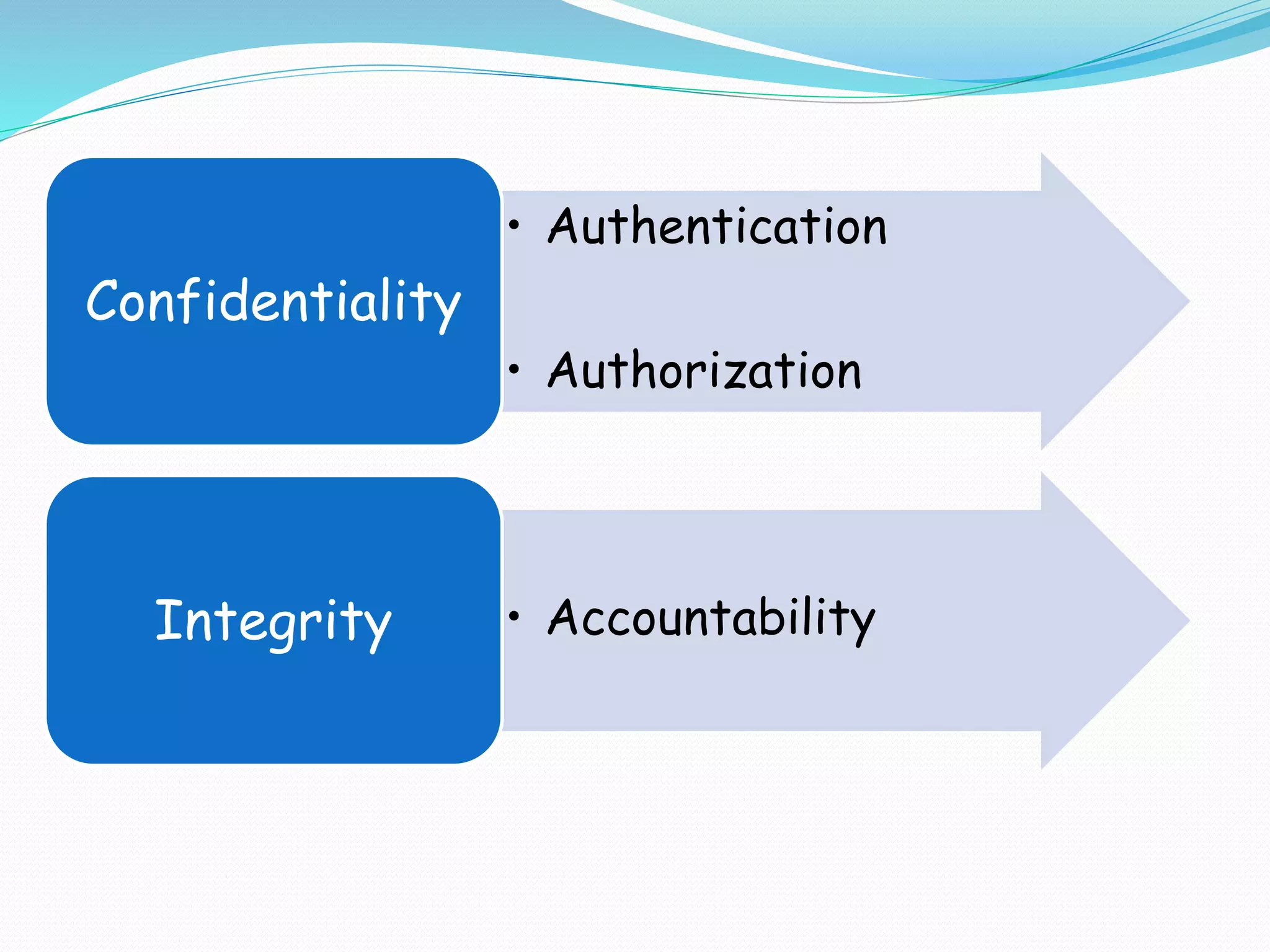
The document discusses information security, highlighting key principles such as confidentiality, integrity, and availability. It covers various types of hackers, including ethical (white hat), malicious (black hat), and hybrid (grey hat) hackers, as well as techniques used in hacking and security breaches. Cryptography and steganography are also mentioned as important tools in protecting information.