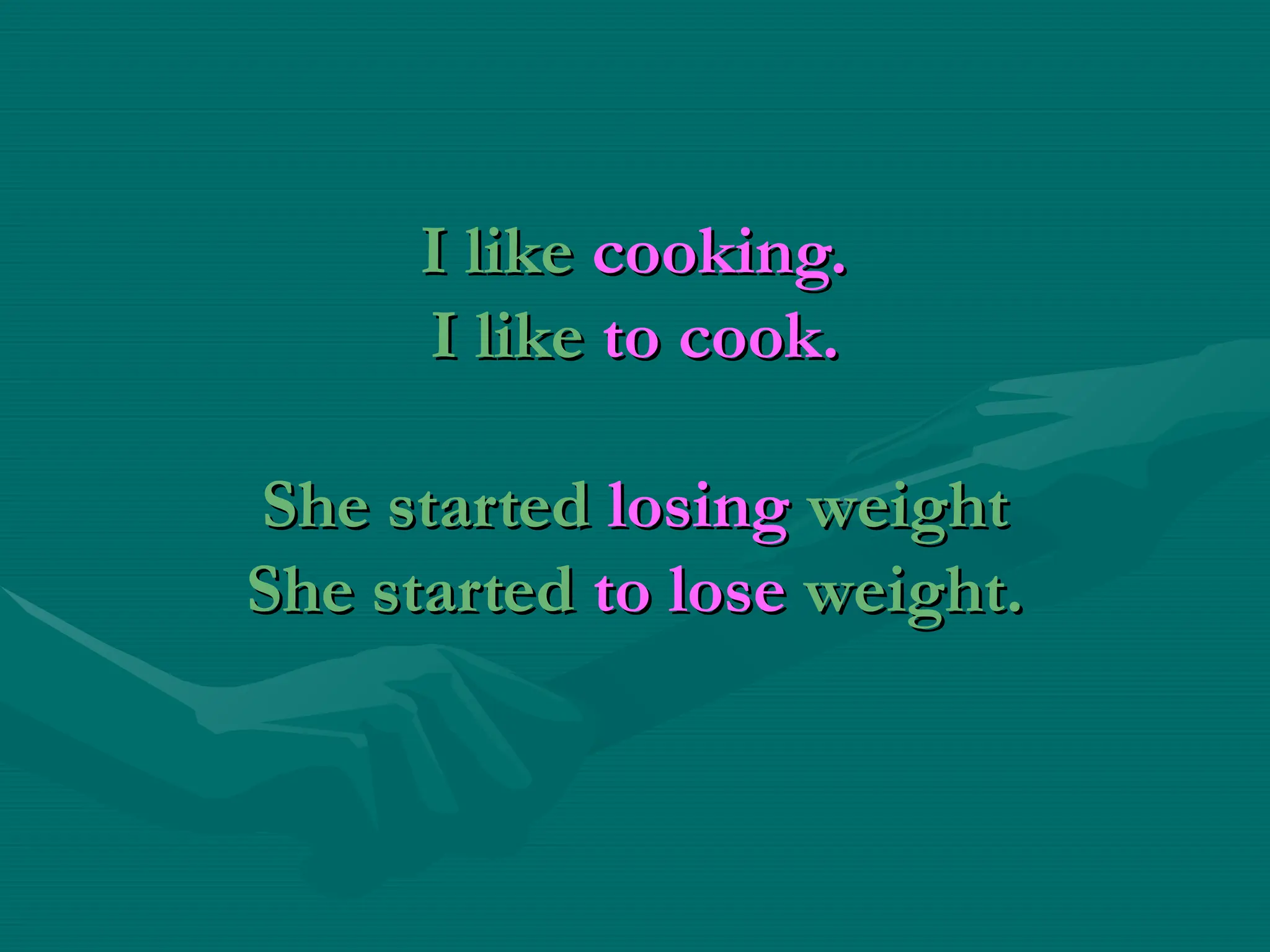The document explains the use of gerunds and infinitives in English grammar, detailing their functions as subjects, objects, and complements. It provides rules for their formation, including how to create negative forms, and highlights verbs that require each form. Additionally, it discusses specific cases, such as verbs that can take both forms and their different meanings, along with examples for clarity.