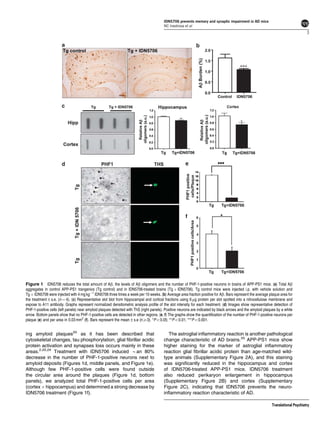
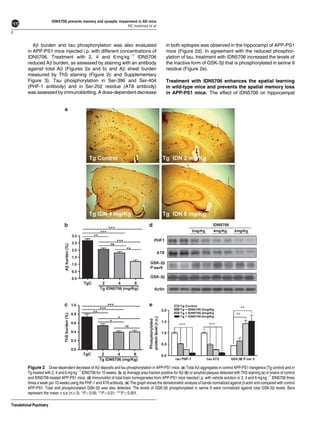
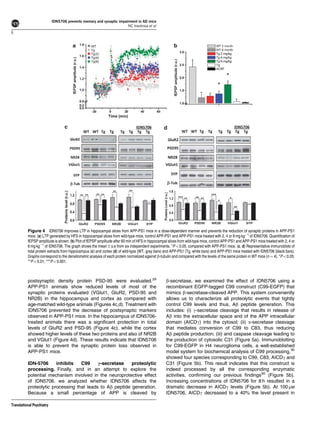
Tetrahydrohyperforin (IDN5706), a derivative of the active molecule hyperforin in St. John's Wort, was examined for its ability to prevent cognitive deficits and synaptic impairment in an Alzheimer's disease mouse model. Five-month old APPswe/PSEN1DE9 mice were treated with IDN5706 for 10 weeks. IDN5706 improved memory, prevented decreases in synaptic proteins and LTP, and reduced amyloid-beta plaque burden, tau hyperphosphorylation, and astrogliosis. In cell cultures, IDN5706 decreased amyloid precursor protein processing leading to amyloid-beta peptide generation. The results suggest IDN5706 may be a potential therapeutic for treating Alzheimer's