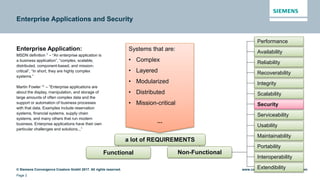
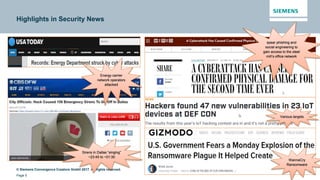
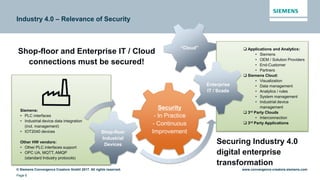
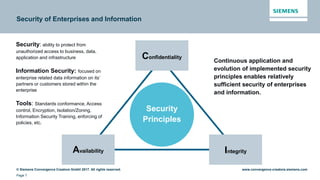
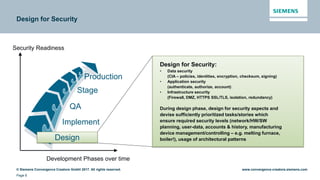
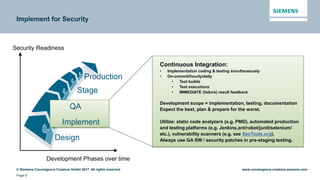
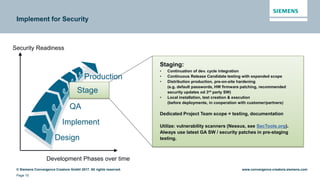
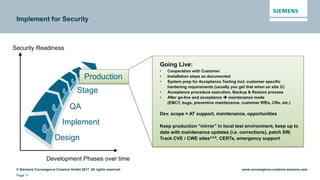
This document discusses security aspects related to developing enterprise applications for Industry 4.0. It begins with an overview of Industry 4.0 and its key components like cyber-physical systems, the internet of things, and smart factories. It then discusses the complexity of enterprise applications and important non-functional requirements like security, performance, and availability. The document outlines the OWASP top 10 security risks and provides examples of recent security incidents. It emphasizes that with Industry 4.0, security must extend from enterprise IT to connected industrial systems and devices. The document concludes with discussing building security into each phase of development from design through implementation, testing, and ongoing maintenance.