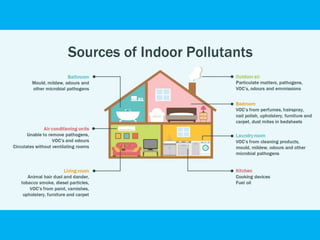
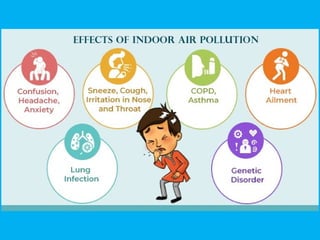
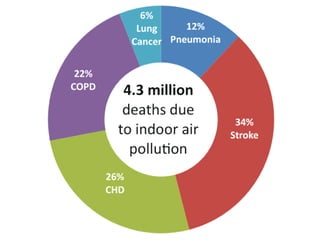
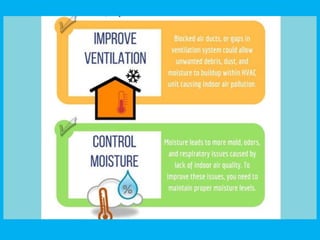
Indoor air pollution (IAP) refers to harmful contaminants in indoor air that adversely affect health, with common pollutants including mold, VOCs, and particulate matter. The EPA estimates indoor pollution can be 2 to 5 times higher than outdoor levels, leading to significant health issues, including millions of deaths annually. Control strategies involve source reduction, improved ventilation, and air purification to enhance indoor air quality and protect health.