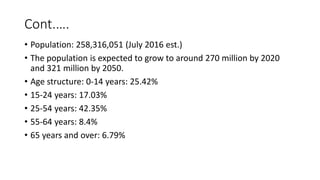
Indonesia is an archipelago country located in Southeast Asia between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It has over 17,000 islands and a population of over 258 million people. The capital and largest city is Jakarta. Indonesia has a developing economy focused on agriculture, mining, and tourism. While it has significant natural resources and the largest economy in Southeast Asia, Indonesia still has relatively low GDP per capita and faces challenges of poverty, inequality, and corruption that have prevented it from becoming a high-income country.