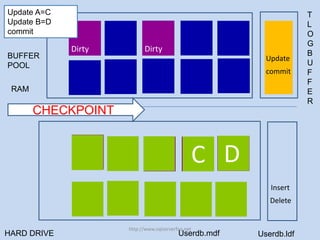
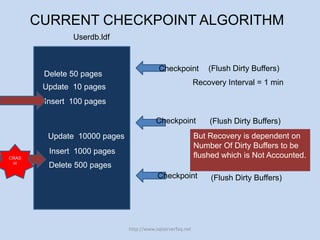
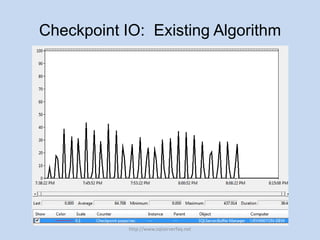
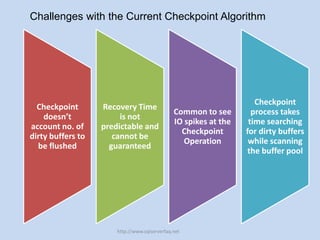
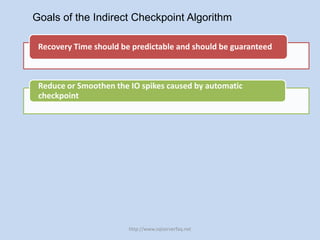
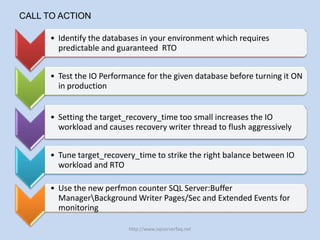
The document discusses SQL Server 2012's new indirect checkpoint algorithm. The current checkpoint algorithm flushes all dirty buffers during a checkpoint, causing unpredictable recovery times and IO spikes. The indirect checkpoint algorithm calculates a new minimum recovery LSN during checkpoints instead of flushing buffers. A background recovery writer thread then flushes pages when the dirty page count exceeds a threshold, maintaining predictable recovery times without heavy IO during checkpoints. The document recommends identifying databases that need predictable recovery times and testing indirect checkpoints before production use.