India's IT sector, comprising IT services and business process outsourcing, has transformed the country's economy and is a significant contributor to GDP, rising from 2% to 4.8% in the early 2000s. Major IT hubs include Bangalore, Hyderabad, Chennai, Delhi, and Mumbai, contributing substantially to exports in software and engineering services. India faces challenges in knowledge-intensive sectors but is projected to capture a larger share of global engineering services spending by 2020.




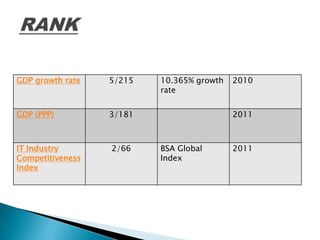
![ The contribution of IT
sector to India’s GDP rose
from about 2% at the turn
of the millennium to 4.8%
at the end of fiscal year
2005-06 (April-March).
Exports are estimated to
account for 31.3 billion
USD out of 39.7 billion
USD turn-over in fiscal
year 2006-07 [NASSCOM,
2007] in software sector.
contd.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/indiasrankinit-160326072530/85/India-s-rank-in-Information-Technology-IT-5-320.jpg)
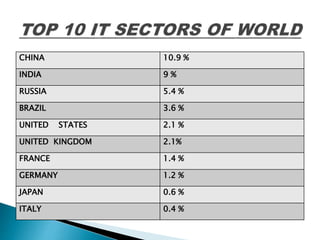
![ Exports are estimated to
account for 31.3 billion USD
out of 39.7 billion USD
turn-over in fiscal year
2006-07 [NASSCOM, 2007].
According to a study ,India,
which currently holds a
share of 12% in offshore
engineering services, is
expected to corner 30%
share in the 1.1 trillion USD
global spending on
engineering services by
2020](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/indiasrankinit-160326072530/85/India-s-rank-in-Information-Technology-IT-6-320.jpg)
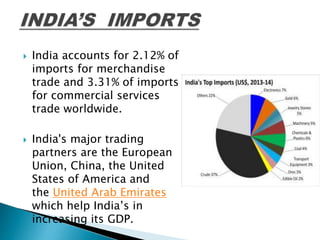
![ Since liberalization, the
value of India's
international trade has
increased
sharply,[199] with the
contribution of total
trade in goods and
services to the GDP rising
from 16% in 1990–91 to
47% in 2008–10.India
accounts for 1.44% of
exports for merchandise
trade and 3.34% of
exports for commercial
services trade worldwide](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/indiasrankinit-160326072530/85/India-s-rank-in-Information-Technology-IT-7-320.jpg)