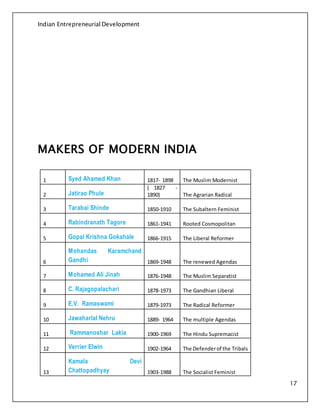
The Indian Entrepreneurial Development course aims to inspire students by highlighting the rich history of Indian business traditions and fostering modern entrepreneurial skills. It covers various aspects including the importance of planning, characteristics of successful entrepreneurs, the advantages of starting a business in India, and the impact of industrialization on the economy. The document also discusses the evolution of India's economic reforms and the significant figures in Indian entrepreneurship.