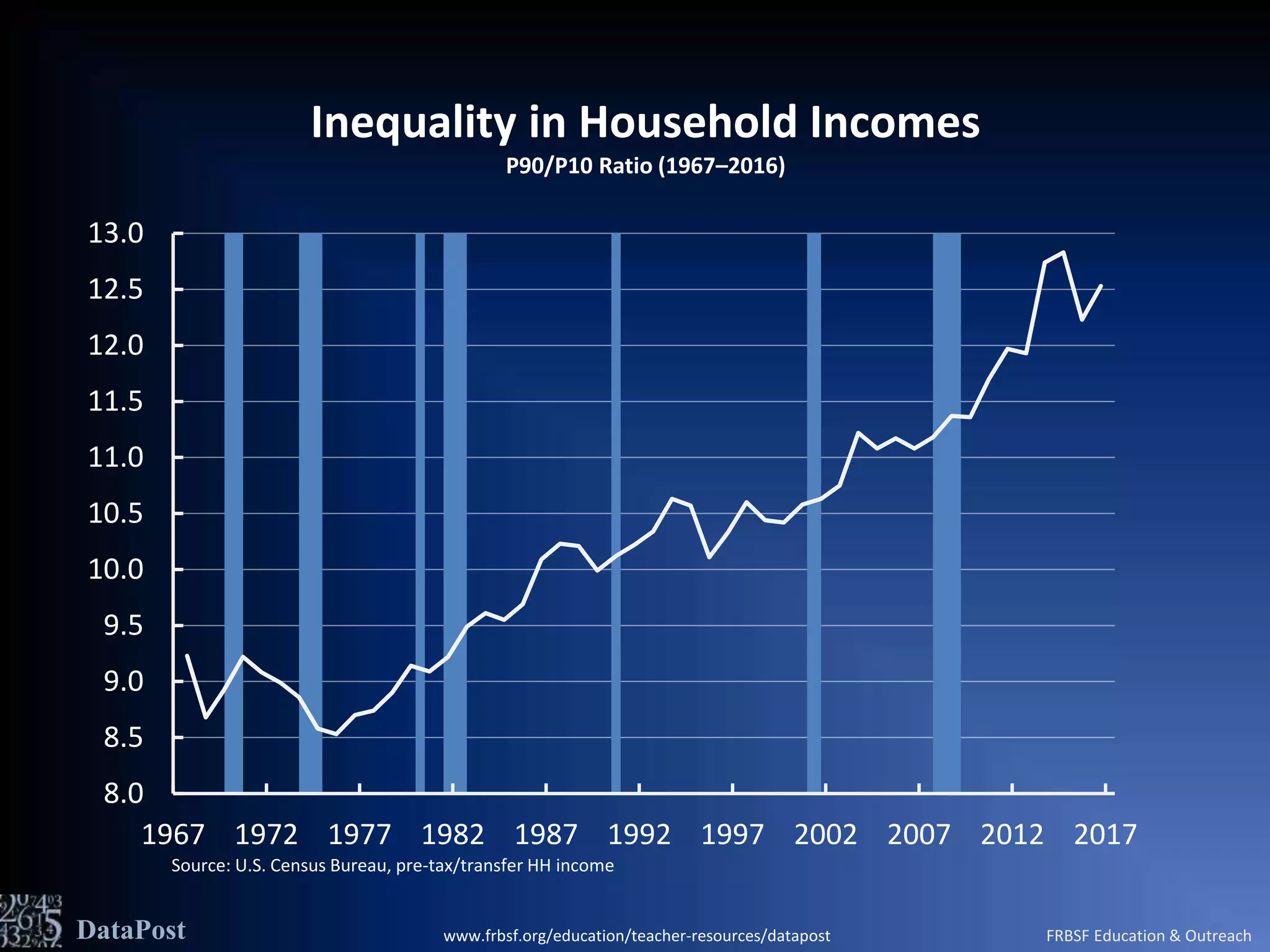
This document discusses income inequality in the United States based on 2016 household income data from the U.S. Census Bureau. It shows that in 2016, the top 10% of households earned over $170,000 while the bottom 10% earned less than $14,000. The ratio of income between the 90th and 10th percentiles (P90/P10 ratio) was 12.53, indicating that the top 10% earned over 12 times as much as the bottom 10%. This ratio has been rising steadily since 1975 and peaked in 2016, showing growing income inequality over time.