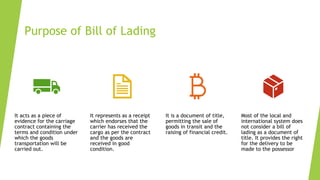
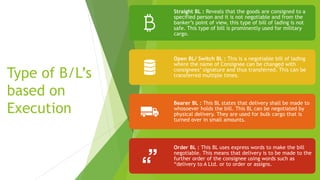
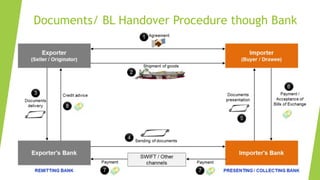
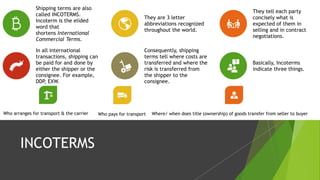
The document discusses shipping terms and processes. It defines shipping as the physical movement of goods from one point to another, controlled by a shipping or logistics company. When goods are shipped in containers, the sender works with shipping lines, freight forwarders, and customs brokers. A bill of lading is the key legal document that details the goods, nature, quantity and destination. It acts as a receipt and can determine ownership. Bills of lading can be negotiable or non-negotiable. INCOTERMS define important shipping terms like DDP, EXW that clarify responsibilities and costs between buyer and seller. The 2020 version of INCOTERMS includes changes like clarifying insurance requirements and costs for different terms.