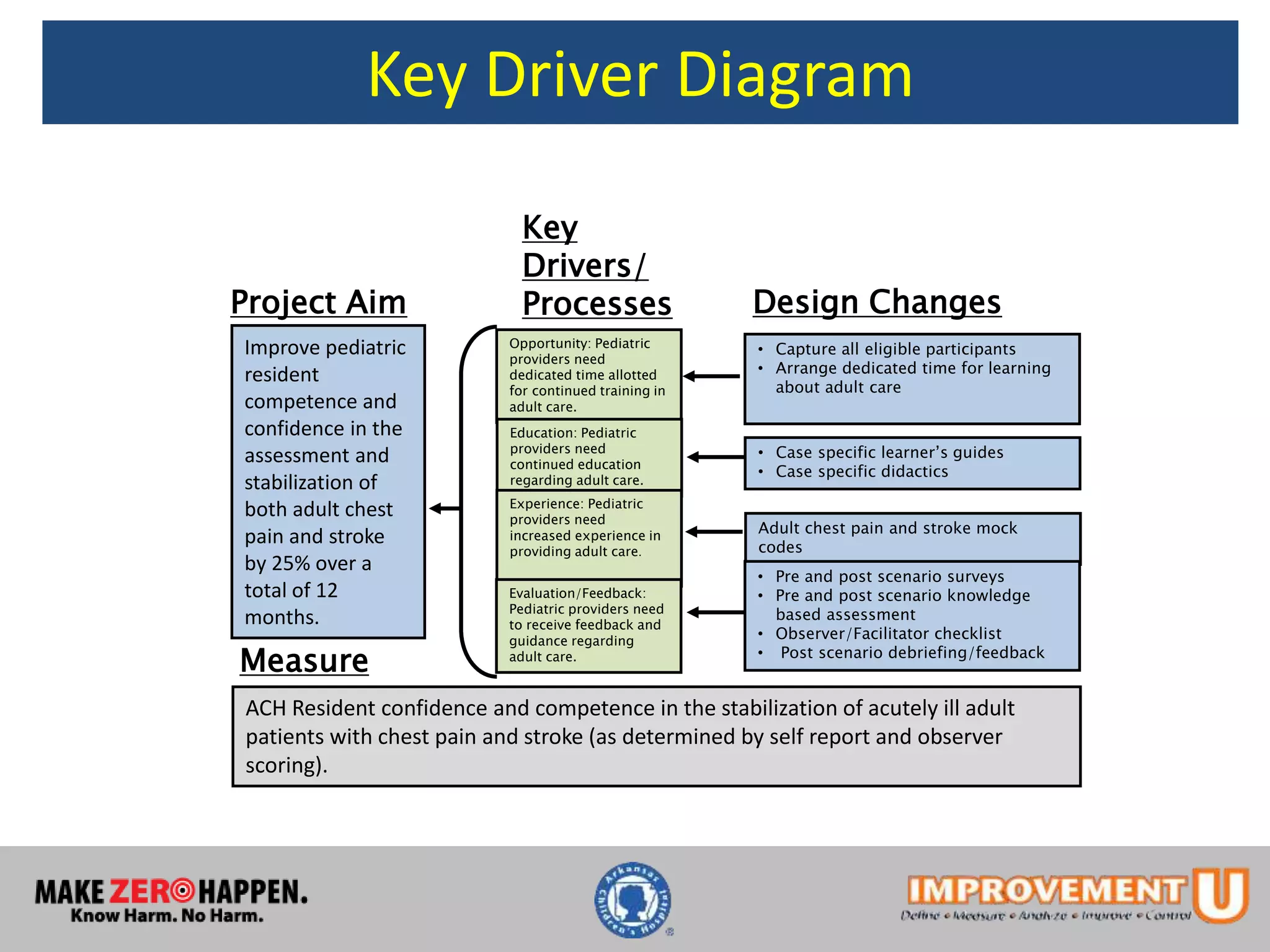
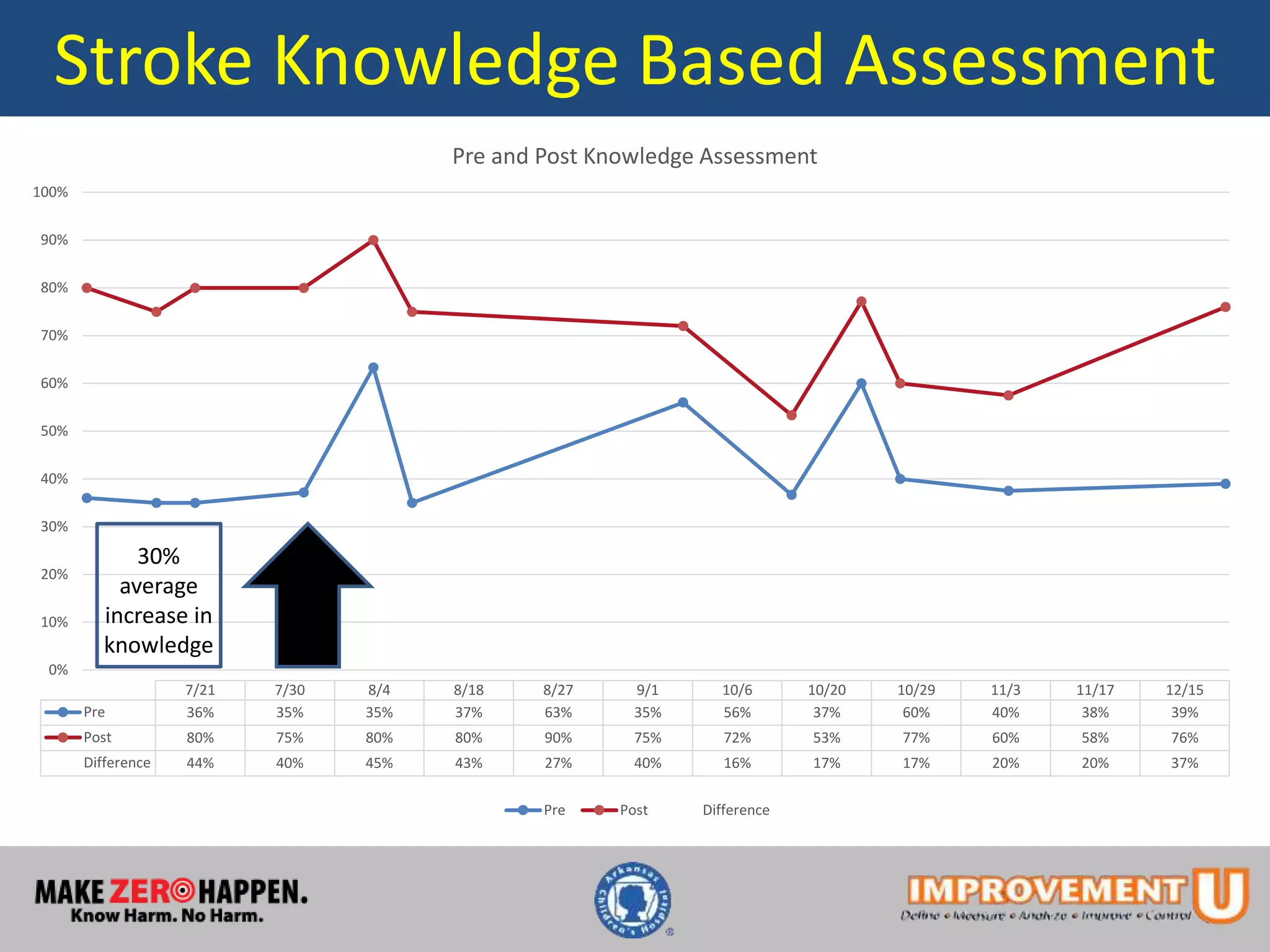
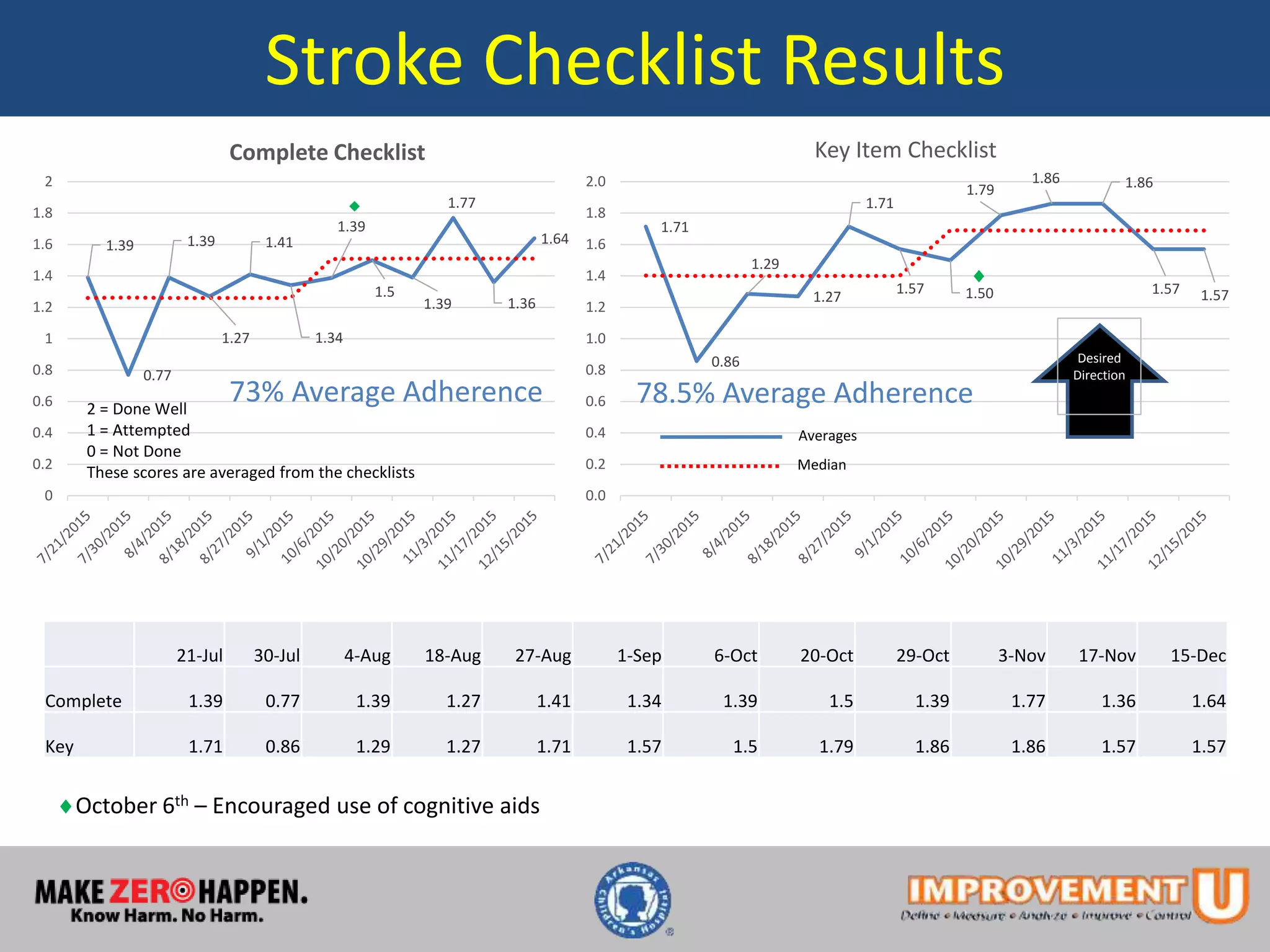
This document describes a quality improvement project to improve pediatric residents' competence and confidence in assessing and stabilizing adult patients presenting with chest pain or stroke. It involved implementing mock code simulations with debriefing and distributing learning guides. Results showed pediatric residents demonstrated a 34-46% increase in confidence and a 30-41% increase in medical knowledge regarding adult chest pain and stroke treatment. Adherence to checklist items during simulations also increased. The project concluded educational interventions like simulations can effectively address knowledge gaps pediatric providers have in treating adult patients.