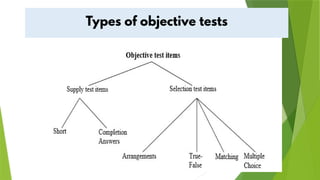
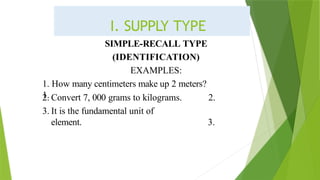
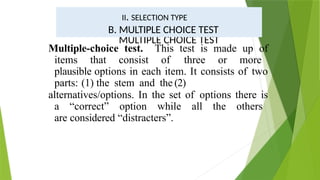
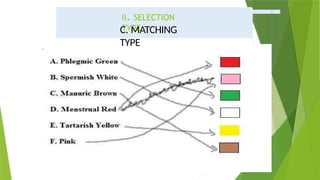
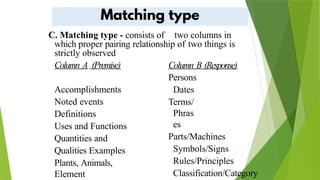
The document discusses various educational measurement tools and test types, highlighting the characteristics and guidelines for constructing identification, fill-in-the-blank, true-false, multiple-choice, and matching type questions. It emphasizes the importance of clarity, specificity, and avoiding ambiguity in test item construction to assess students' knowledge effectively. Additionally, it explores essay testing formats, including restricted and extended responses, and their role in evaluating higher-order thinking skills.