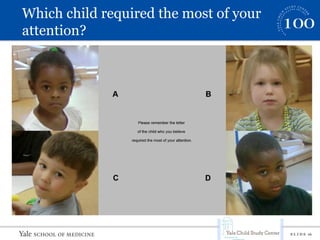
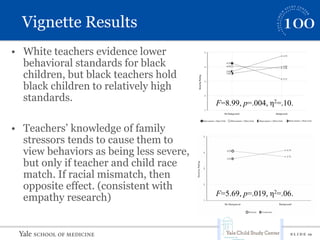
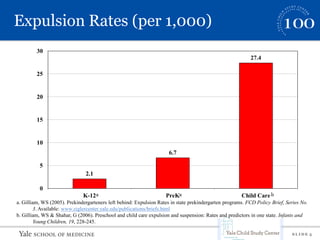
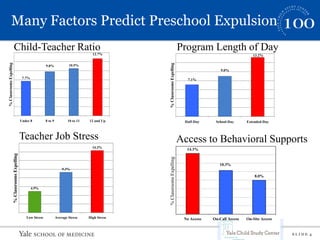
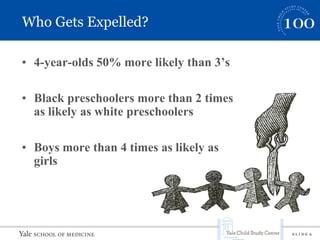
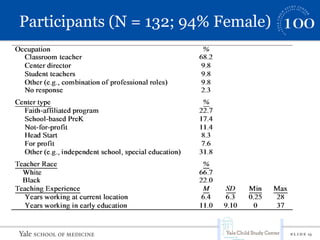
This document summarizes a presentation on implicit bias in preschools. It finds that preschool expulsion rates are much higher than in K-12 schools, with black boys most at risk. Studies show that black preschoolers are more than twice as likely to be expelled as white preschoolers, and boys are over 4 times as likely as girls. Additional research presented found that teachers had stronger implicit biases towards black boys, viewing their behaviors as more problematic and requiring more attention. The presentation argues that reducing disparities in preschool discipline is an issue of social justice and access to early education opportunities.








![S L I D E 14
Eye Tracking Procedures
• Instructions: “Now you are ready to view a series
of video clips lasting 6 minutes. We are interested
in learning about how teachers detect challenging
behavior in the classroom. Sometimes this involves
seeing behavior before it becomes problematic. The
video segments you are about to view are of
preschoolers engaging in various activities. Some
clips may or may not contain challenging
behaviors. Your job is to press the enter key on the
external keypad every time you see a behavior that
could become a potential challenge [experimenter
demonstrates]. Please press the keypad as often as
needed.”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gilliamjsutalk03-170321165630/85/Implicit-Bias-in-Preschools-14-320.jpg)