Embed presentation
Download to read offline




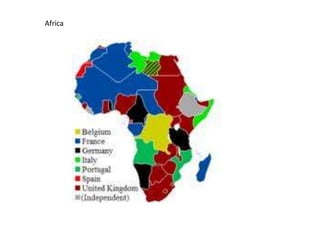
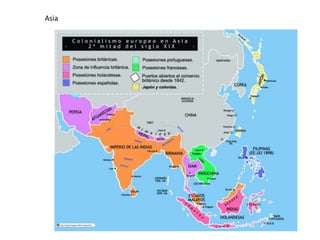



Colonialism and imperialism in the late 19th century were driven by economic causes like slavery and expanding trade networks, as European powers established colonies, protectorates and territories in Africa, Asia and the Caribbean to gain control over resources and markets. For example, India was a colony of England which had full power and sovereignty, while Botswana was a protectorate where England had some power but not full control, and India became a territory of England in 1947 without any English power.








