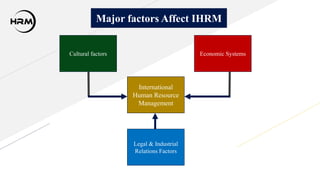
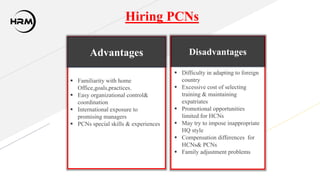
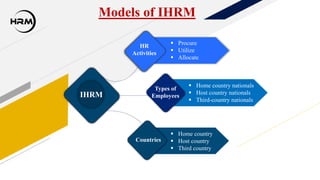
This presentation provides an overview of international human resource management (IHRM). IHRM aims to manage organizational human resources at an international level to achieve objectives and competitive advantage globally. The presentation defines IHRM and its objectives, functions, importance, characteristics, factors that affect it, challenges, and models involving types of employees and countries.