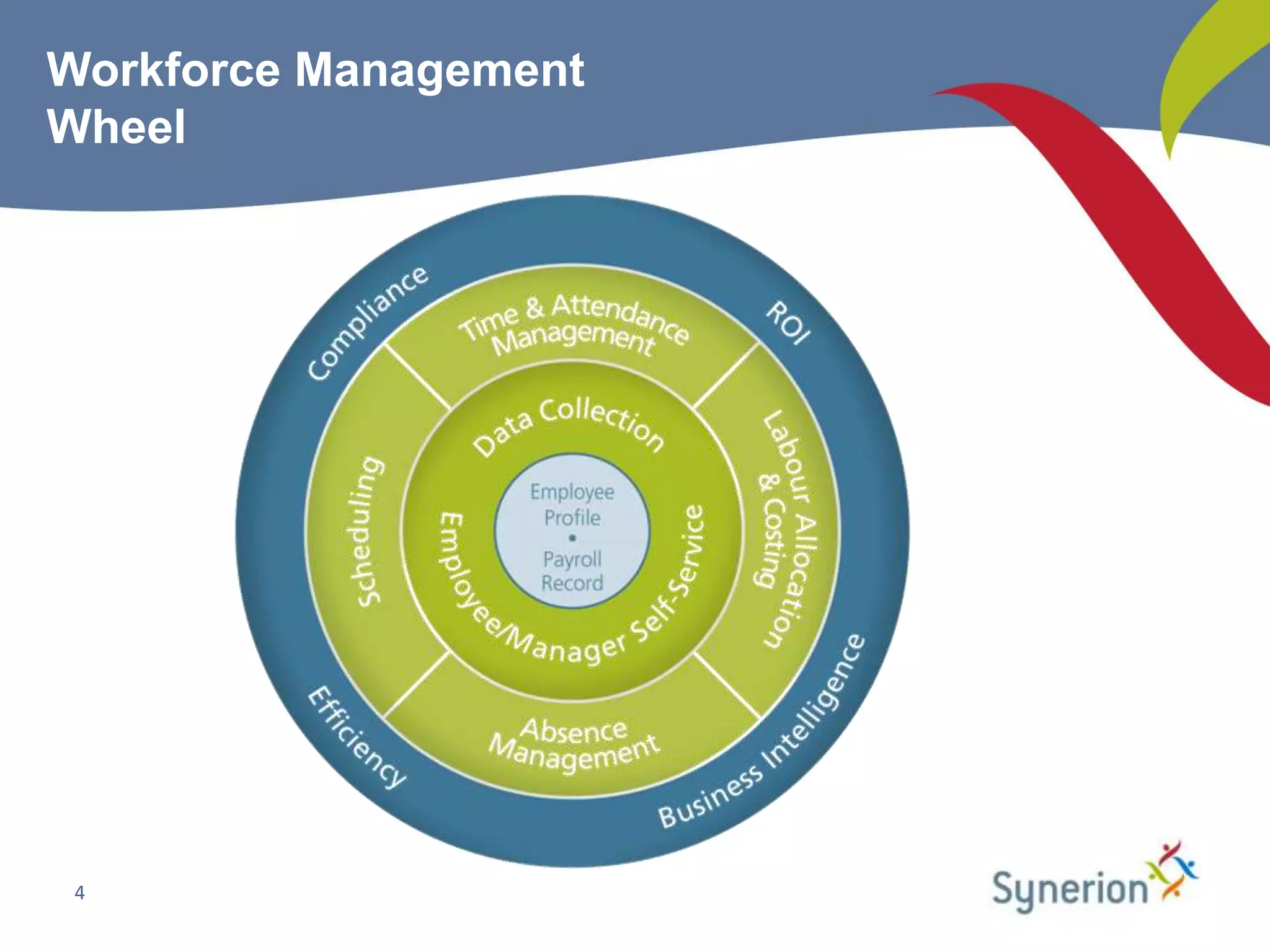
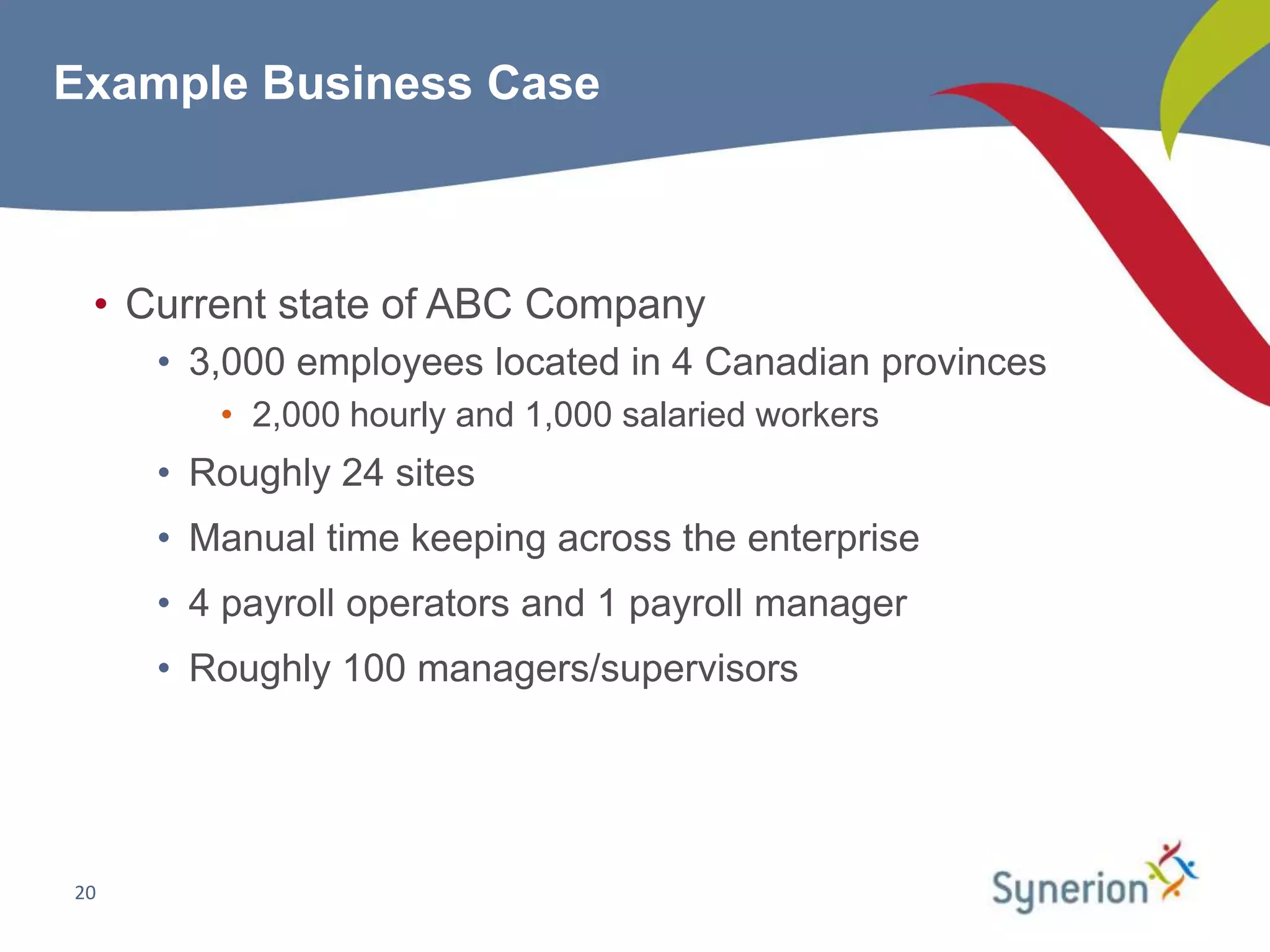
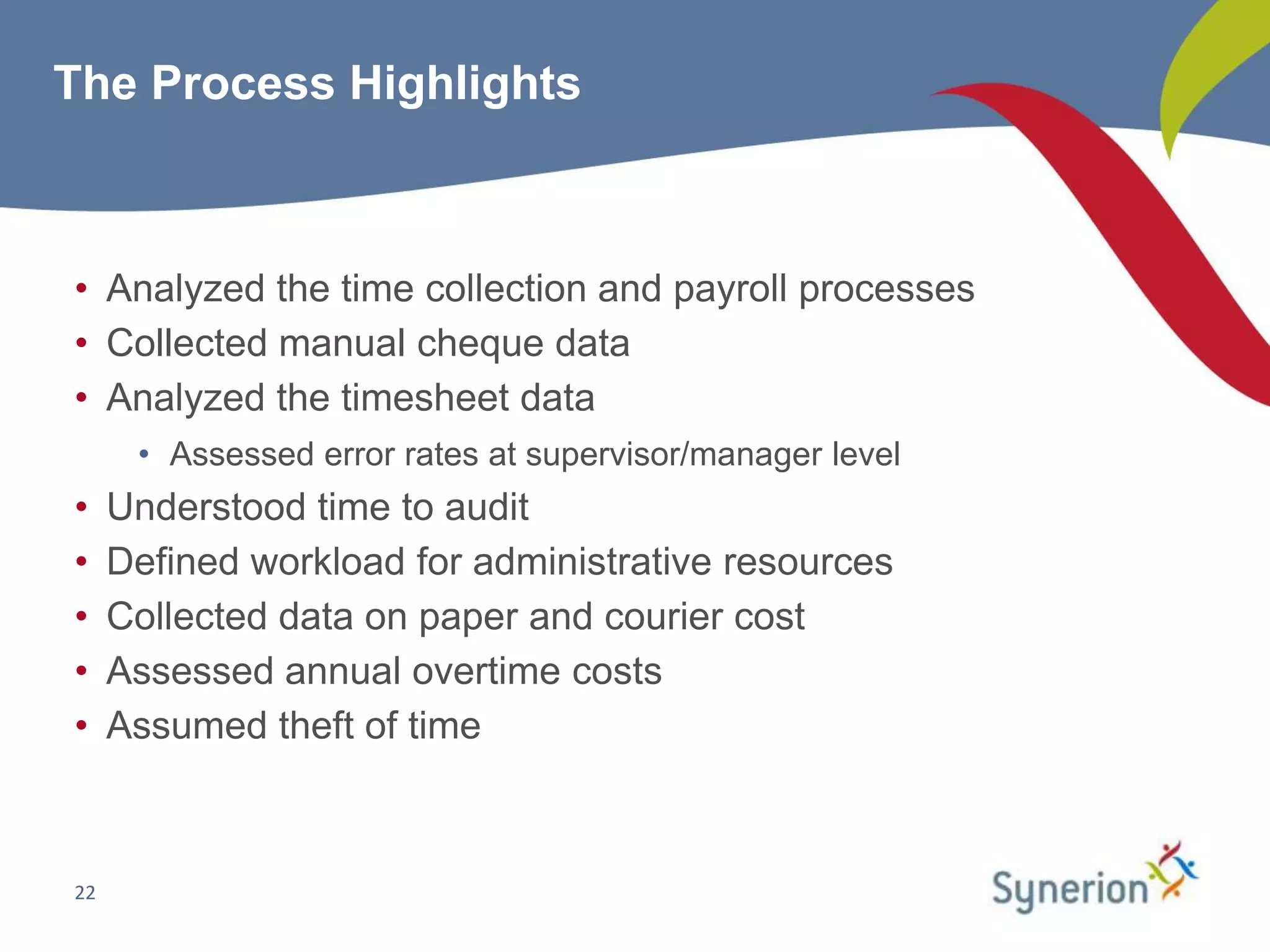
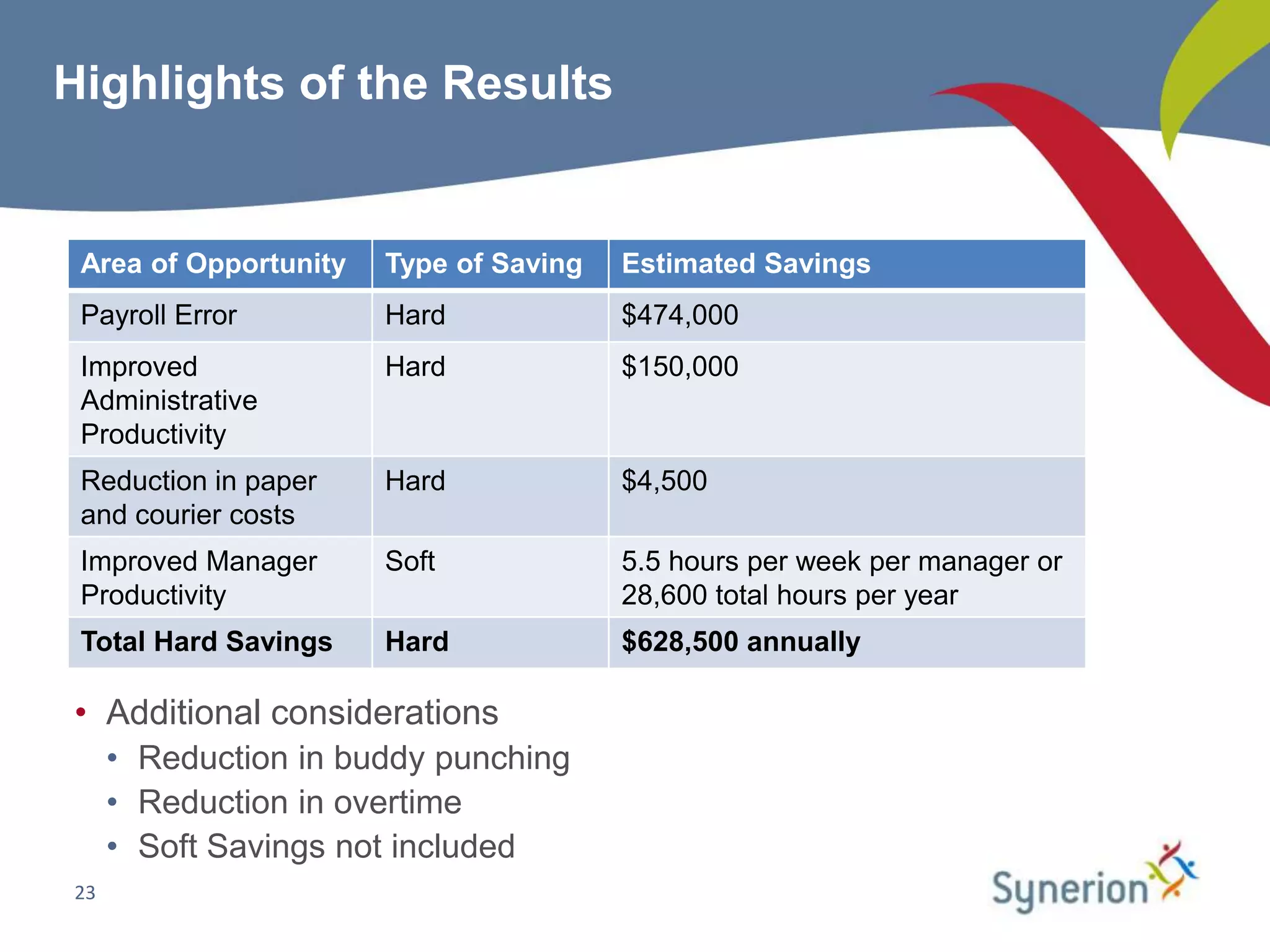
This document discusses workforce management (WFM) and the benefits of automating manual timekeeping processes. It defines WFM as encompassing all activities needed to manage a workforce, including planning, forecasting, scheduling, and tracking workers. The document provides examples of manual timekeeping processes and their limitations. It argues that automating can provide cost savings through reduced errors, increased productivity, and improved decision making. The document also discusses current and future trends in WFM, who should consider automating, and how to select a vendor and define a business case. It provides a hypothetical example of a business case that estimates over $600,000 in annual hard cost savings from automating.