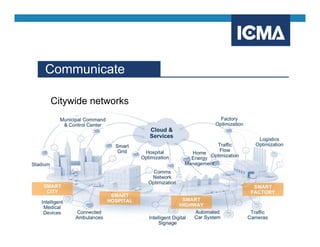
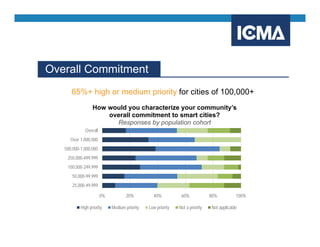
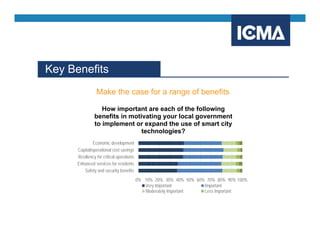
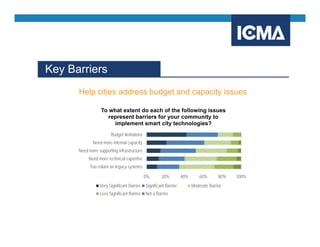
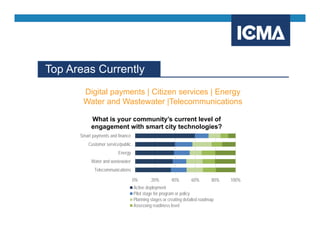
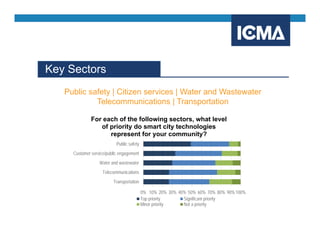
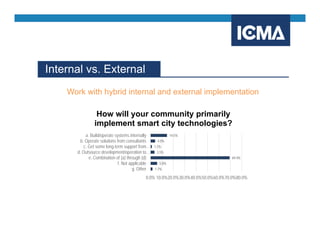
The document outlines the definition and components of smart cities, emphasizing their use of ICT to enhance livability, sustainability, and resilience in urban areas. It summarizes survey findings from U.S. local governments regarding smart city technologies, revealing priorities, motivations, and barriers to implementation. The survey highlights public safety as a key focus area, with budget limitations and legacy systems identified as significant obstacles.